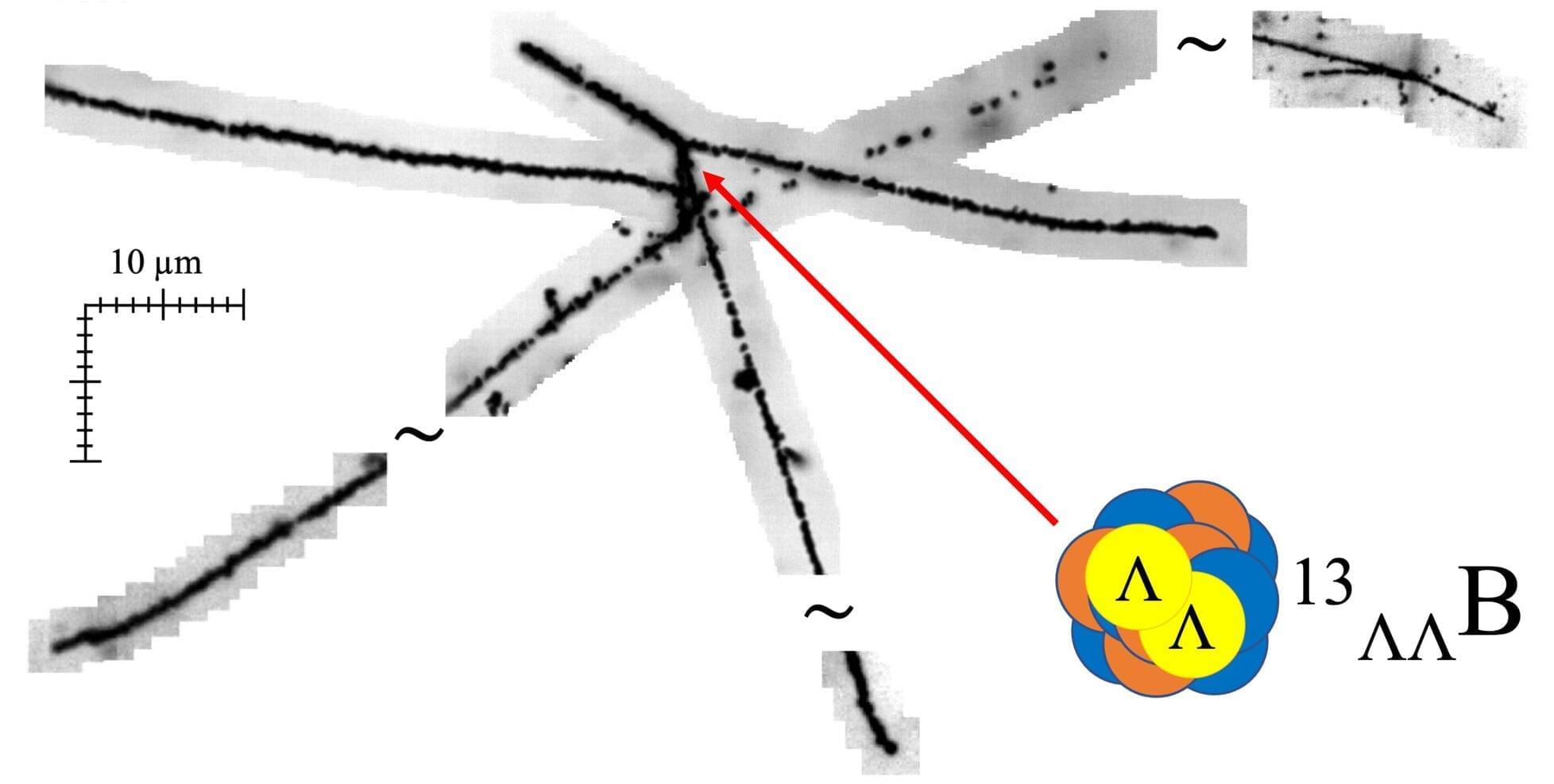
Researchers from the High Energy Nuclear Physics Laboratory at the RIKEN Pioneering Research Institute (PRI) in Japan and their international collaborators have made a discovery that bridges artificial intelligence and nuclear physics. By applying deep learning techniques to a vast amount of unexamined nuclear emulsion data from the J-PARC E07 experiment, the team identified, for the first time in 25 years, a new double-Lambda hypernucleus.
This marks the world’s first AI-assisted observation of such an exotic nucleus—an atomic nucleus containing two strange quarks. The finding, published in Nature Communications, represents a major advance in experimental nuclear physics and provides new insight into the composition of neutron star cores, one of the most extreme environments in the universe.