Openclaw has 18 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.


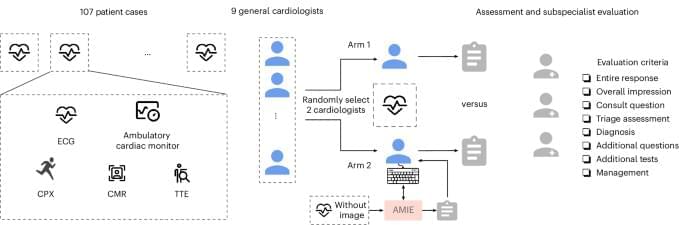
In a randomized study involving 9 general cardiologists and 107 real-world patient cases, assistance from a specifically tailored large language model resulted in preferable responses on complex case management compared to physicians alone, as rated by specialist cardiologists using a multidimensional scoring rubric.
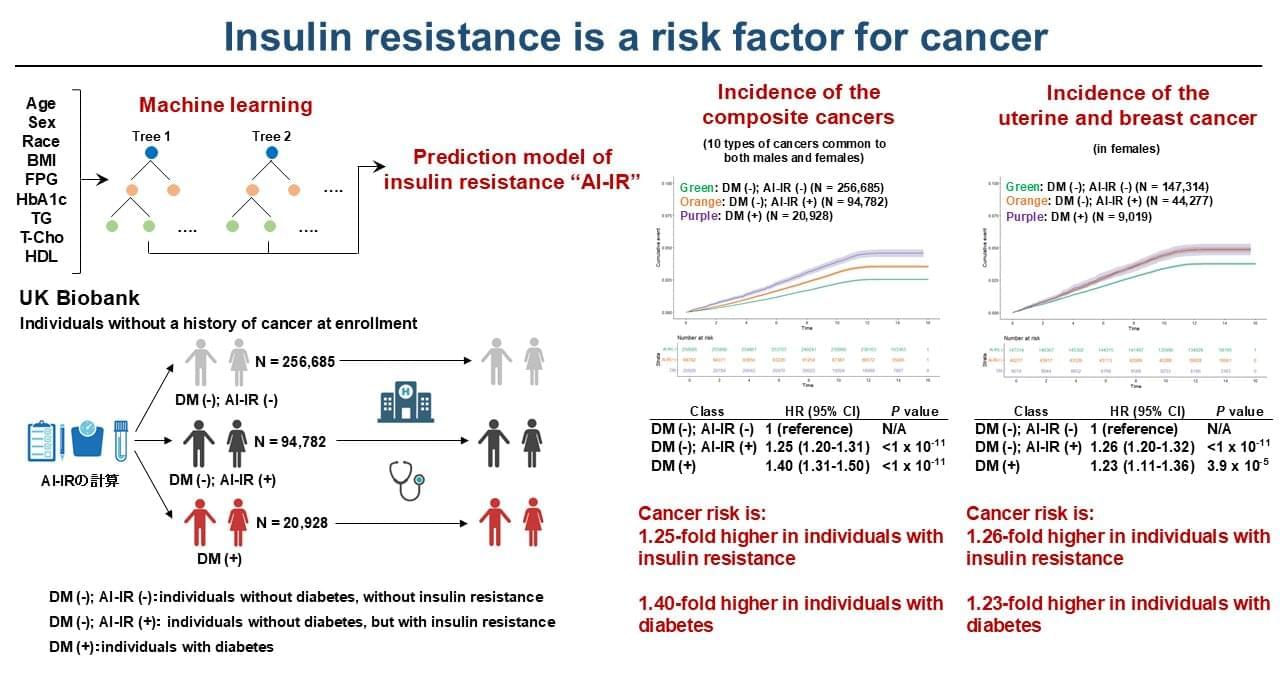
Insulin resistance—when the body doesn’t properly respond to insulin, a hormone that helps control blood glucose levels—is one of the fundamental causes of diabetes. In addition to diabetes, it is widely known that insulin resistance can lead to cardiovascular, kidney and liver diseases. While insulin resistance is tightly associated with obesity, it has been difficult to evaluate insulin resistance itself in the clinic. For the first time, researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, applied a machine learning-based prediction model of insulin resistance to half a million participants from the UK Biobank and demonstrated that insulin resistance is a risk factor for 12 types of cancer.
The research is published in Nature Communications.
Diabetes is a common cause for concern around the world. Its connection to insulin resistance is a familiar concept to many, but what is less well known is that resistance to insulin is also suggested to be a risk factor for several cancers. However, the human body is a complex thing, and ascertaining causal connections between diseases and issues within the body is far from easy.


A new spin on robotics, thanks to a novel 3D printing method
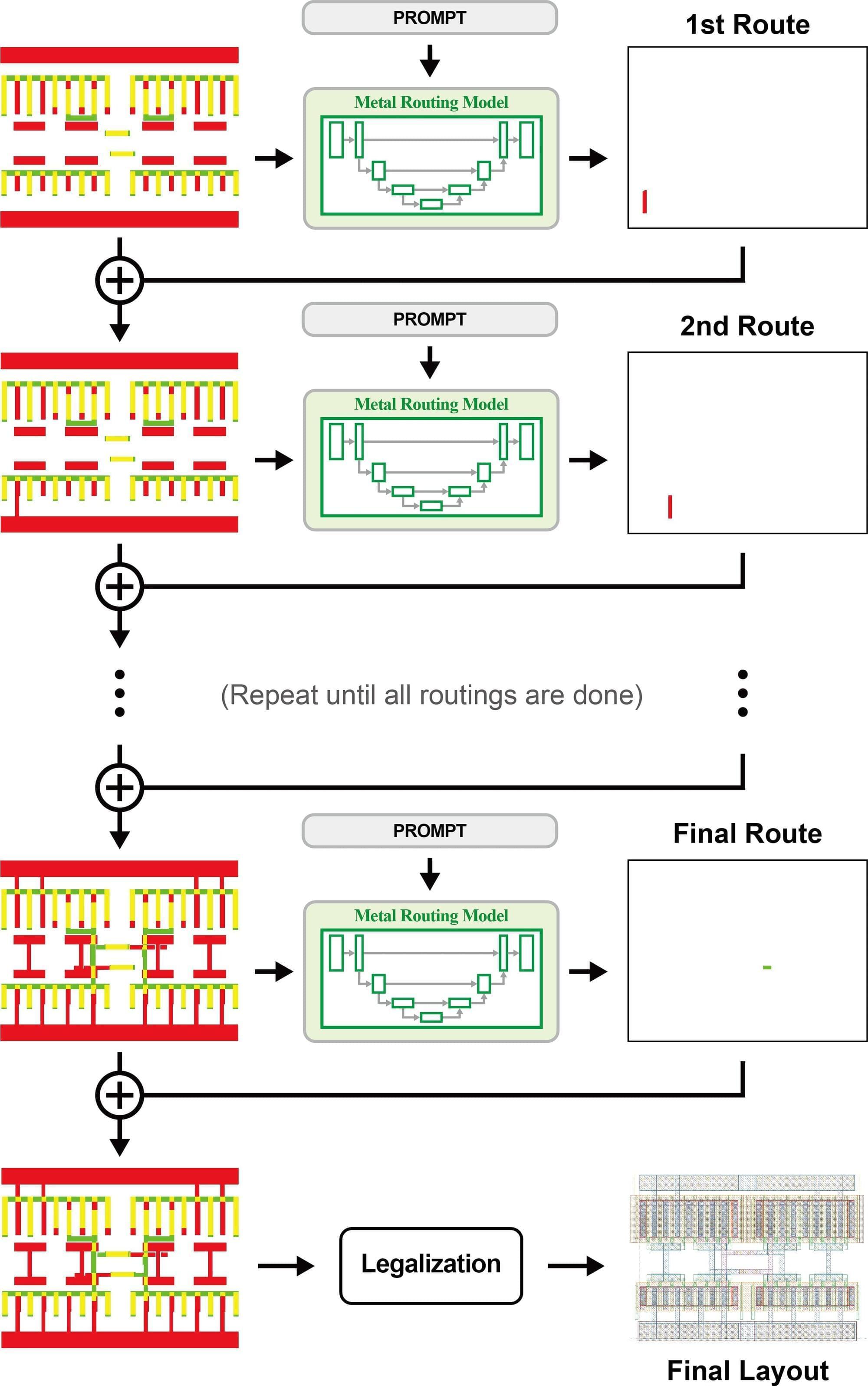
Researchers at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) have developed an artificial intelligence approach that addresses a key bottleneck in analog semiconductor layout design, a process that has traditionally depended heavily on engineers’ experience. The work was recently published in the journal IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers.
Semiconductors are used in a wide range of technologies, including smartphones, vehicles, and AI servers. However, analog layout design remains difficult to automate because designers must manually arrange structures that determine performance and reliability while meeting a large number of design rules.
Automation has been especially challenging in analog design because layouts are too complex and design strategies differ significantly by circuit. In addition, training data is scarce, since layout data is typically treated as proprietary and is rarely shared outside companies.
One of the biggest challenges the researchers faced when designing MAFT-ONN was determining how to map the machine-learning computations to the optical hardware.
“We couldn’t just take a normal machine-learning framework off the shelf and use it. We had to customize it to fit the hardware and figure out how to exploit the physics so it would perform the computations we wanted it to,” Davis says.
When they tested their architecture on signal classification in simulations, the optical neural network achieved 85 percent accuracy in a single shot, which can quickly converge to more than 99 percent accuracy using multiple measurements. MAFT-ONN only required about 120 nanoseconds to perform entire process.

Today, we’re releasing a major upgrade to Gemini 3 Deep Think, our specialized reasoning mode, built to push the frontier of intelligence and solve modern challenges across science, research, and engineering.
We updated Gemini 3 Deep Think in close partnership with scientists and researchers to tackle tough research challenges — where problems often lack clear guardrails or a single correct solution and data is often messy or incomplete. By blending deep scientific knowledge with everyday engineering utility, Deep Think moves beyond abstract theory to drive practical applications.
The new Deep Think is now available in the Gemini app for Google AI Ultra subscribers and, for the first time, we’re also making Deep Think available via the Gemini API to select researchers, engineers and enterprises. Express interest in early access here.