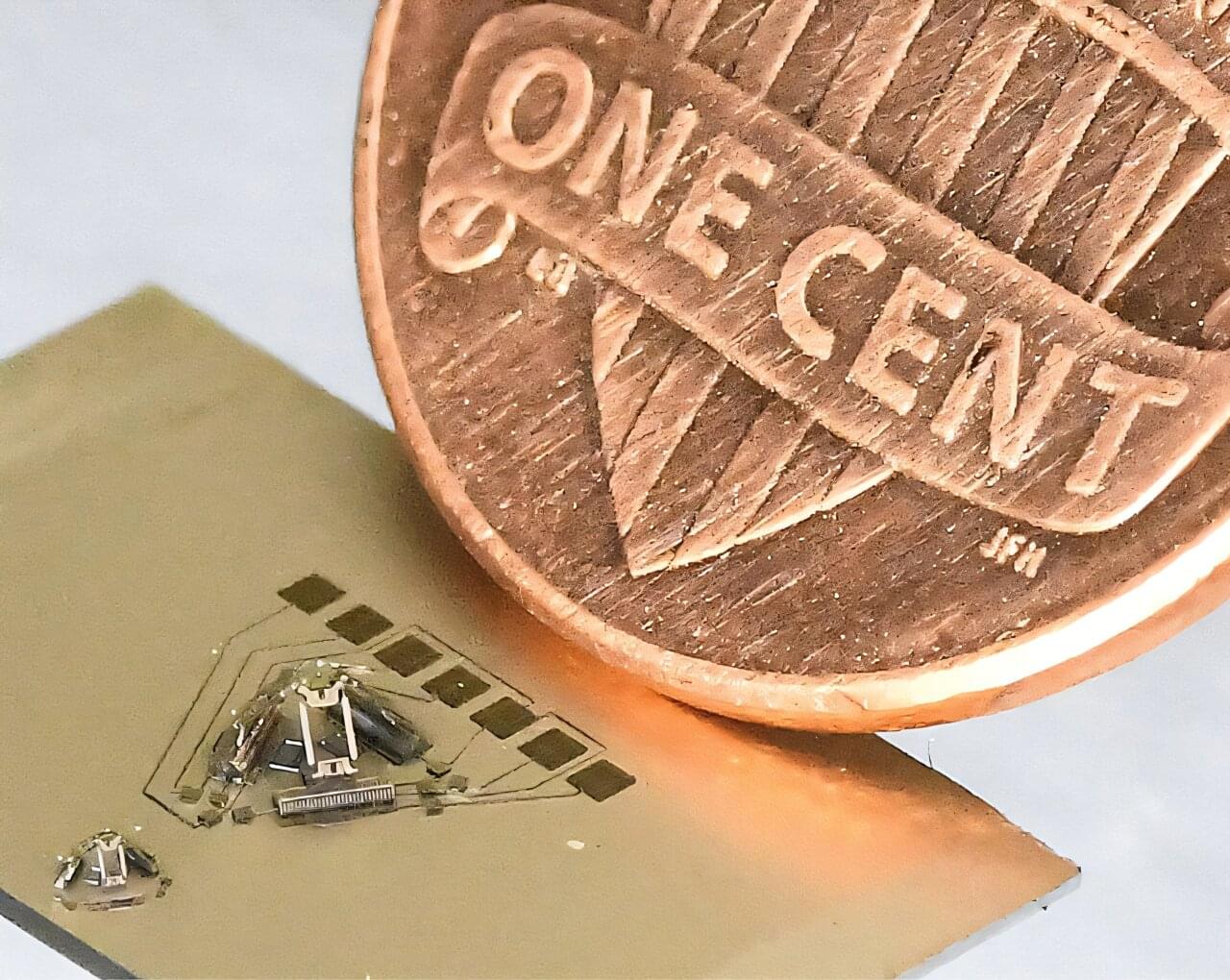
When it comes to navigating their surroundings, machines have a natural disadvantage compared to humans. To help hone the visual perception abilities they need to understand the world, researchers have developed a novel training dataset for improving spatial awareness in robots.
In new research, experiments showed that robots trained with this dataset, called RoboSpatial, outperformed those trained with baseline models at the same robotic task, demonstrating a complex understanding of both spatial relationships and physical object manipulation.
For humans, visual perception shapes how we interact with the environment, from recognizing different people to maintaining an awareness of our body’s movements and position. Despite previous attempts to imbue robots with these skills, efforts have fallen short as most are trained on data that lacks sophisticated spatial understanding.