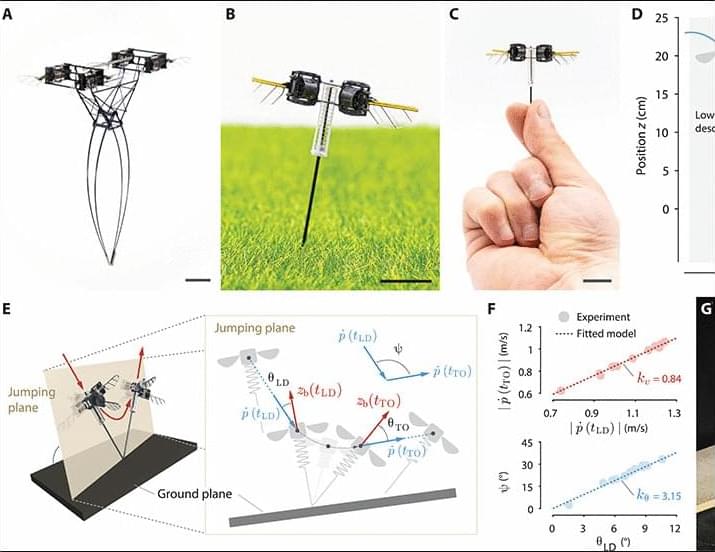
Jumping is ubiquitous among insects because it offers high locomotion versatility with moderate efficiency. Most jumping insects leverage latch-mediated spring actuation (14) principles to store and impulsively release energy—leading to high jumps that exceed 0.7 m or 115 times their body length (15). Subgram jumping robots (16, 17) adopt a similar design where they can reach up to 0.64-m jump height. However, unlike insects, small robots lack the ability to control attitude and landing position while they are aloft, and they cannot reorient themselves and reload the jumping mechanism after landing. Achieving the ability to perform consecutive jumps can substantially improve microrobot mobility. Hopping, or continuous jumping, has been achieved in mesoscale (35 to 100 g) robots (18–20) to demonstrate efficient and versatile locomotion. Unlike single-jump robots (21, 22) that slowly store energy in a spring-latched system, hopping robots (18, 23) need to quickly store energy in series-elastic mechanisms during the aerial phase and release energy during the stance phase. Most hopping designs are based on the spring-loaded inverted pendulum model (24), and the mechanisms are realized on the basis of a combination of multiple linkages and springs (18–20).
However, these mesoscale designs are difficult to implement in insect-scale robots owing to scaling laws, fabrication, and control challenges. As robot size shrinks, robot dynamics become substantially faster, requiring rapid actuation and control in the range of tens of milliseconds. For a subgram robot to hop, the duration of ground contact becomes shorter than 20 ms, exceeding the control bandwidth of microscale actuators. The short ground impact can also cause large body torques and induce fast rotations, which require another set of actuators and mechanisms to stabilize robot’s attitude in the aerial phase. In addition, it becomes increasingly difficult to construct nonlinear springs, flexures, and linkages at the submillimeter scale. Owing to these challenges, existing insect-scale robots have not achieved hopping despite the potential advantages of versatility and efficiency. At the tens-of-gram scale, our prior work presented a different hopping design by adding a passive telescopic leg to a quadcopter, resulting in a 35-g Hopcopter (20). This Hopcopter demonstrated better controllability and efficiency over other existing designs because it could inject energy and exert stronger attitude control in the aerial phase. Applying this design to insect-scale systems is advantageous because it reduces mechanical complexity. However, new challenges arise because of diminishing robot inertia and substantially faster system dynamics that require fast planning and attitude control. Specifically, high-bandwidth actuators and computationally efficient controllers are needed to replace electromagnetic motors and model-based collision planners (20).
In this work, we demonstrate efficient, versatile, and robust hopping in subgram robots by augmenting a micro–aerial vehicle with a passive elastic leg (Fig. 1, A to C Opens in image viewer, and movie S1). Compared to flight, this hopping design reduces energetic cost by 64% and increases the robot’s payload by over 10 times. The robot can precisely control its jump height, frequency, and landing positions to track set points and leap over large obstacles. This hopping design is also adaptive to a wide range of slippery, uneven, rough, or deformable terrains, including wood, glass, ice, soil, grass, and a floating lotus leaf. Owing to fast robot dynamics and the ability to generate large body torques, the robot further demonstrates unparalleled robustness and agility among microrobots. The robot can hop on dynamically inclined surfaces, recover from strong in-air collisions, and perform acrobatic flips in its aerial phase. In addition, diminishing inertial effects enable challenging locomotive tasks that are infeasible for larger-scale robots. Our robot can jump onto a 29-g quadrotor, which shows that impulsive interaction between two heterogeneous aerial robots can enhance mobility. These demonstrations highlight the unique advantages of insect-scale hopping. Our results also have implications on achieving sensing and power autonomy in payload-constrained microrobots that often confront large obstacles. Compared to insect-scale aerial vehicles, our robot retains the capability of overcoming large obstacles while substantially reducing power consumption and increasing payload. The 10 times payload increase opens opportunities for incorporating onboard sensors, electronics, and power sources.