Historically, No Tech Improvement Has Affected Human Jobs. It’s the people who were smart enough to understand the paradigm shift and develop new skills to be better productive.


Structural adhesives play a crucial role in assembling automobiles, aircraft, and buildings. Among these, epoxy adhesives stand out for their exceptional mechanical strength and durability. However, traditional cured epoxy resins are often rigid and lack flexibility, resulting in low peel and impact strength.
Now, a groundbreaking advancement in structural adhesives has emerged from the laboratories of Nagoya University, promising to transform material bonding as we know it. This next-generation adhesive boasts an unprecedented impact strength – 22 times higher than conventional epoxy-based adhesives without rubbery additives.
New adhesive using elastomer makes lighter, more carbon-efficient vehicles possible.


AI gives a thumbs up to Brett Bellmore innovative modifications to Robert Zubrin’s Nuclear Salt Water Rocket (NSWR). Switching from water to polyethene and storing in sausage strings could enhance its performance and safety, particularly focusing on avoiding criticality during storage, minimizing parasitic mass, and addressing practical challenges like micrometeorite protection and fuel state.
Robert Zubrin’s Nuclear Salt Water Rocket (NSWR) design is a rocket that uses known physics and engineering. My previous analysis shows that the first working prototype might be made in space with a 10–20 year development program for 10–30 billion. There are versions that could reach 7–8% of light speed. The use of low grade uranium enrichment for a more near term version is the one that is often described. However, if weapons grade uranium (90% enrichment) is used then he exhaust would be at 1.575% of the speed of light. A 30,000 ton ice asteroid and 7,500 tons of uranium could propel a 300 ton payload including a crew to 7.62% of light speed.
One of key parts of the engineering is to use water to protect the nozzle from the intense heat of the system. A combination of the coatings and space between the pipes would prevent the solution from reaching critical mass until it was pumped into a reaction chamber. It would reach critical mass and it being expelled through a nozzle to generate thrust. The nozzle would be protected by running water.


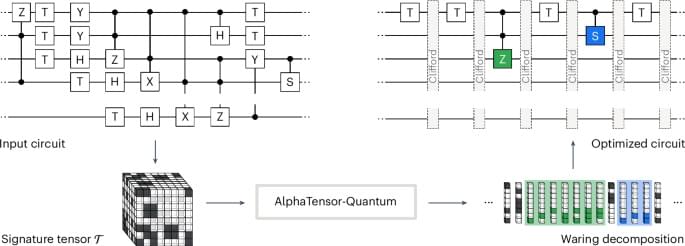
AlphaTensor–Quantum addresses three main challenges that go beyond the capabilities of AlphaTensor25 when applied to this problem. First, it optimizes the symmetric (rather than the standard) tensor rank; this is achieved by modifying the RL environment and actions to provide symmetric (Waring) decompositions of the tensor, which has the beneficial side effect of reducing the action search space. Second, AlphaTensor–Quantum scales up to large tensor sizes, which is a requirement as the size of the tensor corresponds directly to the number of qubits in the circuit to be optimized; this is achieved by a neural network architecture featuring symmetrization layers. Third, AlphaTensor–Quantum leverages domain knowledge that falls outside of the tensor decomposition framework; this is achieved by incorporating gadgets (constructions that can save T gates by using auxiliary ancilla qubits) through an efficient procedure embedded in the RL environment.
We demonstrate that AlphaTensor–Quantum is a powerful method for finding efficient quantum circuits. On a benchmark of arithmetic primitives, it outperforms all existing methods for T-count optimization, especially when allowed to leverage domain knowledge. For multiplication in finite fields, an operation with application in cryptography34, AlphaTensor–Quantum finds an efficient quantum algorithm with the same complexity as the classical Karatsuba method35. This is the most efficient quantum algorithm for multiplication on finite fields reported so far (naive translations of classical algorithms introduce overhead36,37 due to the reversible nature of quantum computations). We also optimize quantum primitives for other relevant problems, ranging from arithmetic computations used, for example, in Shor’s algorithm38, to Hamiltonian simulation in quantum chemistry, for example, iron–molybdenum cofactor (FeMoco) simulation39,40. AlphaTensor–Quantum recovers the best-known hand-designed solutions, demonstrating that it can effectively optimize circuits of interest in a fully automated way. We envision that this approach can accelerate discoveries in quantum computation as it saves the numerous hours of research invested in the design of optimized circuits.
AlphaTensor–Quantum can effectively exploit the domain knowledge (provided in the form of gadgets with state-of-the-art magic-state factories12), finding constructions with lower T-count. Because of its flexibility, AlphaTensor–Quantum can be readily extended in multiple ways, for example, by considering complexity metrics other than the T-count such as the cost of two-qubit Clifford gates or the qubit topology, by allowing circuit approximations, or by incorporating new domain knowledge. We expect that AlphaTensor–Quantum will become instrumental in automatic circuit optimization with new advancements in quantum computing.
Boston Dynamics’ Atlas has elevated robotics by mastering breakdance moves using motion capture and reinforcement learning.
Chinese tech experts have introduced a groundbreaking humanoid robot prototype, setting the stage for its integration into homes.