AI Vs AI: Hackers use Artificial Intelligence for deepfakes and smart malware, while defenders counter with AI threat detection and predictive security.



Just as pilots use flight simulators to safely practice complex maneuvers, scientists may soon conduct experiments on a highly realistic simulation of the mouse brain. In a new study, researchers at Stanford Medicine and their collaborators developed an artificial intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on creating systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. These tasks include understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and learning from experience. AI technologies use algorithms and massive amounts of data to train models that can make decisions, automate processes, and improve over time through machine learning. The applications of AI are diverse, impacting fields such as healthcare, finance, automotive, and entertainment, fundamentally changing the way we interact with technology.

More than two years after the blockbuster launch of ChatGPT, artificial intelligence continues to be the white hot center of venture capital and the business world at large.




Due to ever-accelerating urbanization in recent decades, exploring the contributions of trees in mitigating atmospheric carbon in urban areas has become one of the paramount concerns. Remote sensing-based approaches have been primarily implemented to estimate the tree-stand atmospheric carbon stock (CS) for the trees in parks and streets. However, a convenient yet high-accuracy computation methodology is hardly available. This study introduces an approach that has been tested for a small urban area. A data fusion approach based on a three-dimensional (3D) computation methodology was applied to calibrate the individual tree CS. This photogrammetry-based technique employed an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and spherical image data to compute the total height (H) and diameter at breast height (DBH) for each tree, consequently estimating the tree-stand CS.
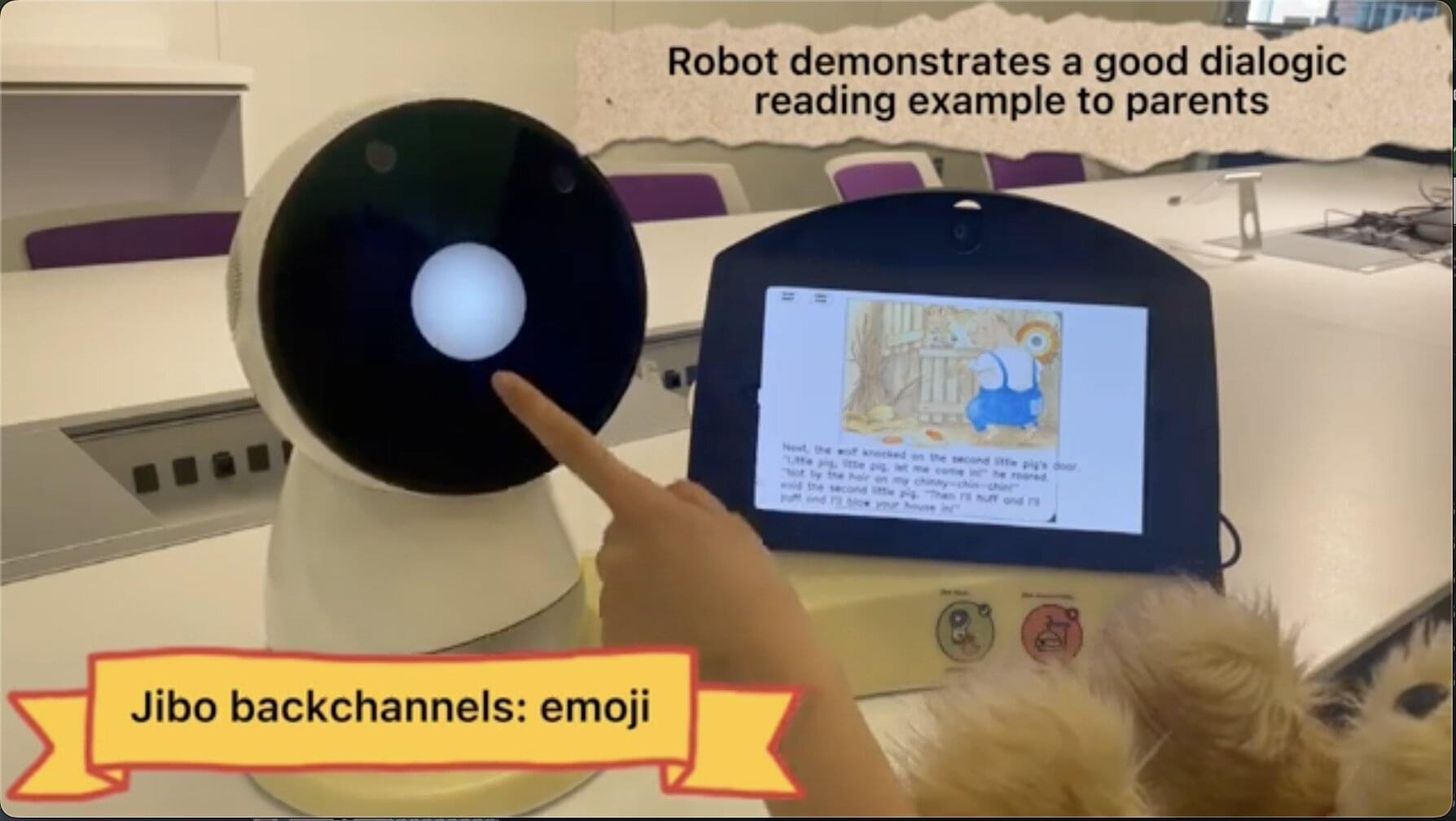
Over the past decades, researchers have developed a wide range of advanced social and assistance robots that could soon be introduced into households worldwide. Understanding how the introduction of these systems might impact the lives of users and their interactions with others living in their homes is crucial, as it could inform the further improvement of robots before their widespread deployment.
Recent studies suggest that household robot companions could foster educational conversations between parents and children, particularly during story-reading sessions. By actively participating in these sessions, for instance by asking questions or assuming the role of a playmate, robots were found to augment interactions between children and their caregivers, enriching their conversations and supporting the children’s acquisition of new vocabulary.
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) recently carried out a study to further explore the potential of social robots as conversation catalysts and tools to enhance interactions between children and parents. Their findings, published in Science Robotics, suggest that English-speaking robots can improve the quality of dialogue between parents and children, with families that fluently speak English benefitting more from their use.