With the Skydio 2 Dock, a drone-in-a-box solution, the California startup wants to let companies rely on its obstacle-dodging, self-flying drone for automated mapping and surveillance — no humans needed.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 2,295
Qingsong Zhu at Ending Age-Related Diseases 2019
Dr. Qingsong Zhu, the COO of Insilico Medicine, discussed the use of deep learning in creating biomarkers for aging. Initially discussing existing clocks and the problems with animal translation, he went on to discuss what sorts of markers are ideal for age-related research and the details of training and testing a model that works with these markers, showing that a deep model compares favorably to other models.
He also used his model to show that smoking does, in fact, cause accelerated aging.
Researchers design new material using artificial intelligence
Researchers at TU Delft have developed a new supercompressible but strong material without conducting any experimental tests at all, using only artificial intelligence (AI). “AI gives you a treasure map, and the scientist needs to find the treasure,” says Miguel Bessa, first author of a publication on this subject in Advanced Materials on 14 October.
Foldable bicycle
Miguel Bessa, assistant professor in materials science and engineering at TU Delft, got the inspiration for this research project during his time at the California Institute of Technology. At a corner of the Space Structures Lab, he noticed a satellite structure that could open long solar sails from a very small package.


“Metabesity and Longevity: USA Special Case Study” is an 85-page open-access analytical report produced jointly
By and Targeting Metabesity to examine the links between metabesity, Longevity and the USA’s current health shortfalls, including low health-adjusted life expectancy (“HALE”) and the large gap between HALE and life expectancy, despite its extremely high per-capita healthcare expenditures, and to chart policy recommendations to neutralize this vast health vs wealth deficit.
Metabesity and Longevity: USA Special Case Study is an 85-page open-access analytical report produced jointly by Aging Analytics Agency and Targeting Metabesity to examine the links between metabesity, Longevity and the USA s current health shortfalls, including low health-adjusted life expectancy ( HALE ) and the large gap between HALE and life expectancy, despite its extremely high per-capita healthcare expenditures, and to chart policy recommendations to neutralize this vast health vs wealth deficit.
Link to Special Case Study: https://aginganalytics.com/longevity-usa/
As the issue of aging population intensifies, sick care will become increasingly expensive and ineffective. America needs to rapidly deploy a government-led shift from treatment to prevention, and from prevention to precision health, using deep diagnostics and prognostics in combination with biomarkers of aging, metabesity, health and intervention-effectiveness, to delay the onset of disease with as minimal intervention as possible, as early as possible. Seeking synergies between Longevity research, P4 (preventive, personalized, precision and participatory) medicine and Artificial Intelligence has the potential to enable rapid and widespread policy and infrastructural reforms for USA healthcare to quickly boost National Healthy Longevity, but only with sufficient government commitment.
Moving Beyond Mind-Controlled Limbs to Prosthetics That Can Actually ‘Feel’
Brain-machine interface enthusiasts often gush about “closing the loop.” It’s for good reason. On the implant level, it means engineering smarter probes that only activate when they detect faulty electrical signals in brain circuits. Elon Musk’s Neuralink—among other players—are readily pursuing these bi-directional implants that both measure and zap the brain.
But to scientists laboring to restore functionality to paralyzed patients or amputees, “closing the loop” has broader connotations. Building smart mind-controlled robotic limbs isn’t enough; the next frontier is restoring sensation in offline body parts. To truly meld biology with machine, the robotic appendage has to “feel one” with the body.
This month, two studies from Science Robotics describe complementary ways forward. In one, scientists from the University of Utah paired a state-of-the-art robotic arm—the DEKA LUKE—with electrically stimulating remaining nerves above the attachment point. Using artificial zaps to mimic the skin’s natural response patterns to touch, the team dramatically increased the patient’s ability to identify objects. Without much training, he could easily discriminate between the small and large and the soft and hard while blindfolded and wearing headphones.

Researchers build a soft robot with neurologic capabilities
In work that combines a deep understanding of the biology of soft-bodied animals such as earthworms with advances in materials and electronic technologies, researchers from the United States and China have developed a robotic device containing a stretchable transistor that allows neurological function.
Cunjiang Yu, Bill D. Cook Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Houston, said the work represents a significant step toward the development of prosthetics that could directly connect with the peripheral nerves in biological tissues, offering neurological function to artificial limbs, as well as toward advances in soft neurorobots capable of thinking and making judgments. Yu is corresponding author for a paper describing the work, published in Science Advances.
He is also a principal investigator with the Texas Center for Superconductivity at the University of Houston.
OpenAI’s AI-powered robot learned how to solve a Rubik’s cube one-handed
Artificial intelligence research organization OpenAI has achieved a new milestone in its quest to build general purpose, self-learning robots. The group’s robotics division says Dactyl, its humanoid robotic hand first developed last year, has learned to solve a Rubik’s cube one-handed. OpenAI sees the feat as a leap forward both for the dexterity of robotic appendages and its own AI software, which allows Dactyl to learn new tasks using virtual simulations before it is presented with a real, physical challenge to overcome.
In a demonstration video showcasing Dactyl’s new talent, we can see the robotic hand fumble its way toward a complete cube solve with clumsy yet accurate maneuvers. It takes many minutes, but Dactyl is eventually able to solve the puzzle. It’s somewhat unsettling to see in action, if only because the movements look noticeably less fluid than human ones and especially disjointed when compared to the blinding speed and raw dexterity on display when a human speedcuber solves the cube in a matter of seconds.
But for OpenAI, Dactyl’s achievement brings it one step closer to a much sought-after goal for the broader AI and robotics industries: a robot that can learn to perform a variety of real-world tasks, without having to train for months to years of real-world time and without needing to be specifically programmed.
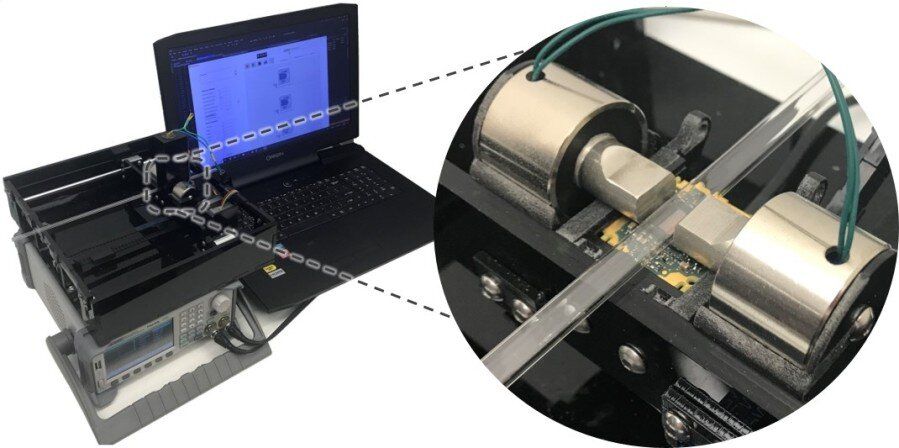
AI-based cytometer detects rare cells in blood using magnetic modulation and deep learning
Detection of rare cells in blood and other bodily fluids has numerous important applications including diagnostics, monitoring disease progression and evaluating immune response. For example, detecting and collecting circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in blood can help cancer diagnostics, study their role in the metastatic cascade and predict patient outcomes. However, because each millilitre of whole blood contains billions of blood cells, the rare cells (such as CTCs) that occur at extremely low concentrations (typically lower than 100‑1000 cells per millilitre) are very difficult to detect. Although various solutions have been developed to address this challenge, existing techniques in general are limited by high cost and low throughput.
Researchers at UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering have developed a new cytometry platform to detect rare cells in blood with high throughput and low cost. Published in Light: Science and Applications, this novel cytometry technique, termed magnetically modulated lensless speckle imaging, first uses magnetic bead labelling to enrich the target cells. Then the enriched liquid sample containing magnetic bead-labelled target cells is placed under an alternating magnetic field, which causes the target cells to oscillate laterally at a fixed frequency. At the same time, a laser diode illuminates the sample from above and an image sensor positioned below the sample captures a high-frame-rate lensless video of the time-varying optical pattern generated by the sample. The recorded spatiotemporal pattern contains the information needed to detect the oscillating target cells.
The researchers built a compact and low-cost prototype of this computational lensless cytometer using off-the-shelf image sensors, laser diodes and electromagnets, and used a custom-built translation stage to allow the imager unit to scan liquid sample loaded in a glass tube. The prototype can screen the equivalent of ~1.2 mL of whole blood sample in ~7 min, while costing only ~$750 and weighing ~2.1 kg. Multiple parallel imaging channels can also be easily added to the system to further increase sample throughput.