ELON MUSK’S ‘mind-boggling’ Neuralink brain-computer interface, could revolutionise the human consciousness – but the cutting-edge tech could come at a cost, an AI expert has warned.
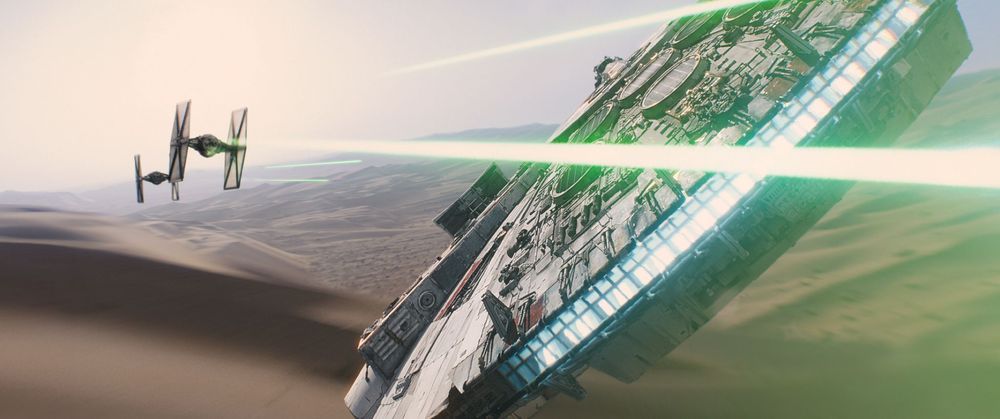





#StarWarsDay #StarWars #StarWarsCelebration #NASA #MayThe4thBeWithYou
Space Screening, ‘TIE’-ins, Tatooine and The Droids You’re Looking For
NASA astronauts “use the force” every time they launch … from a certain point of view. We have real-world droids and ion engines. We’ve seen dual-sun planets like Tatooine and a moon that eerily resembles the Death Star. And with all the excitement around the premiere of Star Wars: The Force Awakens, the Force will soon be felt 250 miles above Earth on the International Space Station. Disney is sending up the new film so the astronauts can watch in orbit, and the station’s commander, Scott Kelly, can hardly wait:
If you’re looking to be a “sky walker” yourself someday, NASA is now taking astronaut applications and we’re offering a list of Star Wars-related reasons you should apply. Recently returned station astronaut Kjell Lindgren is such a fan that he posed with his station crewmates in a Jedi-themed mission poster and talked to StarWars.com about it. Shortly before leaving the station, Lindgren tweeted about the uncanny resemblance of the station’s cupola to the cockpit of an Imperial TIE Fighter:
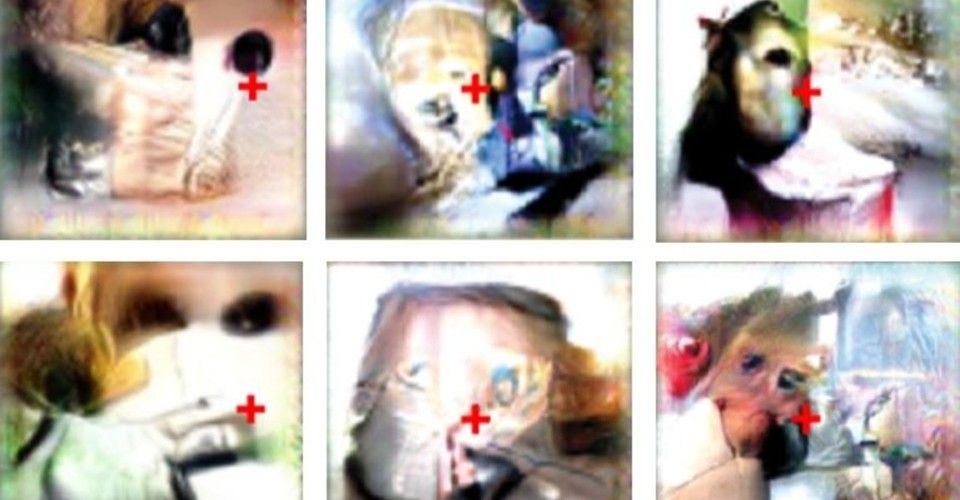

So why not ask the neurons what they want to see?
Read: The human remembering machine
That was the idea behind XDREAM, an algorithm dreamed up by a Harvard student named Will Xiao. Sets of those gray, formless images, 40 in all, were shown to watching monkeys, and the algorithm tweaked and shuffled those that provoked the strongest responses in chosen neurons to create a new generation of pics. Xiao had previously trained XDREAM using 1.4 million real-world photos so that it would generate synthetic images with the properties of natural ones. Over 250 such generations, the synthetic images became more and more effective, until they were exciting their target neurons far more intensely than any natural image. “It was exciting to finally let a cell tell us what it’s encoding instead of having to guess,” says Ponce, who is now at Washington University in St. Louis.
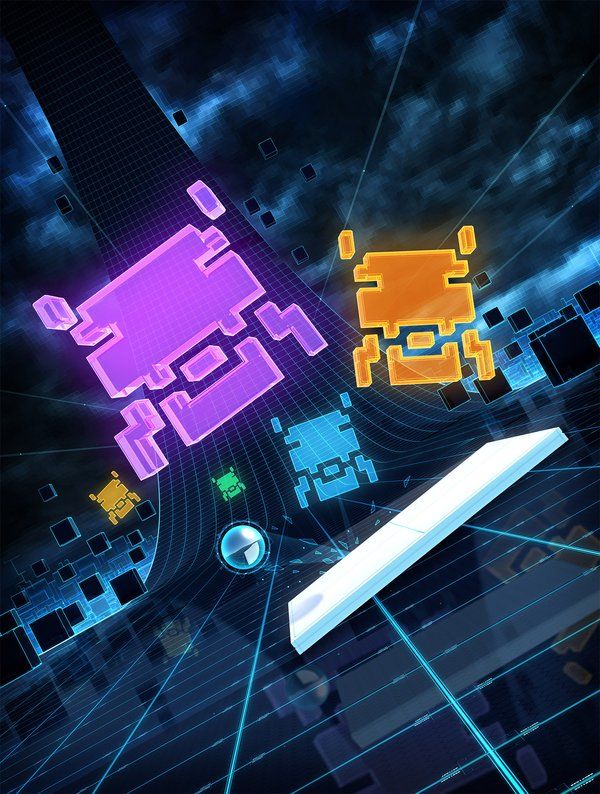


This paper published in Nature on 26th February 2015, describes a DeepRL system which combines Deep Neural Networks with Reinforcement Learning at scale for the first time, and is able to master a diverse range of Atari 2600 games to superhuman level with only the raw pixels and score as inputs.
For artificial agents to be considered truly intelligent they should excel at a wide variety of tasks that are considered challenging for humans. Until this point, it had only been possible to create individual algorithms capable of mastering a single specific domain. With our algorithm, we leveraged recent breakthroughs in training deep neural networks to show that a novel end-to-end reinforcement learning agent, termed a deep Q-network (DQN), was able to surpass the overall performance of a professional human reference player and all previous agents across a diverse range of 49 game scenarios.
