Futuristic rifles may decide who to shoot.
Target acquired.

Ford partnered with Agility Robotics to create Digit, a two-legged robot that could deliver your packages straight to your door in the future. Ford claims this robot can carry packages up to 40 pounds, navigate stairs, and go around unexpected obstacles.
#Ford #Robot #TechInsider
Tech Insider tells you all you need to know about tech: gadgets, how-to’s, gaming, science, digital culture, and more.
Visit us at: https://www.businessinsider.com
TI on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/techinsider
TI on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tech_insider/
TI on Twitter: https://twitter.com/techinsider
TI on Amazon Prime: http://read.bi/PrimeVideo
INSIDER on Snapchat: https://insder.co/2KJLtVo
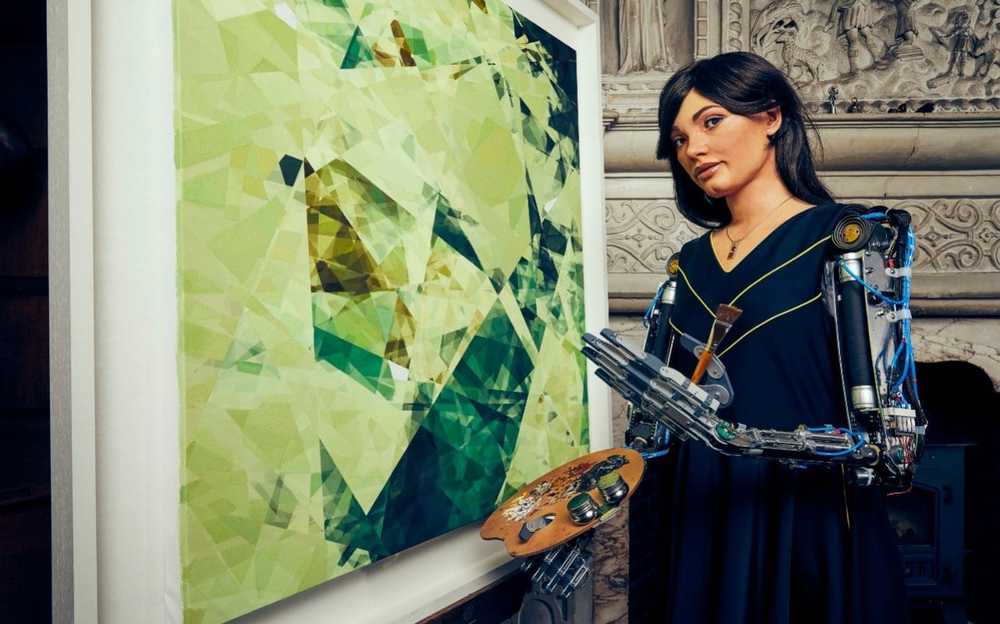

Auguste Rodin spent the best part of four decades working on his epic sculpture The Gates of Hell.
The Mona Lisa, by contrast, took Leonardo da Vinci a mere 15 years or so, although it should be noted the Renaissance master never considered the painting finished.
So we can only imagine what those luminaries would think of an up-and-coming Oxford-based contemporary artist who can knock out complex works in under two hours.
In the “Automate the Freight” series, I’ve concentrated on stories that reflect my premise that the killer app for self-driving vehicles will not be private passenger cars, but will more likely be the mundane but necessary task of toting things from place to place. The economics of replacing thousands of salary-drawing and benefit-requiring humans in the logistics chain are greatly favored compared to the profits to be made by providing a convenient and safe commuting experience to individuals. Advances made in automating deliveries will eventually trickle down to the consumer market, but it’ll be the freight carriers that drive innovation.
While I’ve concentrated on self-driving freight vehicles, there are other aspects to automating the supply chain that I’ve touched on in this series, from UAV-delivered blood and medical supplies to the potential for automating the last hundred feet of home delivery with curb-to-door robots. But automation of the other end of the supply chain holds a lot of promise too, both for advancing technology and disrupting the entire logistics field. This time around: automated packaging lines, or how the stuff you buy online gets picked and wrapped for shipping without ever being touched by human hands.

DARPA’s Air Combat Evolution program aims to find out — and so shape America’s future arsenal.
A U.S. military research program is advancing the study of humans and machines working together by testing how well pilots and artificially intelligent entities trust each other in one of the most challenging of tasks: aerial combat, or dogfighting.
The idea behind DARPAs Air Combat Evolution, or ACE, program, is that human fighter pilots will soon be flying alongside increasingly capable drones — dubbed “Loyal Wingmen” — that will help evade other fighters and air defenses. Military leaders often describe the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter as a kind of flying command center, with the human operator working less like a traditional pilot and more like a team captain. The craft is loaded with AI features that pilots say make it easier to fly than traditional fighters. That enables the pilot to digest and put to use the immense amount of data the F-35 pulls in.
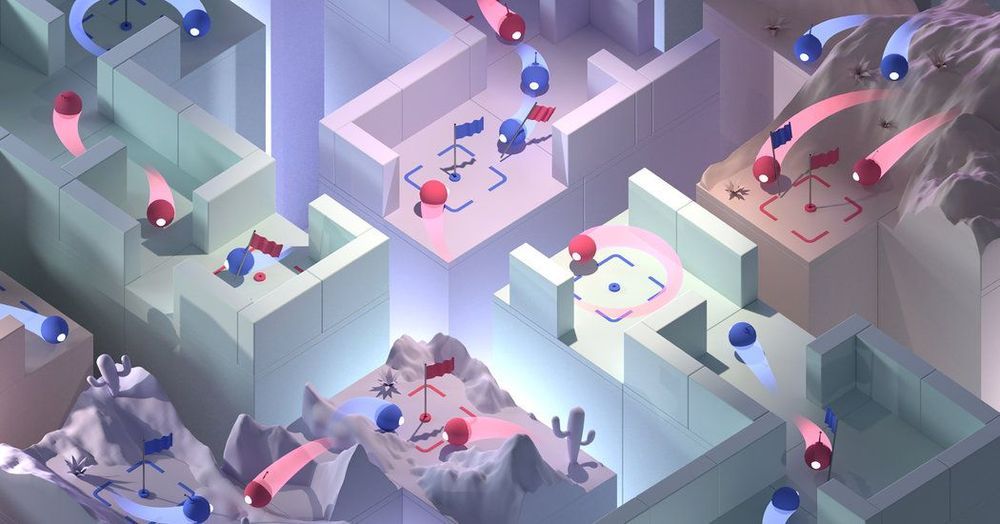

As impressive as such technology has been among gamers, many artificial-intelligence experts question whether it will ultimately translate to solving real-world problems. DeepMind’s agents are not really collaborating, said Mark Riedl, a professor at Georgia Tech College of Computing who specializes in artificial intelligence. They are merely responding to what is happening in the game, rather than trading messages with one another, as human players do. (Even mere ants can collaborate by trading chemical signals.)
Chess and Go were child’s play. Now A.I. is winning at capture the flag. Will such skills translate to the real world?
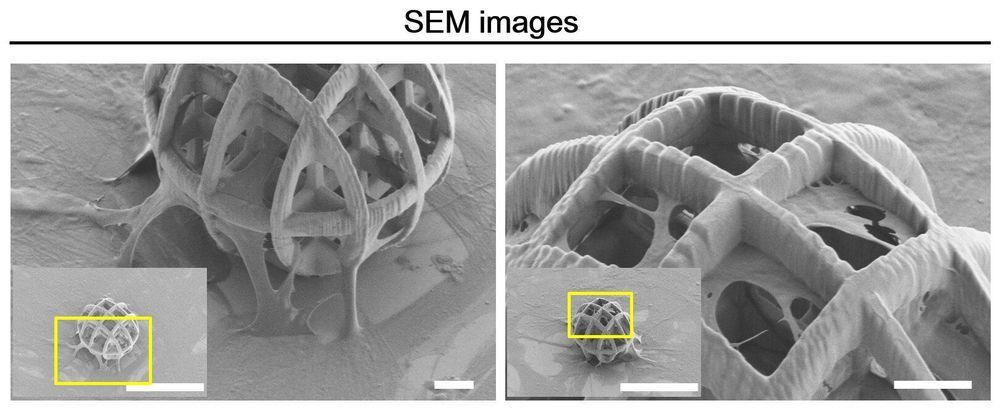
A team of researchers affiliated with several institutions in South Korea and one in Switzerland has demonstrated that it is possible to use magnetically actuated microrobots to deliver stem cells to targeted tissue. In their paper published in the journal Science Robotics, the group describes creating the tiny bots and how well they worked when tested.