Machine learning predicts 43 previously unknown, superhard forms of carbon. Could one offer a cheaper alternative to diamond?


Downloading your brain may seem like science fiction, but some neuroscientists think it’s not only possible, but that we’ve already started down a path to one day make it a reality. So, how close are we to downloading a human brain?
How Close Are We to Fusion Energy? — https://youtu.be/ZW_YCWLyv6A
We’ve Put a Worm’s Mind in a Lego Robot’s Body
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/weve-put-worms-min…399/?no-is
“A wheeled Lego robot may not look like a worm, but it ‘thinks’ like one after programmers gave it the neuron connections in a C. elegans roundworm”
Crumb of Mouse Brain Reconstructed in Full Detail
https://www.nature.com/news/crumb-of-mouse-brain-reconstruct…il-1.18105
“The resulting three-dimensional map is the first complete reconstruction of a piece of tissue in the mammalian neocortex, the most recently evolved region of the brain.”
The Immortalist: Uploading the Mind to a Computer
https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-35786771
“Within the next 30 years,” promises Dmitry Itskov, “I am going to make sure that we can all live forever.”
____________________

Self-driving vehicles will lead to a rise in car sex, according to a new study.
People will be more likely to eat, sleep and engage in on-the-road hanky-panky when robot cars become the new normal, according to research published in the most recent issue of the journal Annals of Tourism Research.
“People will be sleeping in their vehicles, which has implications for roadside hotels. And people may be eating in vehicles that function as restaurant pods,” Scott Cohen, who led the study, told Fast Company magazine.


Hey Google, how many enemy combatants remain standing?
British soldiers could soon be offered a “military Alexa” digital assistant which would provide troops in the field with automated information from combat tactics to repair instructions.
The Ministry of Defence has awarded a £700,000 contract to a British technology company to explore the feasibility of an artificial intelligence “chatbot” which will allow soldiers on deployment to obtain crucial information via computer link.
The specification for the AI system requires that it be accessible via military “tactical radios” and handheld devices, suggesting that it could even be used by troops on the frontline engaged in combat to access intelligence and vital information. Although initially text based, the chatbot could also be further developed to give instructions by voice.
Prof. Steve Fuller is the author of 25 books including a trilogy relating to the idea of a ‘post-’ or ‘trans-‘human future, and most recently, Nietzschean Meditations: Untimely Thoughts at the Dawn of the Transhuman Age.
During this 2h 15 min interview with Steve Fuller we cover a variety of interesting topics such as: the social foundations of knowledge and our shared love of books; Transhumanism as a scientistic way of understanding who we are; the proactionary vs the precautionary principle; Pierre Teilhard de Chardin and the Omega Point; Julian and Aldous Huxley’s diverging takes on Transhumanism; David Pearce’s Hedonistic Imperative as a concept straight out of Brave New World; the concept and meaning of being human, transhuman and posthuman; humanity’s special place in the cosmos; my Socratic Test of (Artificial) Intelligence; Transhumanism as a materialist theology – i.e. religion for geeks; Elon Musk, cosmism and populating Mars; de-extinction, genetics and the sociological elements of a given species; the greatest issues that humanity is facing today; AI, the Singularity and armed conflict; morphological freedom and becoming human; longevity and the “Death is Wrong” argument; Zoltan Istvan and the Transhumanist Wager; Transhumanism as a way of entrenching rather than transcending one’s original views…
As always you can listen to or download the audio file above or scroll down and watch the video interview in full. To show your support you can write a review on iTunes, make a direct donation or become a patron on Patreon.

Particle physicists are planning the successor to CERN’s Large Hadron Collider – but how will they deal with the deluge of data from a future machine and the proliferation of theoretical models? Michela Massimi explains why a new scientific methodology called “model independence” could hold the answer.
It’s been an exciting few months for particle physicists. In May more than 600 researchers gathered in Granada, Spain, to discuss the European Particle Physics Strategy, while in June CERN held a meeting in Brussels, Belgium, to debate plans for the Future Circular Collider (FCC). This giant machine – 100 km in circumference and earmarked for the Geneva lab – is just one of several different projects (including those in astroparticle physics and machine learning) that particle physicists are working on to explore the frontiers of high-energy physics.
CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has been collecting data from vast numbers of proton–proton collisions since 2010 – first at an energy of 8 TeV and then 13 TeV during its second run. These have enabled scientists on the ATLAS and CMS experiments at the LHC to discover the Higgs boson in 2012, while light has also been shed on other vital aspects of the Standard Model of particle physics.

TVs and radios blare that “artificial intelligence is coming,” and it will take your job and beat you at chess.
But AI is already here, and it can beat you — and the world’s best — at chess. In 2012, it was also used by Google to identify cats in YouTube videos. Today, it’s the reason Teslas have Autopilot and Netflix and Spotify seem to “read your mind.” Now, AI is changing the field of synthetic biology and how we engineer biology. It’s helping engineers design new ways to design genetic circuits — and it could leave a remarkable impact on the future of humanity through the huge investment it has been receiving ($12.3b in the last 10 years) and the markets it is disrupting.
The positronic brain was an extremely sophisticated computation device capable of artificial sentience, created by Dr. Noonian Soong, based on an idea from author Isaac Asimov. ( TNG : “ Datalore ”)
This device consisted of an artificial neural network, designed to imitate the humanoid brain. The construction of a positronic brain was extremely complex, and Dr. Soong was the only scientist to have done so successfully – on at least six occasions: two unspecified prototypes, B-4, Lore, Data, and Juliana Soong (although the latter three were the only truly stable units).
One of the difficulties in creating a stable positronic brain was determining how the electron resistance across the neural filaments was to be resolved. ( TNG : ” The Measure Of A Man ”)
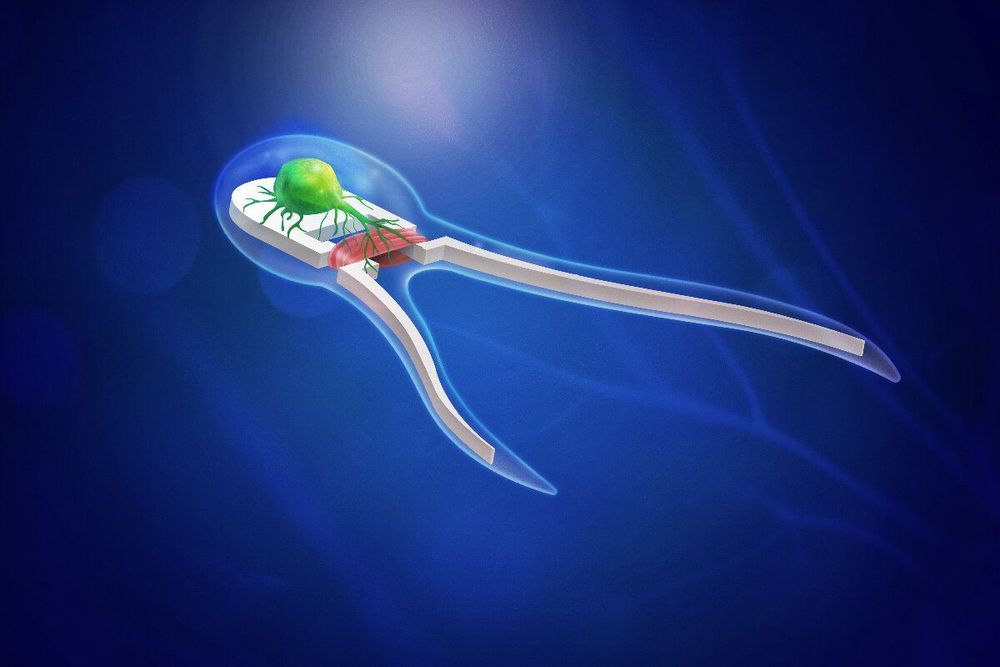
Researchers have developed soft robotic devices driven by neuromuscular tissue that triggers when stimulated by light—bringing mechanical engineering one step closer to developing autonomous biobots.
In 2014, research teams led by mechanical science and engineering professor Taher Saif and bioengineering professor Rashid Bashir at the University of Illinois worked together to developed the first self-propelled biohybrid swimming and walking biobots powered by beating cardiac muscle cells derived from rats.
“Our first swimmer study successfully demonstrated that the bots, modeled after sperm cells, could in fact swim,” Saif said. “That generation of singled-tailed bots utilized cardiac tissue that beats on its own, but they could not sense the environment or make any decisions.”