AI will do the thinking, robots will do the doing. What place do humans have in this arrangement – and do tech CEOs care? says Ed Newton-Rex, founder of Fairly Trained


Engineers at RMIT University have invented a small “neuromorphic” device that detects hand movement, stores memories and processes information like a human brain, without the need for an external computer.
The findings are published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
Team leader Professor Sumeet Walia said the innovation marked a step toward enabling instant visual processing in autonomous vehicles, advanced robotics and other next-generation applications for improved human interaction.

We discuss Michael Levin’s paper “Self-Improvising Memory: A Perspective on Memories as Agential, Dynamically Reinterpreting Cognitive Glue.” Levin is a scientist at Tufts University, his lab studies anatomical and behavioral decision-making across biological, artificial, and hybrid systems. His work spans developmental biology, artificial life, bioengineering, synthetic morphology, and cognitive science. 🎥 Next, watch my first interview with Michael Levin… What are Cognitive Light Cones? • What are Cognitive Light Cones? (Mich… ❶ Memories as Agents 0:00 Introduction 1:40 2024 Highlights from Levin Lab 3:20 Stress sharing paper summary 6:15 Paradox of change: Species persist don’t evolve 7:20 Bow-tie architectures 10:00 🔥 Memories as messages from your past self 12:50 Polycomputing 16:45 Confabulation 17:55 What evidence supports the idea that memories are agential? 22:00 Thought experiment: Entities from earth’s core ❷ Information Patterns 31:30 Memory is not a filing cabinet 32:30 Are information patterns agential? 35:00 🔥 Caterpillar/butterfly… sea slug memory transfer 37:40 Bow-tie architectures are EVERYWHERE 43:20 Bottlenecks “scary” for information ❸ Connections & Implications 45:30 🔥 Black holes/white holes as bow-ties (Lee Smolin) 47:20 What is confabulation? AI hallucinations 52:30 Gregg Henriques & self-justifying apes… all good agents storytellers 54:20 Information telling stories… Joseph Campbell’s journey for a single cell 1:00:50 What comes next? 🚾 Works Cited 🚩 Self-Improvising Memory: A Perspective on Memories as Agential, Dynamically Reinterpreting Cognitive Glue https://www.mdpi.com/1099-4300/26/6/481 https://thoughtforms.life/suti-the-se… our way to health with robot cells | Michael Levin (Big Think 2023)
• Biohacking our way to health with rob… https://peregrinecr.com/ 🚀 What is this channel? Exploring Truth in philosophy, science, & art. We’ll uncover concepts from psychology, mythology, spirituality, literature, media, and more. If you like Lex Fridman or Curt Jaimungal, you’ll love this educational channel. p.s. Please subscribe! Young channel here. =) #science #memory #biology #computing #mind #intelligence #attractor #polycomputing #bioelectric #cybernetics #research #life
At the Artificiality Summit 2024, Michael Levin, distinguished professor of biology at Tufts University and associate at Harvard’s Wyss Institute, gave a lecture about the emerging field of diverse intelligence and his frameworks for recognizing and communicating with the unconventional intelligence of cells, tissues, and biological robots. This work has led to new approaches to regenerative medicine, cancer, and bioengineering, but also to new ways to understand evolution and embodied minds. He sketched out a space of possibilities—freedom of embodiment—which facilitates imagining a hopeful future of \.
Recorded 6 November 2024. Michael Levin of Tufts University presents “Non-neural intelligence: biological architectures for problem-solving in diverse spaces” at IPAM’s Naturalistic Approaches to Artificial Intelligence Workshop. Abstract: The familiar, readily-recognized intelligence of brainy animals has long served as inspiration for AI. However, biological intelligence is far older than neurons, and indeed than multicellularity. My lab studies problem-solving in cells, tissues, and even subcellular components, operating in different spaces and at different scales than conventional intelligent agents. In this talk, I will describe a framework for detecting, communicating with, and creating collective intelligences, and show examples of how the fundamental properties of life suggest novel approaches for ethically relating to diverse and fascinating engineered and hybrid intelligences. Learn more online at: https://www.ipam.ucla.edu/programs/wo…

Artificial intelligence could be affecting the scientific rigor of new research, according to a study from the University of Surrey.
The research team has called for a range of measures to reduce the flood of “low-quality” and “science fiction” papers, including stronger peer review processes and the use of statistical reviewers for complex datasets.
In a study published in PLOS Biology, researchers reviewed papers proposing an association between a predictor and a health condition using an American government dataset called the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), published between 2014 and 2024.
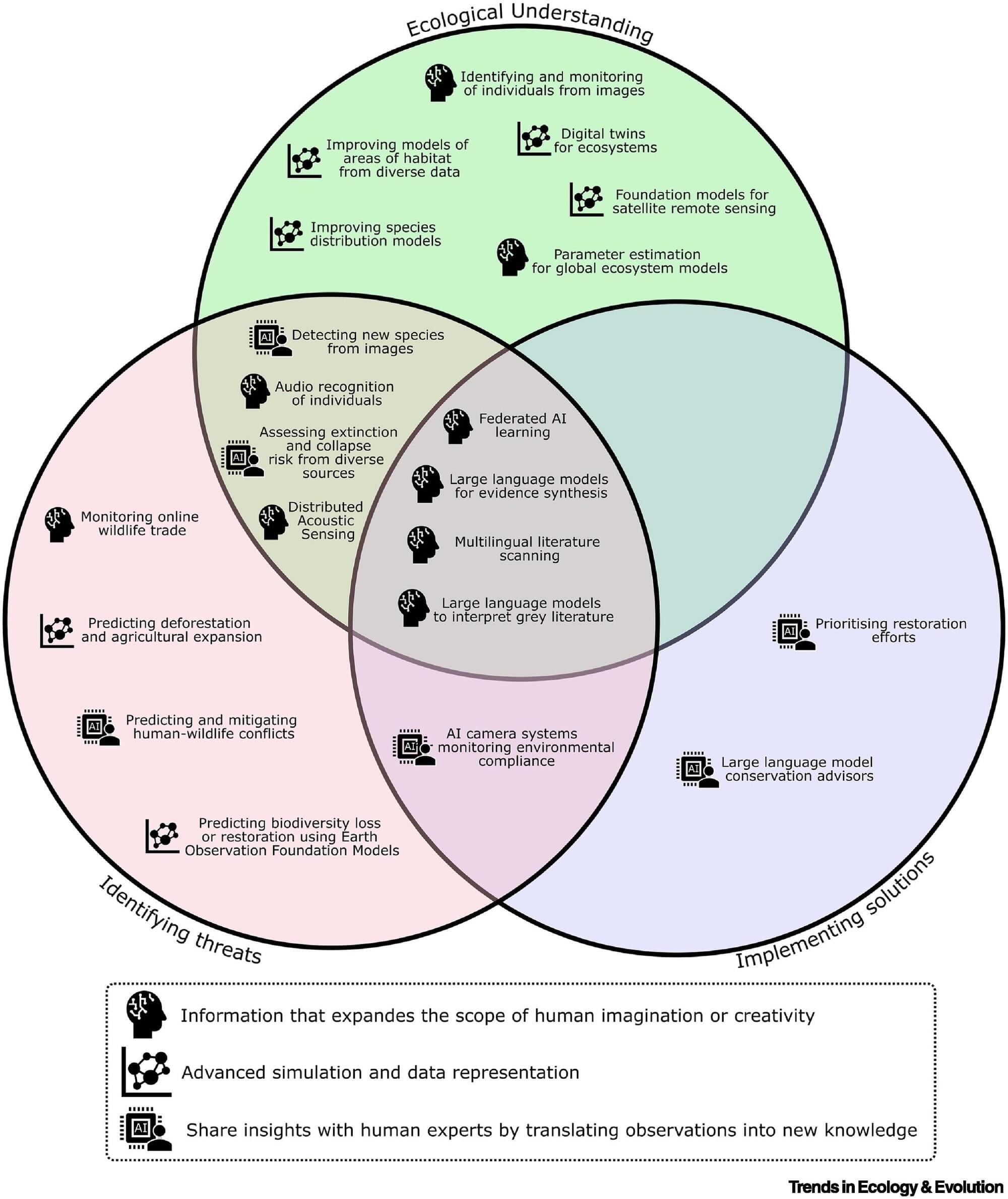
AI is a computing tool. It can process and interrogate huge amounts of data, expand human creativity, generate new insights faster and help guide important decisions. It’s trained on human expertise, and in conservation that’s informed by interactions with local communities or governments—people whose needs must be taken into account in the solutions. How do we ensure this happens?
Last year, Reynolds joined 26 other conservation scientists and AI experts in an “Horizon Scan”—an approach pioneered by Professor Bill Sutherland in the Department of Zoology—to think about the ways AI could revolutionize the success of global biodiversity conservation. The international panel agreed on the top 21 ideas, chosen from a longlist of 104, which are published in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution.
Some of the ideas extrapolate from AI tools many of us are familiar with, like phone apps that identify plants from photos, or birds from sound recordings. Being able to identify all the species in an ecosystem in real time, over long timescales, would enable a huge advance in understanding ecosystems and species distributions.
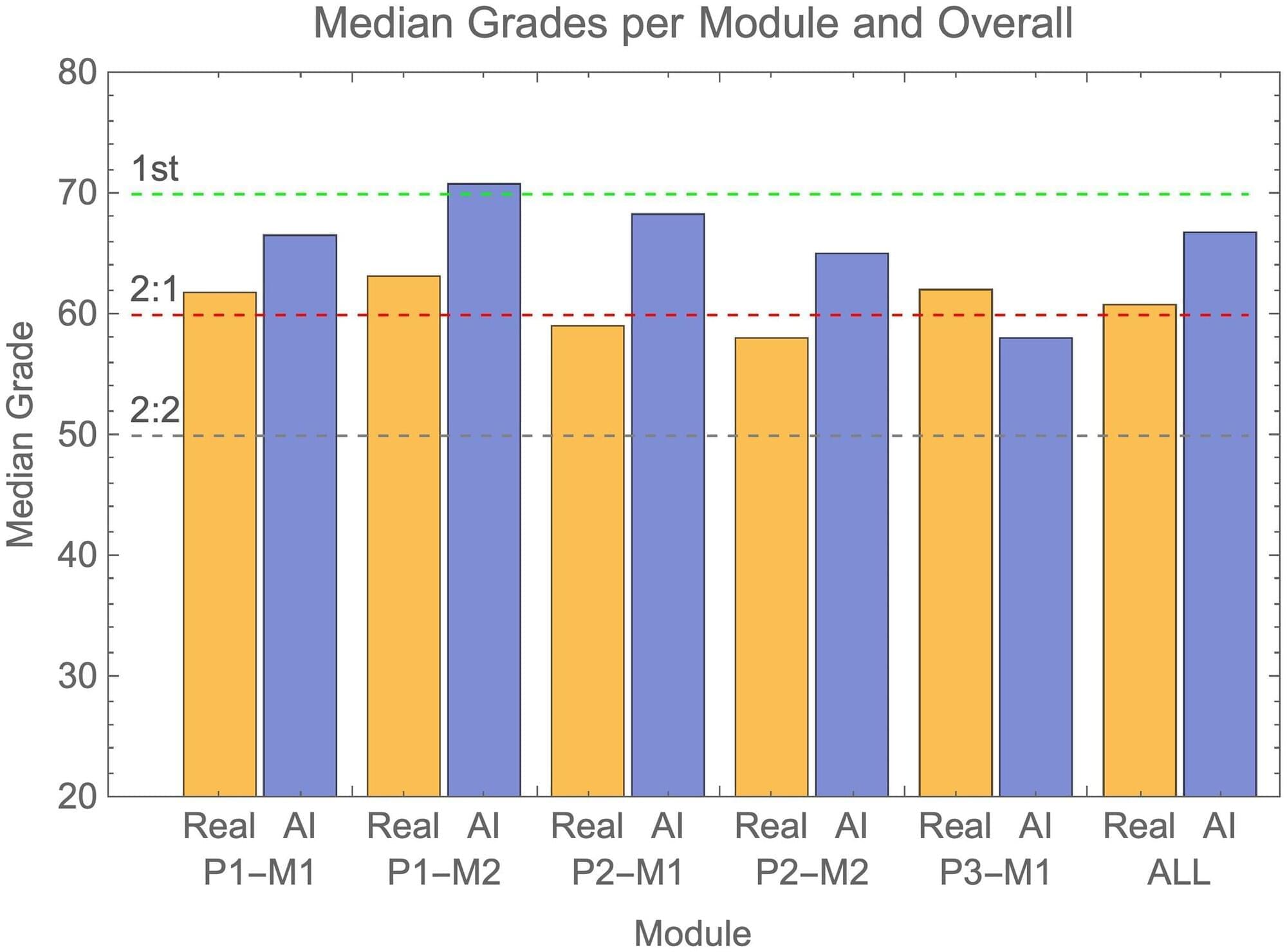
In a test of the examinations system of the University of Reading in the UK, artificial intelligence (AI)-generated submissions went almost entirely undetected, and these fake answers tended to receive higher grades than those achieved by real students. Peter Scarfe of the University of Reading and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 26.
In recent years, AI tools such as ChatGPT have become more advanced and widespread, leading to concerns about students using them to cheat by submitting AI-generated work as their own. Such concerns are heightened by the fact that many universities and schools transitioned from supervised in-person exams to unsupervised take-home exams during the COVID-19 pandemic, with many now continuing such models. Tools for detecting AI-generated written text have so far not proven very successful.
To better understand these issues, Scarfe and colleagues generated answers that were 100% written by the AI chatbot GPT-4 and submitted on behalf of 33 fake students to the examinations system of the School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences at the University of Reading. Exam graders were unaware of the study.
In this episode, Dr. Michael Levin, Distinguished Professor of Biology at Tufts University, joins Nathan to discuss embodied minds, his research into limb regeneration and collective intelligence, cognitive light cones, and much more. Dr. Levin and the Levin Lab work at the intersection of biology, artificial life, bioengineering, synthetic morphology, and cognitive science.
LINKS:
The Levin Lab and Dr. Michael Levin’s research: https://drmichaellevin.org/resources/
Dr Michael Levin’s blog: https://thoughtforms.life/about/
Tufts University Faculty Profile: https://as.tufts.edu/biology/people/f… Levin @ Wyss Institute: https://wyss.harvard.edu/team/associa… Dr. Levin’s Research on Limb Regeneration: https://news.uchicago.edu/how-bioelec… SPONSORS: The Brave search API can be used to assemble a data set to train your AI models and help with retrieval augmentation at the time of inference. All while remaining affordable with developer first pricing, integrating the Brave search API into your workflow translates to more ethical data sourcing and more human representative data sets. Try the Brave search API for free for up to 2000 queries per month at https://brave.com/api Omneky is an omnichannel creative generation platform that lets you launch hundreds of thousands of ad iterations that actually work customized across all platforms, with a click of a button. Omneky combines generative AI and real-time advertising data. Mention “Cog Rev” for 10% off www.omneky.com NetSuite has 25 years of providing financial software for all your business needs. More than 36,000 businesses have already upgraded to NetSuite by Oracle, gaining visibility and control over their financials, inventory, HR, eCommerce, and more. If you’re looking for an ERP platform ✅ head to NetSuite: http://netsuite.com/cognitive and download your own customized KPI checklist. X/SOCIAL @labenz (Nathan)@drmichaellevin (Michael) @CogRev_Podcast TIMESTAMPS: (00:00) Preview (01:07) Intro and brief summary (05:40) Xenobots, anthrobots and the other creatures created by Mike Levin (09:39) Bioelectric memory rewriting (15:01) Sponsor | BraveSearch API (16:09) The difficulty of conducting simulations, which involve running forward passes to predict and alter electrical patterns (20:30) The concept of backpropagation and mode switching in AI models (23:06) Why humans do not regenerate their limbs (37:10) Sponsor | Netsuite (39:40) Learning from small and biological systems onto the concept of possible emergence (45:16) The criticality of multiple scale questions and would a single scale? (55:49) The concept of the cognitive light cone (59:43) Advice on habits of mind and suggestions for inspiration on the AI side (1:13:36) Mike’s suggested directions for the AI developers (1:24:49) Wrap & Sponsor | Omneky The Cognitive Revolution is produced by Turpentine: a media network covering technology, business, and culture. Producer: Vivian Meng Editor: Graham Bessellieu For sponsor or guest inquiries, email: [email protected] Music licenses: ABZUSWHJII08TSRH 376I29BQPJASOLX2
Michael Levin @ Wyss Institute: https://wyss.harvard.edu/team/associa…
Dr. Levin’s Research on Limb Regeneration: https://news.uchicago.edu/how-bioelec…
SPONSORS:
The Brave search API can be used to assemble a data set to train your AI models and help with retrieval augmentation at the time of inference. All while remaining affordable with developer first pricing, integrating the Brave search API into your workflow translates to more ethical data sourcing and more human representative data sets. Try the Brave search API for free for up to 2000 queries per month at https://brave.com/api.
Omneky is an omnichannel creative generation platform that lets you launch hundreds of thousands of ad iterations that actually work customized across all platforms, with a click of a button. Omneky combines generative AI and real-time advertising data. Mention \.