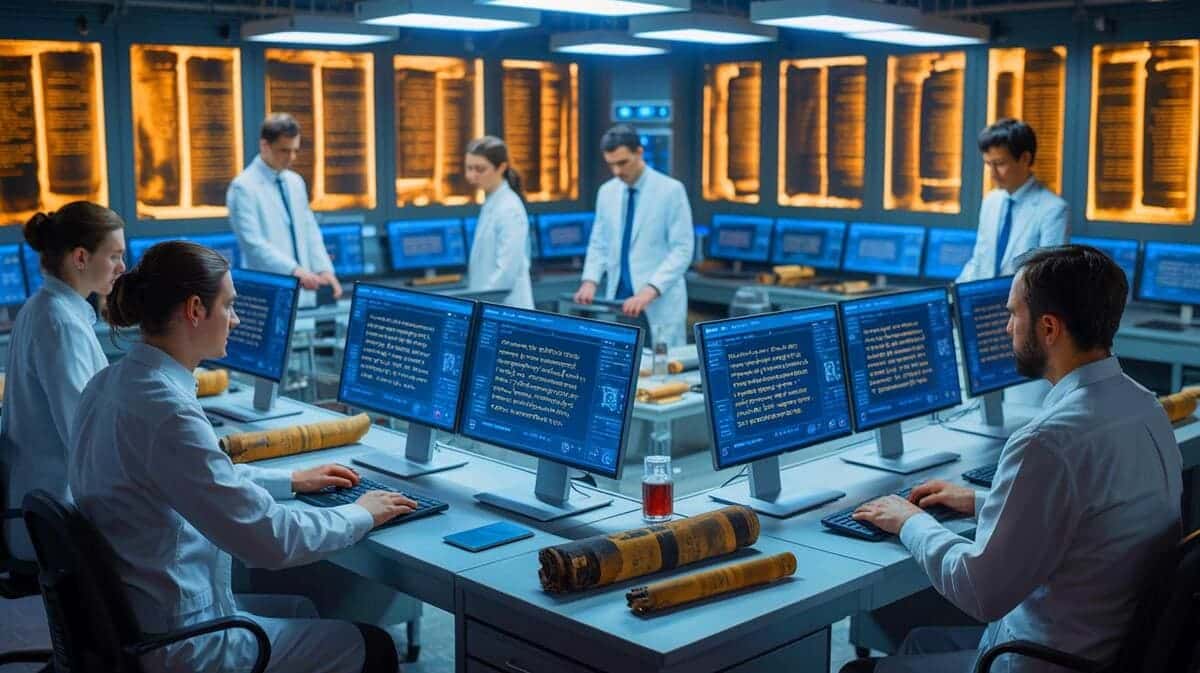
In a groundbreaking achievement, scientists have used advanced artificial intelligence (AI) to decode the contents of a 2,000-year-old Greek scroll without ever unrolling it, unveiling new insights into ancient intellectual life.



🏗️ Q: What are the potential benefits of off-worlding heavy industry to space?
A: Space-based manufacturing can produce sustainable energy, food, and water for a trillion-dollar space economy, allowing Earth to recover as a garden planet for future generations.
Space-Based Manufacturing.
🧬 Q: How can microgravity in low-Earth orbit advance biotech manufacturing?
A: Enable unique manufacturing of protein crystals, tissues, and novel drugs impossible on Earth, with high-throughput production of exceptional quality organoids for Alzheimer’s and cancer drug testing.
☀️ Q: How can space-based solar power solve Earth’s energy challenges?

Please consider joining my Substack at https://rupertsheldrake.substack.com.
In this talk, Rupert Sheldrake explores panentheism—the idea that the divine is not separate from the world but present throughout it, while also transcending it. With the grip of mechanistic materialism loosening, Rupert invites us to reconsider how we see nature, mind, and spirit. Tracing a broad arc from ancient philosophies and Christian mysticism to AI-generated worldviews, panpsychism, and psychedelics, he reflects on how the sacred presence in nature—-long affirmed by spiritual traditions-—is re-emerging through science, experience, and renewed practices of attention.
This talk was recorded at St James Church, Piccadilly, a longstanding hub for open spiritual inquiry and progressive theology in the heart of London.
Table of Contents.
00:00:00 — What Is Panentheism?
00:00:37 — The Dominant Worldview: Mechanistic Materialism.
00:01:46 — The Decline of Materialism & Rise of Alternatives.
00:02:21 — AI & Worldview Generation: A Symptom of Our Time.
00:03:55 — Return to a Living World: Gaia Hypothesis & Distributed Consciousness.
00:05:01 — God: Immanent vs. Transcendent (with Cultural Examples)
00:07:27 — Historical Tour: European Intellectual History.
00:07:42 — Pre-Christian & Ancient Greek Animism (Aristotle’s Souls)
00:09:51 — Medieval Period: Christianization of Greek Thought (Aquinas)
00:11:20 — Early British/Celtic Nature Mysticism.
00:12:51 — The Protestant Reformation: De-sacralizing Nature.
00:16:00 — The Scientific Revolution & Cartesian Dualism (Nature as Machine)
00:18:05 — From Deism to Atheism.
00:20:59 — The “Hard Problem” of Consciousness for Materialism.
00:23:28 — Panpsychism: Consciousness as Fundamental (Even in Stars)
00:26:26 — Pantheism (Spinoza) and Idealism (Kastrup) as Alternatives.
00:28:55 — Revival of Mystical Sense: Meditation.
00:31:00 — Psychedelics and Experiences of Greater Consciousness.
00:33:16 — The Experiential Roots of Religion (David Bentley Hart)
00:35:23 — Models of Ultimate Reality: Hindu Perspectives.
00:37:35 — Models of Ultimate Reality: The Christian Trinity & Speech Metaphor.
00:41:15 — Nature Reflecting Trinitarian Principles.
00:43:15 — The Cosmic Christ & Universe as Incarnation (Bede Griffiths)
00:44:57 — Aquinas: Nature Striving for Divine Perfection.
00:46:50 — Reconciling Immanence & Transcendence in an Evolving, Creative Universe.
00:48:17 — Spiritual Practices for Experiencing Panentheism (Singing, Festivals, Nature Connection)
00:53:46 — End of Lecture / Start of Q&A
By joining Rupert’s Substack, you’ll receive articles, ad-free episodes, early access to videos, and exclusive content:
👉 https://rupertsheldrake.substack.com.
#Panentheism.
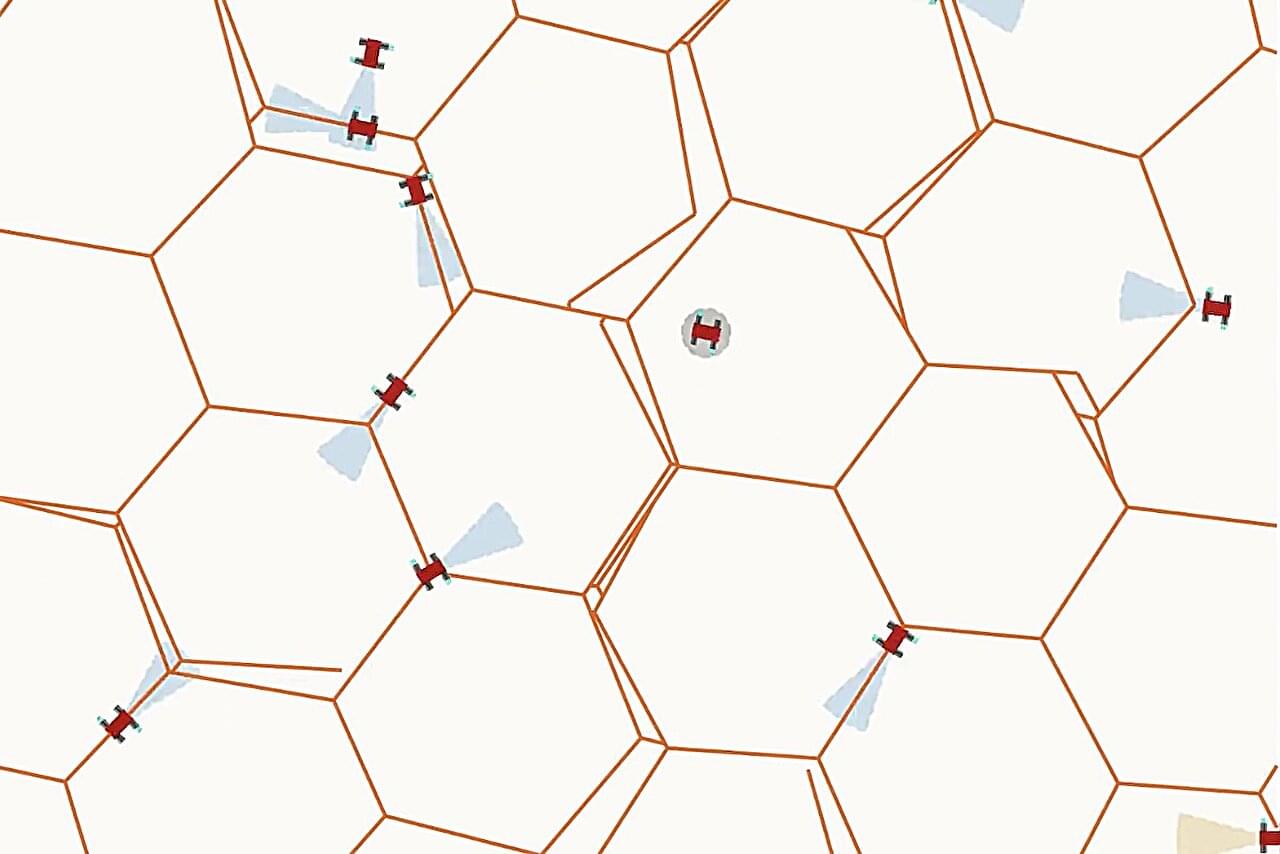
Bees, ants and termites don’t need blueprints. They may have queens, but none of these species breed architects or construction managers. Each insect worker, or drone, simply responds to cues like warmth or the presence or absence of building material. Unlike human manufacturing, the grand design emerges simply from the collective action of the drones—no central planning required.
Now, researchers at Penn Engineering have developed mathematical rules that allow virtual swarms of tiny robots to do the same. In computer simulations, the robots built honeycomb-like structures without ever following—or even being able to comprehend—a plan.
“Though what we have done is just a first step, it is a new strategy that could ultimately lead to a new paradigm in manufacturing,” says Jordan Raney, Associate Professor in Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics (MEAM), and the co-senior author of a new paper in Science Advances. “Even 3D printers work step by step, resulting in what we call a brittle process. One simple mistake, like a clogged nozzle, ruins the entire process.”
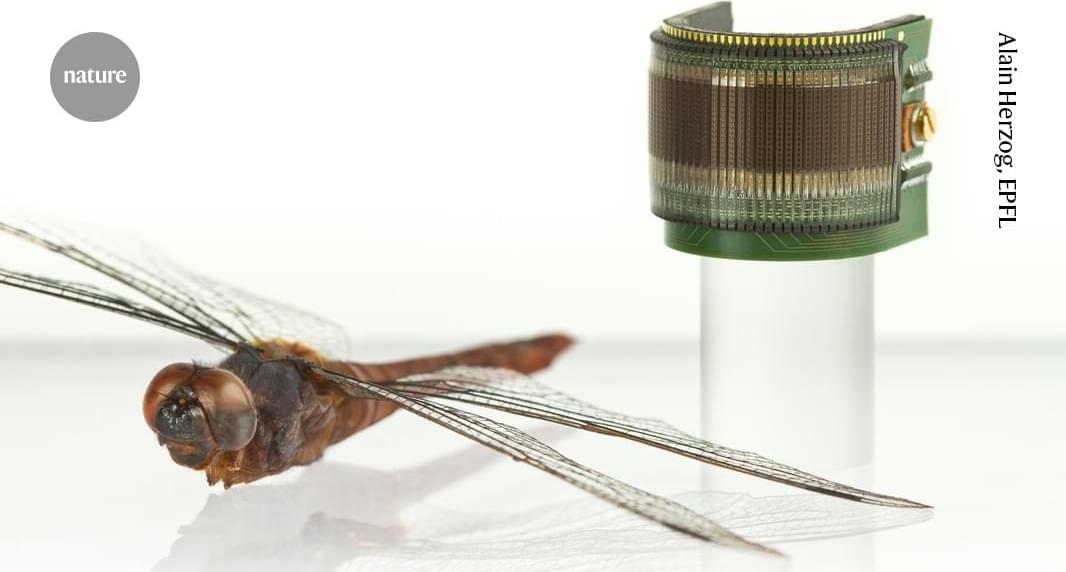

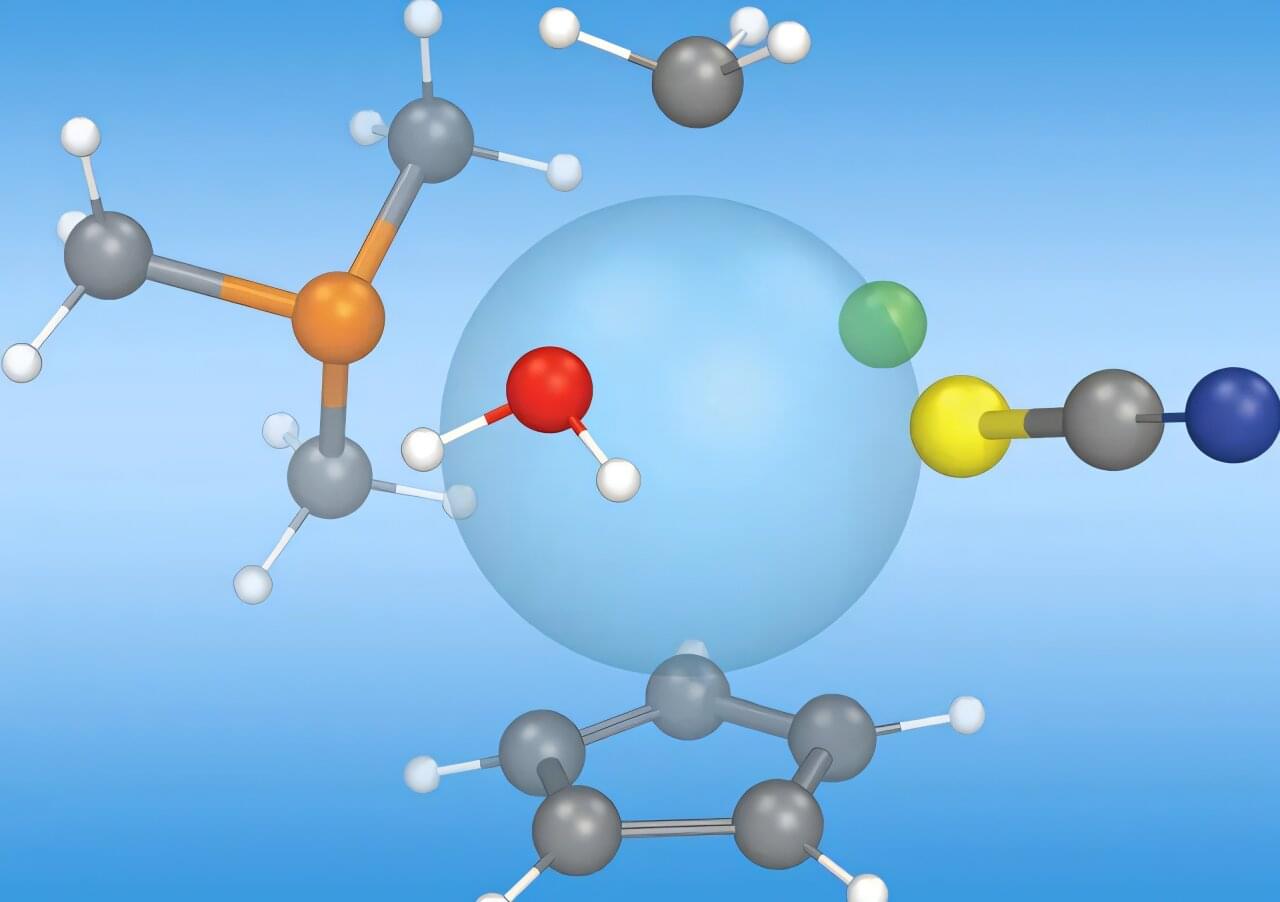
A collaborative effort between Meta, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Los Alamos National Laboratory leverages Los Alamos’ expertise in building tools for molecular screening capabilities. The release of “Open Molecules 2025”, an unprecedented dataset of molecular simulations, can accelerate opportunities for machine learning to transform research in fields such as biology, materials science and energy technologies.
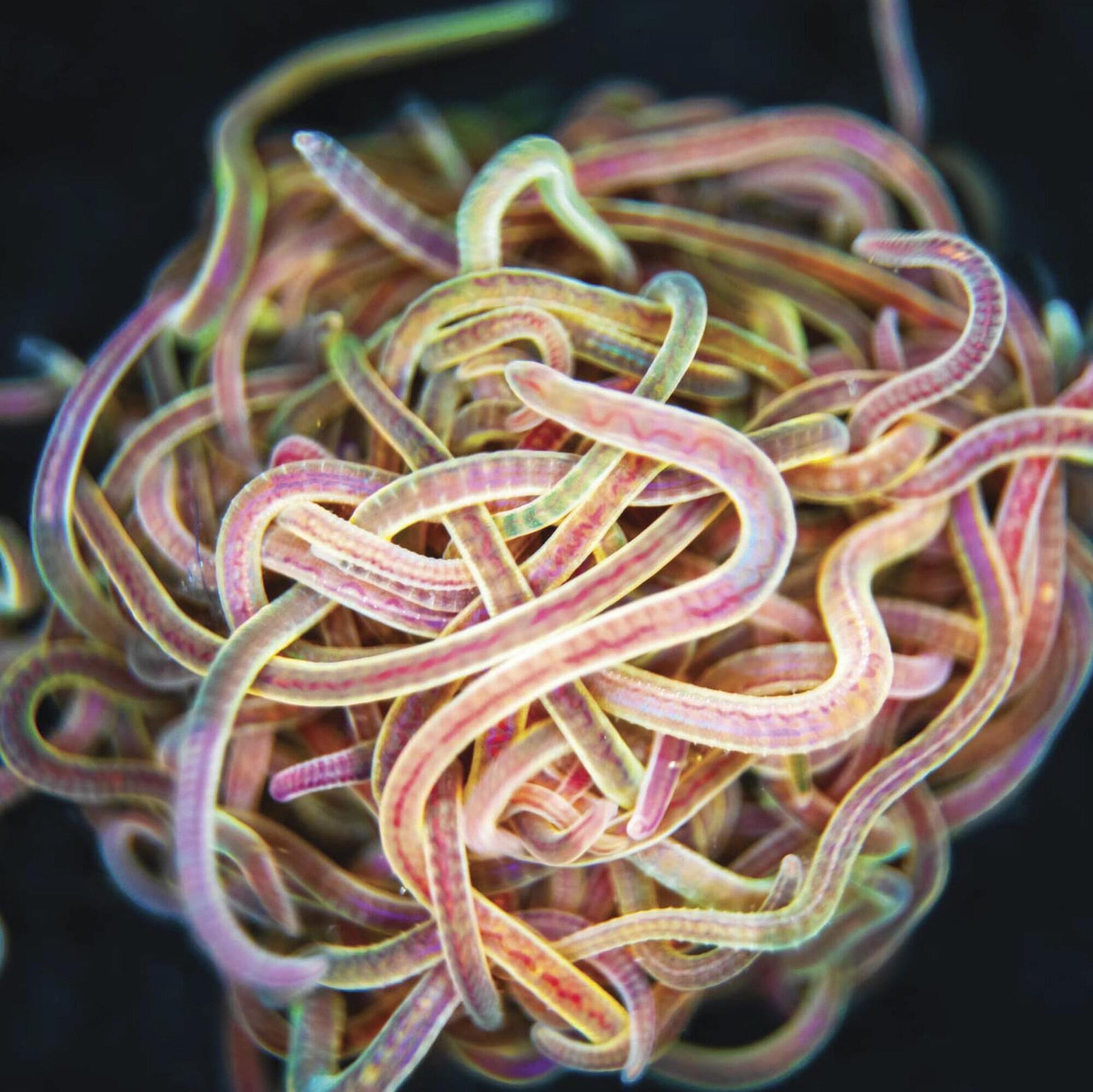


Earthworms often form a cluster, from which they can barely free themselves. A similarly active, writhing structure forms when the tentacles of lion’s mane jellyfish become entangled. Robotic grippers utilize this principle by using multiple synthetic flexible arms to grip and move objects. And such interlinked self-propelled filaments can also be found at the smaller micrometer scale, for example in a biological cell.