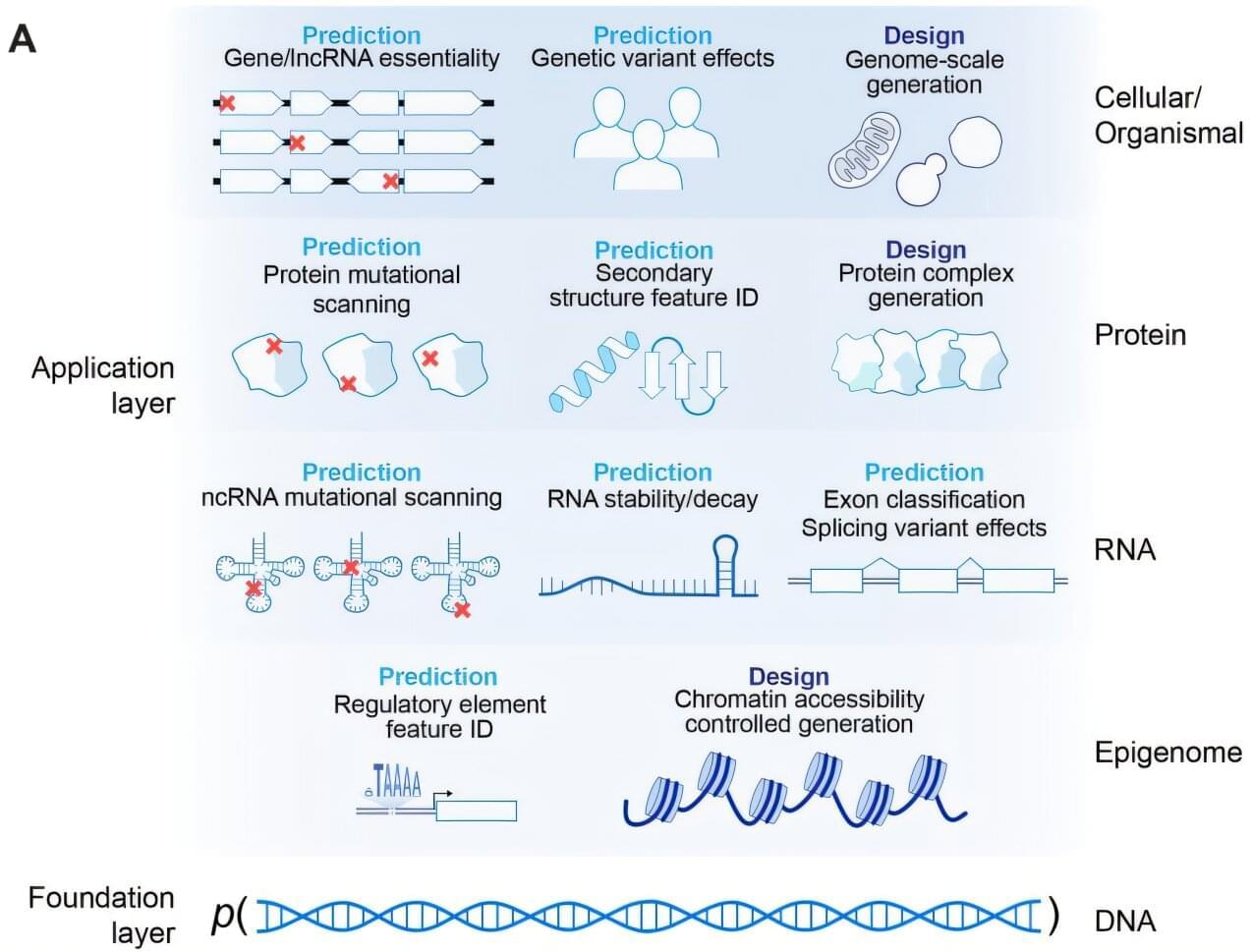
Researchers at the Arc Institute, Stanford University, and NVIDIA have developed Evo 2, an advanced AI model capable of predicting genetic variations and generating genomic sequences across all domains of life.
Testing shows that Evo 2 accurately predicts the functional effects of mutations across prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. It also successfully annotated the woolly mammoth genome from raw genomic sequences without a direct training reference, showing an ability to generalize function from the sequence alone.
Current genomic models struggle with predicting functional impacts of mutations across diverse biological systems, particularly for eukaryotic genomes. Machine learning approaches have demonstrated some success in modeling protein sequences and prokaryotic genomes. The complexity of eukaryotic DNA, with its long-range interactions and regulatory elements, presents more of a challenge.