For decades, electronics engineers have been trying to develop increasingly advanced devices that can perform complex computations faster and consuming less energy. This has become even more salient after the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning algorithms, which typically have substantial requirements both in terms of data storage and computational load.
A promising approach for running these algorithms is known as analog in-memory computing (AIMC). As suggested by its name, this approach consists of developing electronics that can perform computations and store data on a single chip. To realistically achieve both improvements in speed and energy consumption, this approach should ideally also support on-chip digital operations and communications.
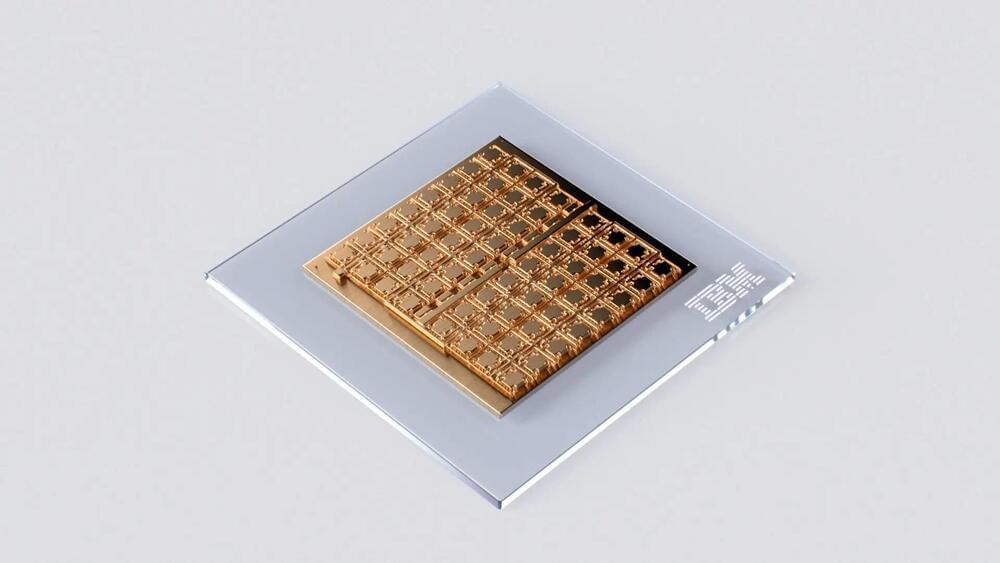
Researchers at IBM Research Europe recently developed a new 64-core mixed-signal in-memory computing chip based on phase-change memory devices that could better support the computations of deep neural networks. Their 64-core chip, presented in a paper in Nature Electronics, has so far attained highly promising results, retaining the accuracy of deep learning algorithms, while reducing computation times and energy consumption.




 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)