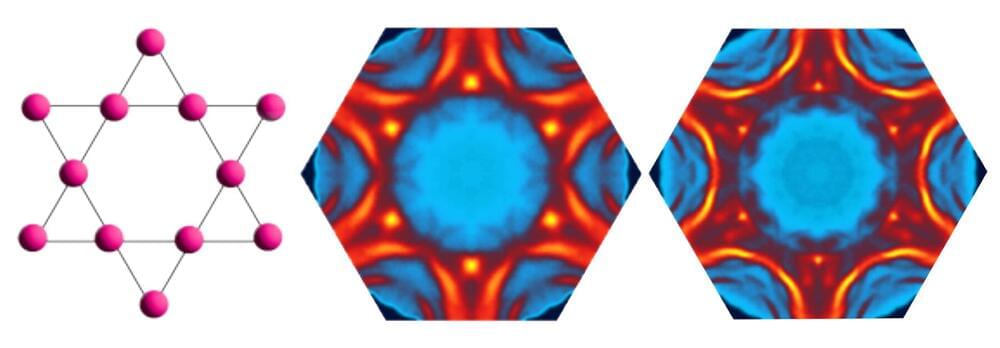
Physicists were surprised by the 2022 discovery that electrons in magnetic iron-germanium crystals could spontaneously and collectively organize their charges into a pattern featuring a standing wave. Magnetism also arises from the collective self-organization of electron spins into ordered patterns, and those patterns rarely coexist with the patterns that produce the standing wave of electrons physicists call a charge density wave.
In a study published this week in Nature Physics, Rice University physicists Ming Yi and Pengcheng Dai, and many of their collaborators from the 2022 study, present an array of experimental evidence that shows their charge density wave discovery was rarer still, a case where the magnetic and electronic orders don’t simply coexist but are directly linked.
“We found magnetism subtly modifies the landscape of electron energy states in the material in a way that both promotes and prepares for the formation of the charge density wave,” said Yi, a co-corresponding author of the study.