A former physics teacher says America could lose its technological edge if it doesn’t do a better job of teaching quantum information science – starting in high school.
Category: quantum physics – Page 495
Scientists kill brain cancer with quantum therapy in a first
Scientists propose a spray that will make the most aggressive brain cancer tumors commit suicide. This spray contains bio-nanoantennae, special molecules that can alter cells at the quantum level.
Scientists at the University of Nottingham have devised a unique spray treatment method to cure glioblastoma, a highly aggressive brain cancer that annually kills over 10,000 people in the US.
They also claim this is the first-ever quantum therapeutic approach that shows cancer can be eliminated via quantum signaling, i.e., by making changes in the biology of cells at a quantum level.

City-wide quantum communication network in China is most advanced yet
A network that connects quantum devices and a central server that spans Hefei, China, can allow multiple secure quantum chats at once.
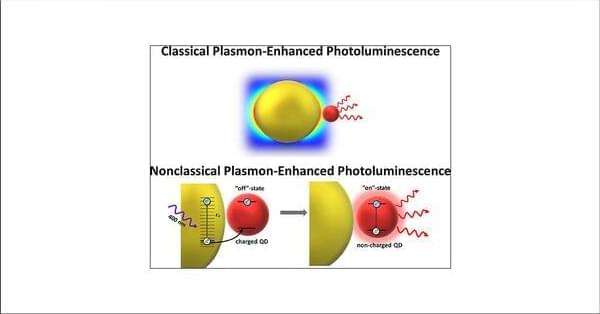
Nonclassical Mechanism of Metal-Enhanced Photoluminescence of Quantum Dots
Metal-enhanced photoluminescence is able to provide a robust signal even from a single emitter and is promising in applications in biosensors and optoelectronic devices. However, its realization with semiconductor nanocrystals (e.g., quantum dots, QDs) is not always straightforward due to the hidden and not fully described interactions between plasmonic nanoparticles and an emitter. Here, we demonstrate nonclassical enhancement (i.e., not a conventional electromagnetic mechanism) of the QD photoluminescence at nonplasmonic conditions and correlate it with the charge exchange processes in the system, particularly with high efficiency of the hot-hole generation in gold nanoparticles and the possibility of their transfer to QDs.
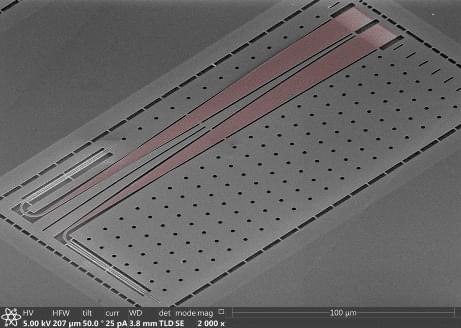
Researchers make a significant step towards reliably processing quantum information
Using laser light, researchers have developed the most robust method currently known to control individual qubits made of the chemical element barium. The ability to reliably control a qubit is an important achievement for realizing future functional quantum computers.
The paper, “A guided light system for agile individual addressing of Ba+ qubits with 10−4 level intensity crosstalk,” was published in Quantum Science and Technology.
This new method, developed at the University of Waterloo’s Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC), uses a small glass waveguide to separate laser beams and focus them four microns apart, about four-hundredths of the width of a single human hair. The precision and extent to which each focused laser beam on its target qubit can be controlled in parallel is unmatched by previous research.

REM Atoms and Nanophotonic Resonator Offer Path to Quantum Networks
Researchers at Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics (MPQ) and Technical University of Munich (TUM) demonstrated a potential platform for large-scale quantum computing and communication networks. Secure quantum networks are of interest to financial institutions, medical facilities, government agencies, and other organizations that handle personal data and classified information due to their much higher level of security.
To create an environment that supported quantum computing, the researchers excited individual atoms of the rare-earth metal erbium. The excitation process caused the erbium atoms to emit single photons with properties suitable for the construction of quantum networks.
Physicists create powerful magnets to de-freeze quantum computing
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize the world, allowing massive health and science computation problems to be solved exponentially faster than by classic computing. But quantum computers have a big drawback—they can only operate in subzero temperatures.
“In order to make quantum computers work, we cannot use them at room temperature,” said Ahmed El-Gendy, Ph.D., an associate professor of physics at The University of Texas at El Paso. “That means we will need to cool the computers and cool all the materials, which is very expensive.”
Now, physicists at The University of Texas at El Paso believe they have made a quantum leap in that regard. Led by El-Gendy, the team has developed a highly magnetic quantum computing material—100 times more magnetic than pure iron—that functions at regular temperature. The material is described in a summer issue of the journal Applied Physics Letters.
A linear path to efficient quantum technologies
Researchers at the University of Stuttgart have demonstrated that a key ingredient for many quantum computation and communication schemes can be performed with an efficiency that exceeds the commonly assumed upper theoretical limit—thereby opening up new perspectives for a wide range of photonic quantum technologies.
Quantum science has not only revolutionized our understanding of nature—it is also inspiring groundbreaking new computing, communication and sensor devices. Exploiting quantum effects in such “quantum technologies” typically requires a combination of deep insight into the underlying quantum-physical principles, systematic methodological advances, and clever engineering.
And it is precisely this combination that researches in the group of Prof. Stefanie Barz at the University of Stuttgart and the Center for Integrated Quantum Science and Technology (IQST) have delivered in a recent study, in which they have improved the efficiency of an essential building block of many quantum devices beyond a seemingly inherent limit. The work is published in the journal Science Advances.
Arrays of quantum rods could enhance TVs or virtual reality devices
Flat screen TVs that incorporate quantum dots are now commercially available, but it has been more difficult to create arrays of their elongated cousins, quantum rods, for commercial devices. Quantum rods can control both the polarization and color of light, to generate 3D images for virtual reality devices.
Using scaffolds made of folded DNA, MIT engineers have come up with a new way to precisely assemble arrays of quantum rods. By depositing quantum rods onto a DNA scaffold in a highly controlled way, the researchers can regulate their orientation, which is a key factor in determining the polarization of light emitted by the array. This makes it easier to add depth and dimensionality to a virtual scene.
“One of the challenges with quantum rods is: How do you align them all at the nanoscale so they’re all pointing in the same direction?” says Mark Bathe, an MIT professor of biological engineering and the senior author of the new study. “When they’re all pointing in the same direction on a 2D surface, then they all have the same properties of how they interact with light and control its polarization.”