Breakthrough realized for retaining quantum information in a single-electron quantum bit.

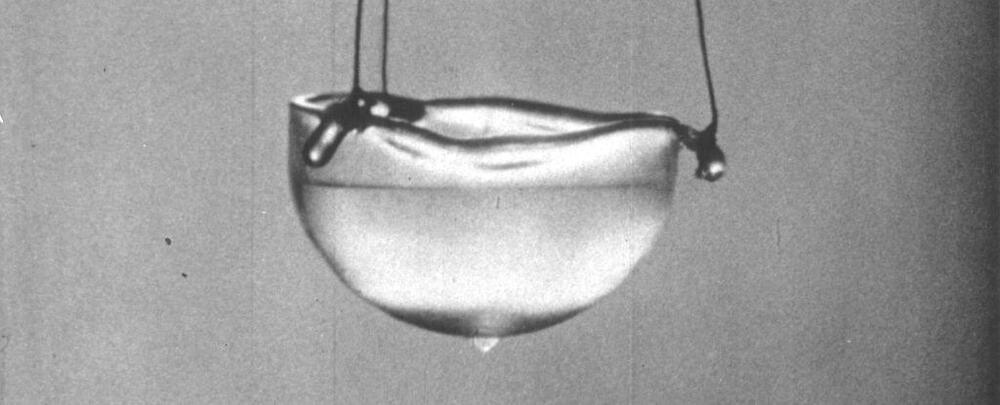
An experiment has finally revealed how it might feel to touch a quantum superfluid.
Physicists dunked a special, finger-sized probe into an isotope of helium cooled to just a smidge over absolute zero, and recorded the physical properties therein.
It is, they say, the first time we have gleaned an inkling of what the quantum Universe might feel like. And no one had to get horrific frostbite, or ruin an experiment, to find out for real.

China has announced a plan to produce its first humanoid robots by 2025, as part of its push to develop the future industry.
China has long been eyeing the top spot in emerging fields like AI and quantum computing. Now, it has a new goal: to create realistic robots that can mimic human actions and emotions.
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has unveiled a plan to produce China’s first humanoid robots by 2025. The program also aims to foster more startups in the sector, set industry norms, cultivate talent, and enhance international cooperation.
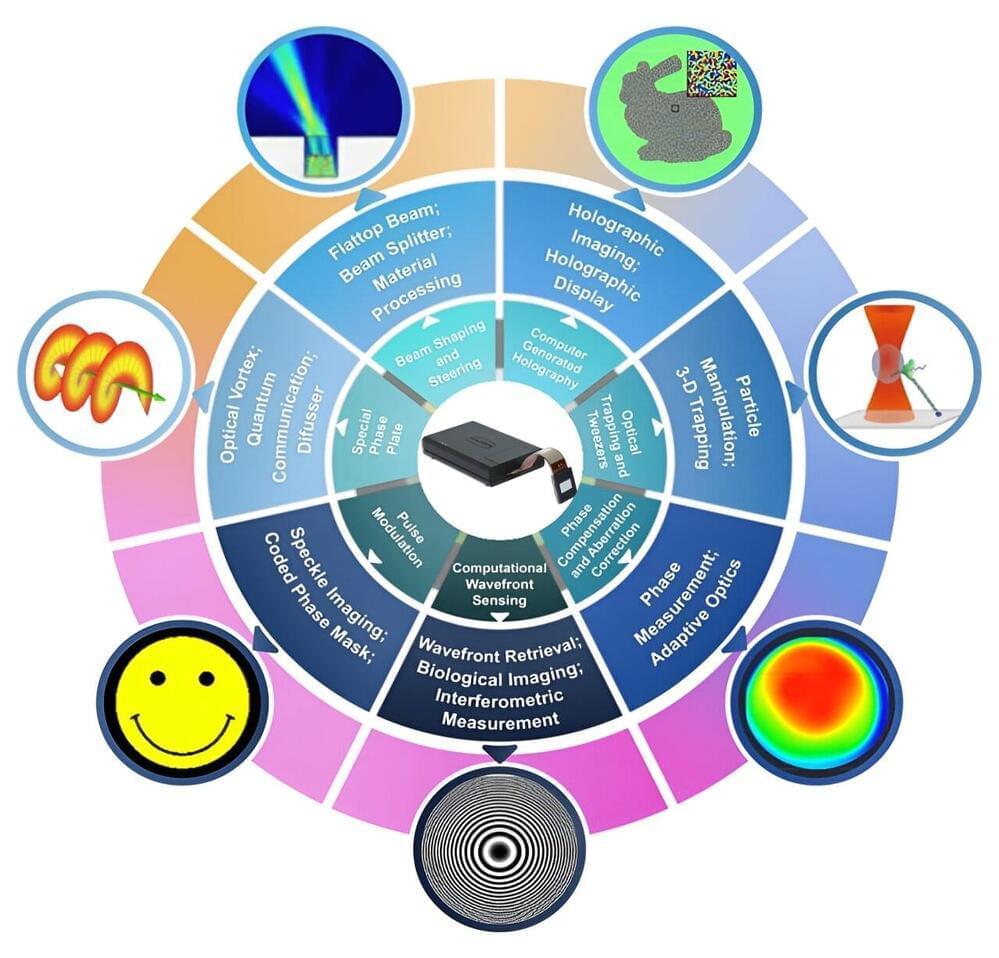
Technology to control and harness light has existed for centuries, often as static solutions that must be custom-designed. It is only in the past couple of decades that the digital era of micro-electronics and computing has seen fast rewritable technology meant for displays find its way into the mainstream of optics.
In a new review published in Opto-Electronic Science, the authors showcase the recent advances in replacing the traditional static optical toolkit with a modern digital toolkit for “light on demand.” The result has been the introduction of digitally controlled light to nearly all major optical laboratories worldwide, opening new paths for the creation, control, detection, and harnessing of exotic forms of structured light. The advanced toolkit promises novel applications from classical to quantum, ushering in a new chapter in on-demand structured light.
The authors of this article reviewed recent progress in using a modern digital toolkit for on-demand forms of sculptured light, offering new insights and perspectives on this nascent topic. The core technology that has advanced this field is the liquid crystal spatial light modulator (SLM), allowing high resolution tailoring of light in amplitude, phase, polarization, or even more exotic degrees of freedom such as path, orbital angular momentum, and even spatiotemporal control. These simple yet highly effective devices are made up of millions of pixels that can be modulated in phase, for spatial control of light in an in-principle lossless manner.
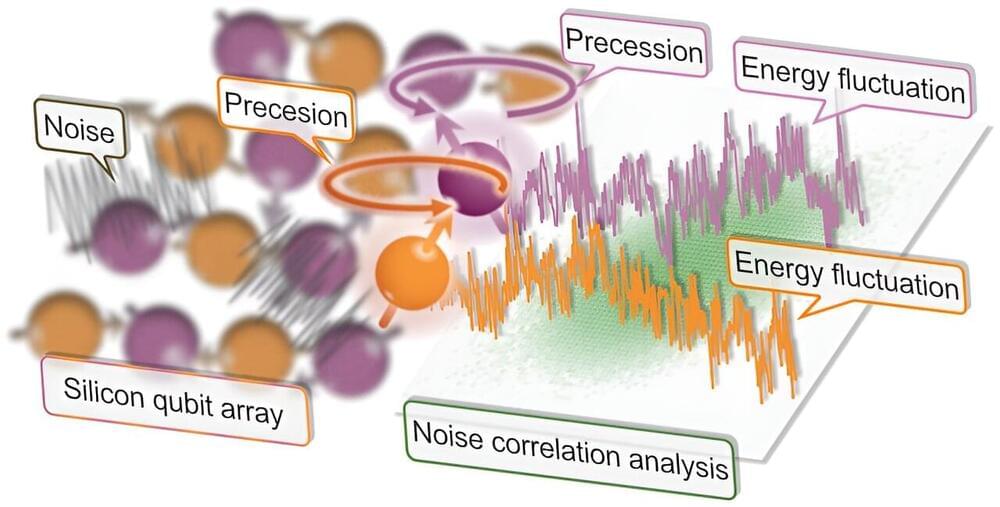
To build highly performing quantum computers, researchers should be able to reliably derive information about the noise inside them, while also identifying effective strategies to suppress this noise. In recent years, significant progress has been made in this direction, enabling operation errors below 1% in various quantum computing platforms.
A research team at Tokyo Institute of Technology and RIKEN recently set out to reliably quantify the correlations between the noise produced by pairs of semiconductor-based qubits, which are very appealing for the development of scalable quantum processors. Their paper, published in Nature Physics, unveiled strong interqubit noise correlations between a pair of neighboring silicon spin qubits.
“A useful quantum computer would practically require millions of densely packed, well-controlled qubits with errors not only small but also sufficiently uncorrelated,” Jun Yoneda, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “We set out to address the potentially serious issue of error correlation in silicon qubits, as they have become a compelling platform for large quantum computations otherwise.”

Taking advantage of a quantum phenomenon called indefinite causal order could make quantum batteries charge more efficiently.
A scientist claims to have developed an inexpensive system for using quantum computing to crack RSA, which is the world’s most commonly used public key algorithm.
See Also: Live Webinar | Generative AI: Myths, Realities and Practical Use Cases
The response from multiple cryptographers and security experts is: Sounds great if true, but can you prove it? “I would be very surprised if RSA-2048 had been broken,” Alan Woodward, a professor of computer science at England’s University of Surrey, told me.

Researchers from Lancaster University in the UK have discovered how superfluid helium 3 He would feel if you could put your hand into it. Dr. Samuli Autti is the lead author of the research published in Nature Communications.
The interface between the exotic world of quantum physics and classical physics of the human experience is one of the major open problems in modern physics.
Dr. Autti said, In practical terms, we don’t know the answer to the question ‘How does it feel to touch quantum physics?’ These experimental conditions are extreme and the techniques complicated, but I can now tell you how it would feel if you could put your hand into this quantum system.
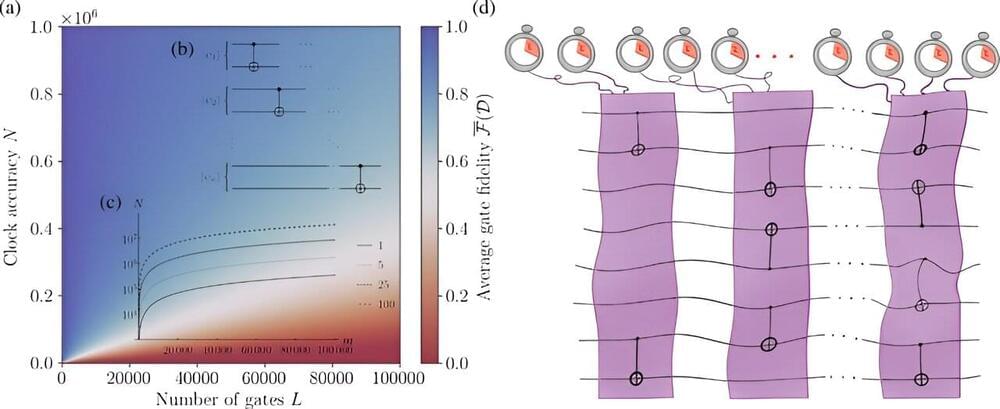
New research from a consortium of quantum physicists, led by Trinity College Dublin’s Dr. Mark Mitchison, shows that imperfect timekeeping places a fundamental limit to quantum computers and their applications. The team claims that even tiny timing errors add up to place a significant impact on any large-scale algorithm, posing another problem that must eventually be solved if quantum computers are to fulfill the lofty aspirations that society has for them.
The paper is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
It is difficult to imagine modern life without clocks to help organize our daily schedules; with a digital clock in every person’s smartphone or watch, we take precise timekeeping for granted—although that doesn’t stop people from being late.
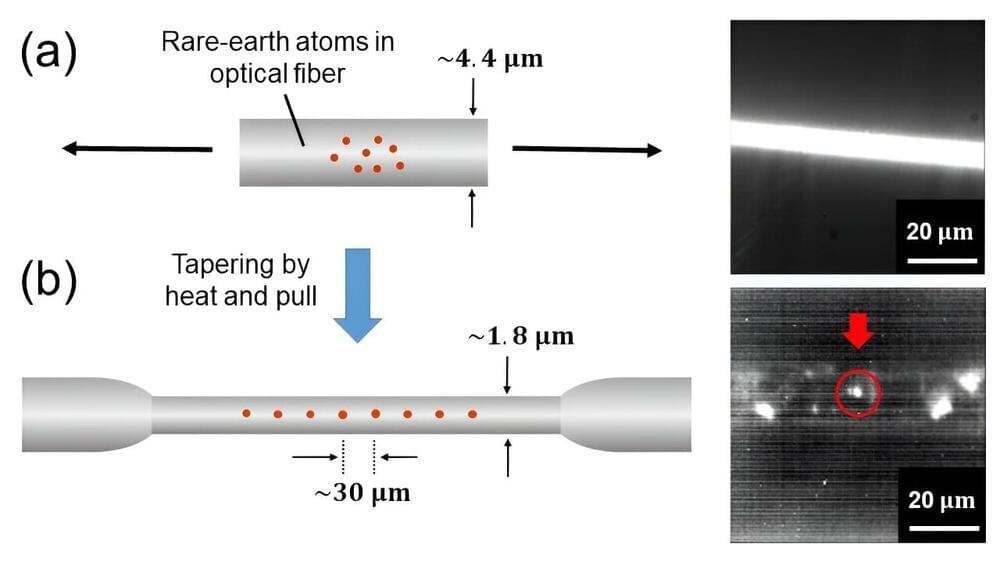
Quantum-based systems promise faster computing and stronger encryption for computation and communication systems. These systems can be built on fiber networks involving interconnected nodes which consist of qubits and single-photon generators that create entangled photon pairs.
In this regard, rare-earth (RE) atoms and ions in solid-state materials are highly promising as single-photon generators. These materials are compatible with fiber networks and emit photons across a broad range of wavelengths. Due to their wide spectral range, optical fibers doped with these RE elements could find use in various applications, such as free-space telecommunication, fiber-based telecommunications, quantum random number generation, and high-resolution image analysis. However, so far, single-photon light sources have been developed using RE-doped crystalline materials at cryogenic temperatures, which limits the practical applications of quantum networks based on them.
In a study published in Physical Review Applied on 16 October 2023, a team of researchers from Japan, led by Associate Professor Kaoru Sanaka from Tokyo University of Science (TUS) has successfully developed a single-photon light source consisting of doped ytterbium ions (Yb3+) in an amorphous silica optical fiber at room temperature. This newly developed single-photon light source eliminates the need for expensive cooling systems and has the potential to make quantum networks more cost-effective and accessible.