R&d and field deployment of orchestrated objective reduction


“Metaphysical Experiments: Physics and the Invention of the Universe” by Bjørn Ekeberg Book Link: https://amzn.to/4imNNk5
“Metaphysical Experiments, Physics and the Invention of the Universe,” explores the intricate relationship between physics and metaphysics, arguing that fundamental metaphysical assumptions profoundly shape scientific inquiry, particularly in cosmology. The author examines historical developments from Galileo and Newton to modern cosmology and particle physics, highlighting how theoretical frameworks and experimental practices are intertwined with philosophical commitments about the nature of reality. The text critiques the uncritical acceptance of mathematical universality in contemporary physics, suggesting that cosmology’s reliance on hypological and metalogical reasoning reveals a deep-seated faith rather than pure empirical validation. Ultimately, the book questions the limits and implications of a science that strives for universal mathematical truth while potentially overlooking its own inherent complexities and metaphysical underpinnings. Chapter summaries:
- Cosmology in the Cave: This chapter examines the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva to explore the metaphysics involved in the pursuit of a “Theory of Everything” linking subatomic physics to cosmology.
- Of God and Nature: This chapter delves into the seventeenth century to analyze the invention of the universe as a concept alongside the first telescope, considering the roles of Galileo, Descartes, and Spinoza.
- Probability and Proliferation: This chapter investigates the nineteenth-century shift in physics with the rise of probabilistic reasoning and the scientific invention of the particle, focusing on figures like Maxwell and Planck.
- Metaphysics with a Big Bang: This chapter discusses the twentieth-century emergence of scientific cosmology and the big bang theory, shaped by large-scale science projects and the ideas of Einstein and Hawking.
- Conclusion: This final section questions the significance of large-scale experiments like the JWST as metaphysical explorations and reflects on our contemporary scientific relationship with the cosmos.
#Physics.
#Cosmology.
#Universe.
#Science.
#Metaphysics.
#PhilosophyofScience.
#JWST
#LHC
#BigBangTheory.
#DarkMatter.
#DarkEnergy.
#SpaceTelescope.
#ParticlePhysics.
#HistoryofPhysics.
#ScientificInquiry #scienceandreligion #meaningoflife #consciousness #universe #god #spirituality #faith #reason #creationtheory #finetuninguniverse #astrophysics #quantumphysics #intelligentdesign #cosmicconsciousness #reality #Consciousness #QuantumPhysics #Universe #Nonlocality #QuantumEntanglement #CosmicInformation #ScienceOfMind #NatureOfReality #Spirit #BigLibraryHypothesis #NLSETI #QuantumBrain #Multiverse #InformationTheory #ExtrasensoryPerception #SciencePhilosophy #deepdive #skeptic #podcast #synopsis #books #bookreview #ai #artificialintelligence #booktube #aigenerated #history #alternativehistory #aideepdive #ancientmysteries #hiddenhistory #futurism #videoessay

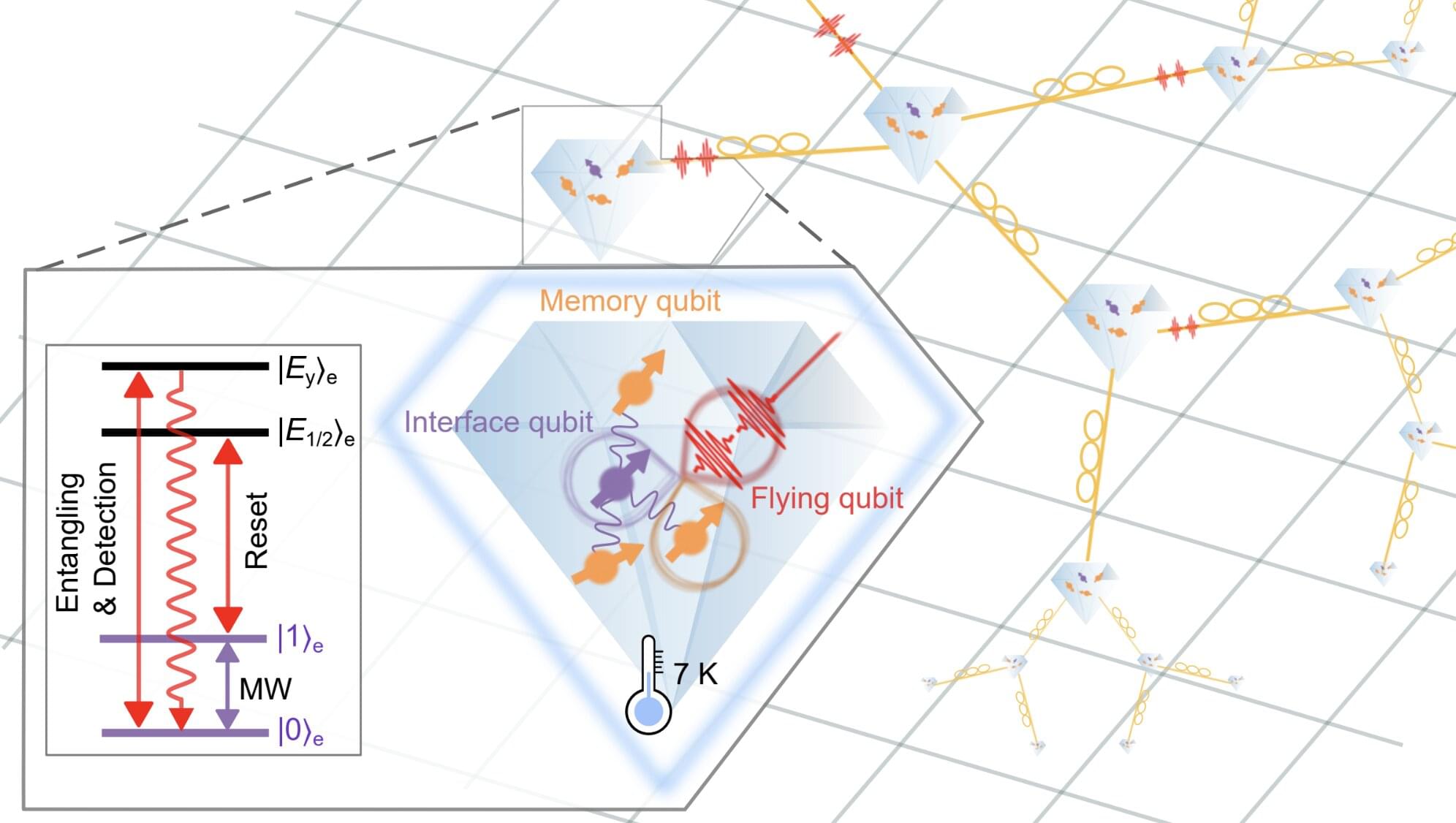
Quantum technologies, which operate leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena, have the potential to outperform their classical counterparts in some optimization and computational tasks. These technologies include so-called quantum networks, systems designed to transmit information between interconnected nodes and process it, using quantum phenomena such as entanglement and superposition.
Quantum networks could eventually contribute to the advancement of communications, sensing and computing. Before this can happen, however, existing systems will need to be improved and perfected, to ensure that they can transfer and process data both reliably and efficiently, minimizing errors.
Researchers at Tsinghua University, Hefei National Laboratory and the Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences recently demonstrated the coherent control of a hybrid and scalable quantum network node. Their demonstration, outlined in Nature Physics, was realized by combining solutions and techniques that they developed as part of their earlier work.

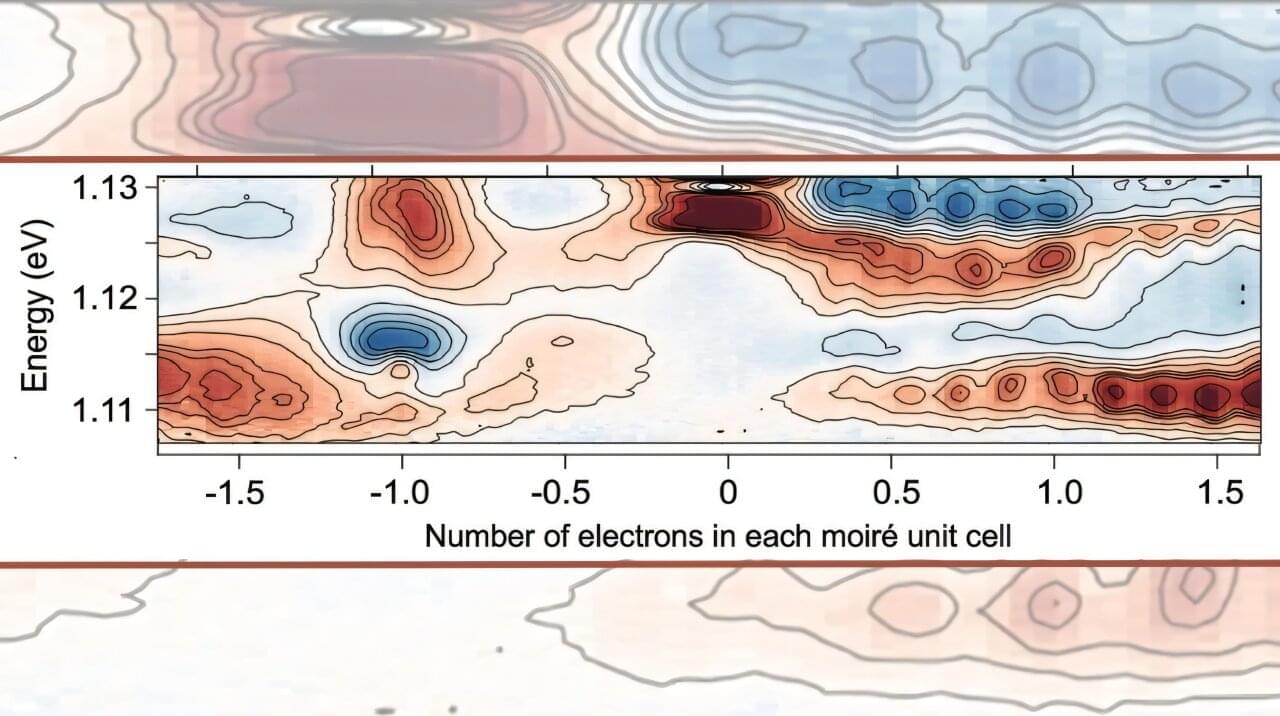
The fractional quantum anomalous Hall (FQAH) effect was recently discovered in twisted MoTe2 bilayers (tMoTe2)1–4. Experiments to date have revealed Chern insulators from hole doping at ν =-1,-2/3,-3/5, and-4/7 (per moiré unit cell) 1–6. In parallel, theories predict that, between v =-1 and-3, there exist exotic quantum phases 7–15, such as the coveted fractional topological insulators (FTI), fractional quantum spin Hall (FQSH) states, and non-abelian fractional states. Here we employ transient optical spectroscopy 16,17 on tMoTe2 to reveal nearly 20 hidden states at fractional fillings that are absent in static optical sensing or transport measurements. A pump pulse selectively excites charge across the correlated or pseudo gaps, leading to the disordering (melting) of correlated states 18. A probe pulse detects the subsequent melting and recovery dynamics via exciton and trion sensing 1,3,19–21. Besides the known states, we observe additional fractional fillings between ν = 0 and-1 and a large number of states on the electron doping side (ν 0). Most importantly, we observe new states at fractional fillings of the Chern bands at ν =-4/3,-3/2,-5/3,-7/3,-5/2, and-8/3. These states are potential candidates for the predicted exotic topological phases 7–15. Moreover, we show that melting of correlated states occurs on two distinct time scales, 2–4 ps and 180–270 ps, attributed to electronic and phonon mechanisms, respectively. We discuss the differing dynamics of the electron and hole doped states from the distinct moiré conduction and valence bands.
In a jaw-dropping scientific development, scientists are now exploring how to teleport an entire human using quantum technology. What began as a theory in 1993 is now becoming tangible thanks to quantum teleportation, which allows the transfer of quantum states — not matter — across vast distances. Though the dream of instant human transfer remains full of challenges, the progress is real, and the implications are as exciting as they are unsettling.
There are a seemingly endless number of quantum states that describe quantum matter and the strange phenomena that emerge when large numbers of electrons interact. For decades, many of these states have been theoretical: mathematical and computational predictions potentially hiding among real-life materials—a zoo, as many scientists are coming to refer to it, with new “species” just waiting to be discovered and described.
In a new study published on April 3 in Nature, researchers added over a dozen states to the growing quantum zoo.
“Some of these states have never been seen before,” said lead author Xiaoyang Zhu, Howard Family Professor of Nanoscience at Columbia. “And we didn’t expect to see so many either.”
Quantum magnetometers can detect incredibly small changes in magnetic fields by tapping into the strange and powerful features of quantum physics. These devices rely on the discrete nature and coherence of quantum particles—behaviors that give them a major edge over classical sensors. But how far can their sensitivity go? And what actually makes a magnetometer “quantum?”
A new study explores the theoretical boundaries of these devices, comparing multiple methods for defining their limits. The findings shed light not only on performance but also on what truly separates quantum sensors from their classical counterparts.
Quantum Magnetometers and Ultra-High Sensitivity.
A team of researchers at Q-CTRL, a quantum infrastructure software-maker based in Sydney, Australia, has announced the successful demonstration of its newly developed quantum navigation system called “Ironstone Opal.”
The group has written a paper describing how their system works and how well it tested against currently available backup GPS systems and has posted it on the arXiv preprint server.
With the advent and subsequent reliance on GPS by private and military vehicles and aircraft for navigation, governments have come to understand how vulnerable such systems can be. Outages can lead to drivers being stranded, pilots scrambling to use outdated systems and difficulties deploying military assets. Because of that, scientists around the world have been looking for reasonable backup systems, or even possible alternatives to GPS.