This sounds very promising! The researchers are investigating the use of nuclear microreactors to power faster and more efficient electric propulsion systems.☢️🚀
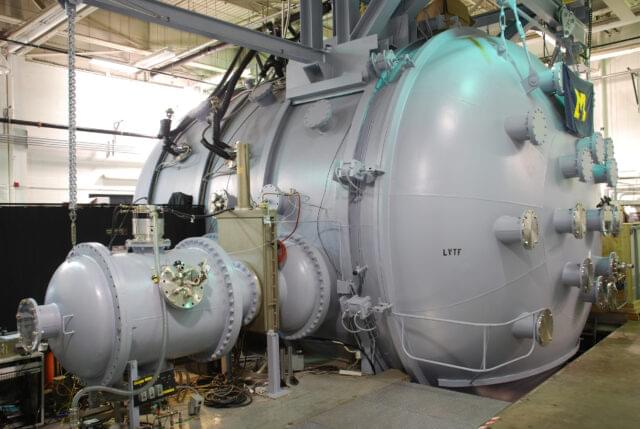
To develop spacecraft that can “maneuver without regret,” the U.S. Space Force is providing $35 million to a national research team led by the University of Michigan. It will be the first to bring fast chemical rockets together with efficient electric propulsion powered by a nuclear microreactor.
The newly formed Space Power and Propulsion for Agility, Responsiveness and Resilience Institute involves eight universities, and 14 industry partners and advisers in one of the nation’s largest efforts to advance space power and propulsion, a critical need for national defense and space exploration.
Right now, most spacecraft propulsion comes in one of two flavors: chemical rockets, which provide a lot of thrust but burn through fuel quickly, or electric propulsion powered by solar panels, which is slow and cumbersome but fuel efficient. Chemical propulsion comes with the highest risk of regret, as fuel is limited. But in some situations, such as when a collision is imminent, speed may be necessary.