Can we connect human brains together? What are the limits of what we can do with our brain? Is BrainNet our future?
In science fiction movies, scientists’ brains are downloaded into computers and criminal brains are connected to the Internet. Interesting, but how does it work in real life?
Original title: The greedy brain.
Scientific journalist Rob van Hattum wondered what information we can truly get from our brain and came across an extraordinary scientific experience.
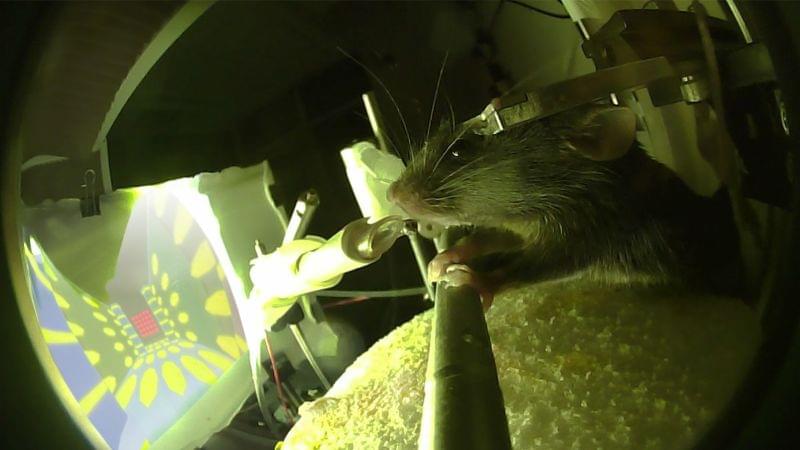
An experiment where the brains of two rats were directly connected: one rat was in the United States and the other rat was in Brazil. They could influence the brain of the other directly. Miguel Nicolelis is the Brazilian neurologist who conducted this experiment. In his book ‘Beyond Boundaries’ he describes his special experiences in detail and predicts that it should be possible to create a kind of BrainNet.
For Backlight, Rob van Hattum went to Sao Paulo and also visited all Dutch neuroscientists, looking for what the future holds for our brain. He connected his own brain to computers and let it completely be scanned, searching for the limits of reading out the brain.
Originally broadcasted by VPRO in 2014.
© VPRO Backlight July 2014
On VPRO broadcast you will find nonfiction videos with English subtitles, French subtitles and Spanish subtitles, such as documentaries, short interviews and documentary series.
VPRO Documentary publishes one new subtitled documentary about current affairs, finance, sustainability, climate change or politics every week. We research subjects like politics, world economy, society and science with experts and try to grasp the essence of prominent trends and developments.
Visit additional youtube channels bij VPRO broadcast:
VPRO Broadcast, all international VPRO programs: https://www.youtube.com/VPRObroadcast.
VPRO DOK, German only documentaries: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCBi0VEPANmiT5zOoGvCi8Sg.
VPRO Metropolis, remarkable stories from all over the world: https://www.youtube.com/user/VPROmetropolis.
VPRO World Stories, the travel series of VPRO: https://www.youtube.com/VPROworldstories.
VPRO Extra, additional footage and one off’s: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCTLrhK07g6LP-JtT0VVE56A
www.VPRObroadcast.com.
Credits:
Director: Rob van Hattum.
English, French and Spanish subtitles: Ericsson.
French and Spanish subtitles are co-funded by European Union.