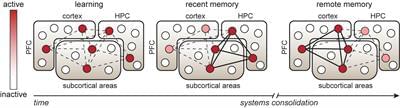
The ability to store and retrieve learned information over prolonged periods of time is an essential and intriguing property of the brain. Insight into the neurobiological mechanisms that underlie memory consolidation is of utmost importance for our understanding of memory persistence and how this is affected in memory disorders. Recent evidence indicates that a given memory is encoded by sparsely distributed neurons that become highly activated during learning, so-called engram cells. Research by us and others confirms the persistent nature of cortical engram cells by showing that these neurons are required for memory expression up to at least 1 month after they were activated during learning. Strengthened synaptic connectivity between engram cells is thought to ensure reactivation of the engram cell network during retrieval. However, given the continuous integration of new information into existing neuronal circuits and the relatively rapid turnover rate of synaptic proteins, it is unclear whether a lasting learning-induced increase in synaptic connectivity is mediated by stable synapses or by continuous dynamic turnover of synapses of the engram cell network. Here, we first discuss evidence for the persistence of engram cells and memory-relevant adaptations in synaptic plasticity, and then propose models of synaptic adaptations and molecular mechanisms that may support memory persistence through the maintenance of enhanced synaptic connectivity within an engram cell network.
Our memories define who we are, help us make decisions and guide our behavior. The ability to effectively encode, store and retrieve information is therefore an essential feature of life. Although the recollection of most experiences fades with time, certain memories are retained for many years or even a lifetime. How the brain is able to process and persistently store learned information has been a topic of intense research for a long time and great progress has been made in recent years toward a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying memory persistence.
Memory formation is initiated by the integration of external and interoceptive sensory stimuli in neuronal circuits, forming a cohesive representation of a specific event. Subsequently, the neurons involved are thought to undergo physical changes that enable retrieval of the learned information. The physical representation of experience-driven changes in the brain is collectively referred to as a memory engram (Box 1), a term that gained popularity in recent years (Josselyn et al., 2015), but that was first introduced by the German scientist Richard Semon in the early 20th century (Semon, 1911). Learning-induced changes do not occur globally or randomly within memory-relevant brain regions. Instead, accumulating evidence indicates that sparse ensembles of neurons become highly activated during learning and act as a substrate for the storage of a memory engram (Whitaker and Hope, 2018; Josselyn and Tonegawa, 2020).