Year 2021 Biocomputing is the future for the biological singularity because we could control all inputs and outputs of our bodies even evolve them eventually.
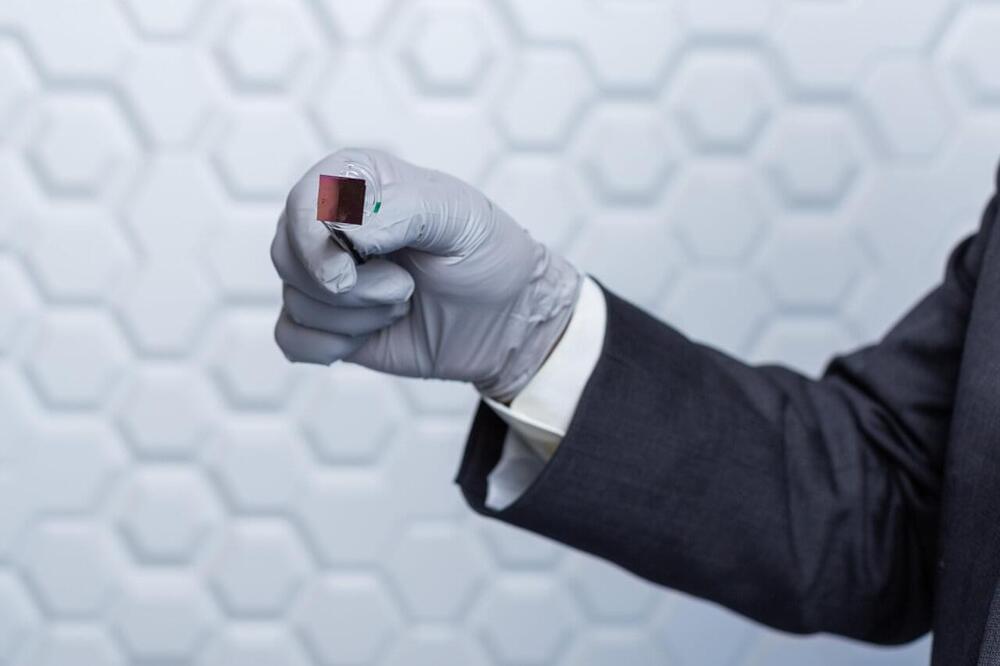
A silicon device that can change skin tissue into blood vessels and nerve cells has advanced from prototype to standardized fabrication, meaning it can now be made in a consistent, reproducible way. As reported in Nature Protocols, this work, developed by researchers at the Indiana University School of Medicine, takes the device one step closer to potential use as a treatment for people with a variety of health concerns.
The technology, called tissue nanotransfection, is a non-invasive nanochip device that can reprogram tissue function by applying a harmless electric spark to deliver specific genes in a fraction of a second. In laboratory studies, the device successfully converted skin tissue into blood vessels to repair a badly injured leg. The technology is currently being used to reprogram tissue for different kinds of therapies, such as repairing brain damage caused by stroke or preventing and reversing nerve damage caused by diabetes.
“This report on how to exactly produce these tissue nanotransfection chips will enable other researchers to participate in this new development in regenerative medicine,” said Chandan Sen, director of the Indiana Center for Regenerative Medicine and Engineering, associate vice president for research and Distinguished Professor at the IU School of Medicine.