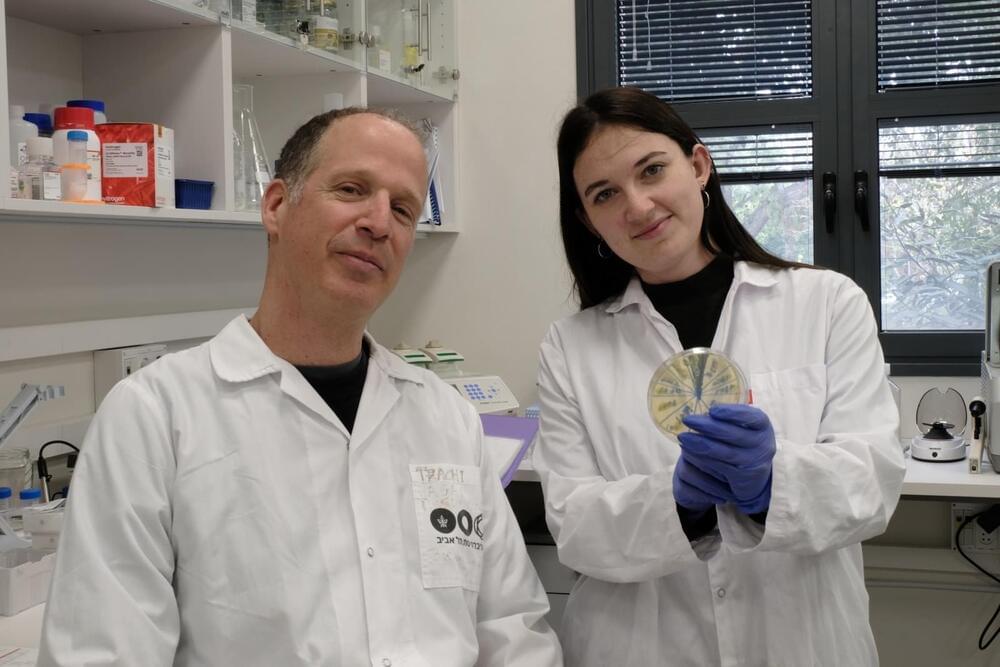
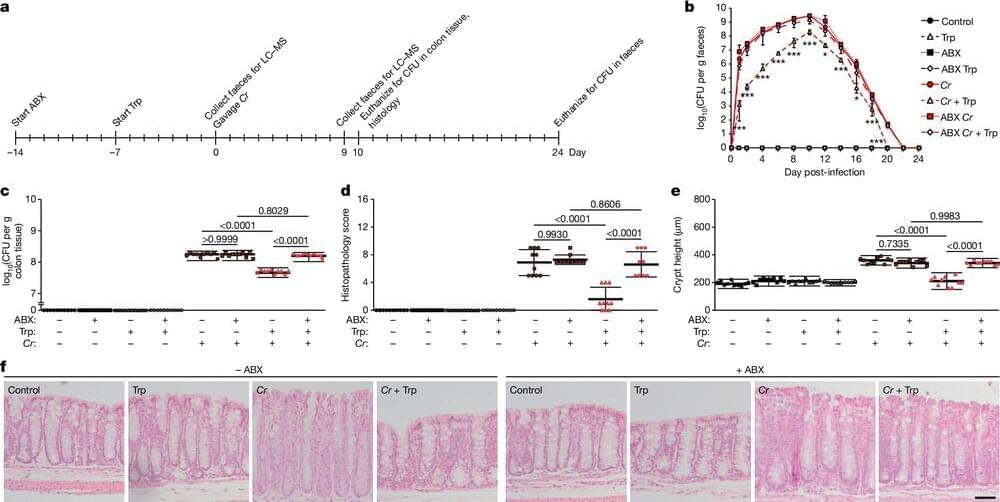
Gut bacteria and a diet rich in the amino acid tryptophan can play a protective role against pathogenic E. coli, which can cause severe stomach upset, cramps, fever, intestinal bleeding and renal failure, according to a study published March 13 in Nature.
The research reveals how dietary tryptophan—an amino acid found mostly in animal products, nuts, seeds, whole grains and legumes—can be broken down by gut bacteria into small molecules called metabolites. It turns out a few of these metabolites can bind to a receptor on gut epithelial (surface) cells, triggering a pathway that ultimately reduces the production of proteins that E. coli use to attach to the gut lining where they cause infection. When E. coli fail to attach and colonize the gut, the pathogen benignly moves through and passes out of the body.
The research describes a previously unknown role in the gut for a receptor, DRD2 has otherwise been known as a dopamine (neurotransmitter) receptor in the central and peripheral nervous systems.