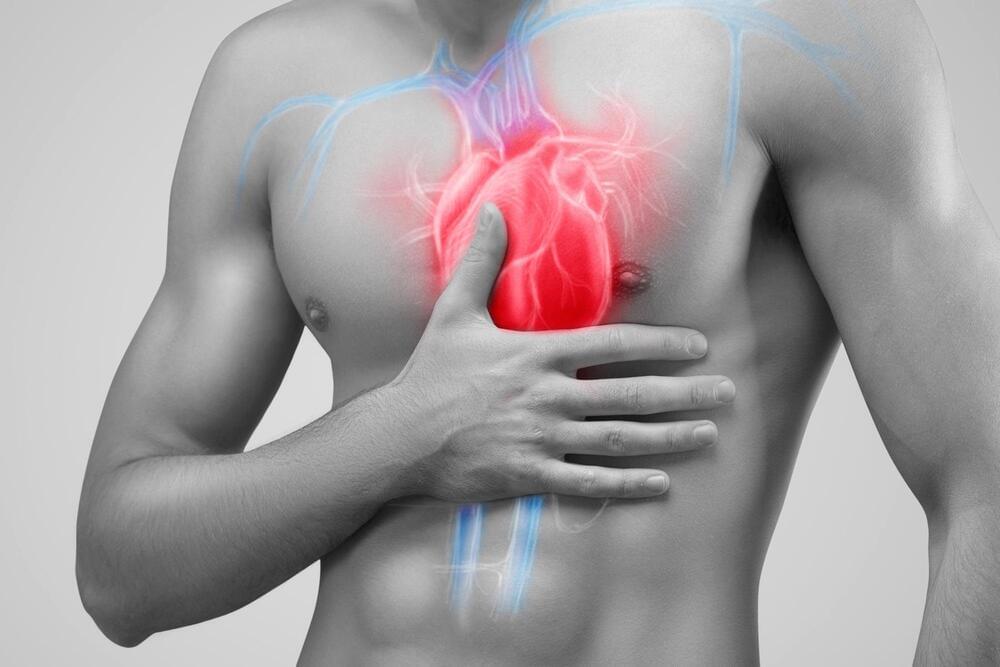
A new analysis involving over 13,000 people has found changes to blood vessels in the brain that can increase the risk of stroke and dementia are common in people with a range of heart conditions, regardless of whether they have experienced a stroke.
The new research, published in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, is the most comprehensive systematic review of ‘hidden’ brain changes in people with a range of heart conditions to date.
Lead author Dr Zien Zhou from The George Institute for Global Health said that identifying these changes could play an important role in choosing treatments for these patients.