Scientists say that long genes — which are more susceptible to DNA damage — might be a main cause of the body’s aging and could play a role in. the development of diseases like Alzheimer’s.

If someone tells you that you have a big head, take that as a compliment.
Humankind’s brains have apparently gotten bigger and bigger over the years, according to a team of scientists, who are surmising that bigger brains may stave off dementia as folks age.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of California Davis Health, arrived at this finding after studying the MRIs of people starting with those born in the 1930s, all the way through the 1970s.

Can light be a factor in eliminating traumatic memories? Japanese scientists found that the long-term memory of flies can be affected if they are kept in the dark. This is the first discovery of the role of environmental light on such memories. The scientists hope to extend this approach to human victims of life-affecting traumas.
Events that are shocking can become a part of our long-term memory (LTM), with new proteins synthesized and the neuronal circuits in our brain becoming altered, explains the press release from researchers at the Tokyo Metropolitan University, who made the breakthrough. These memories can be hard to erase and may lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Through their research, the team led by Professor Takaomi Sakai from Tokyo Metropolitan University discovered a particular molecular mechanism in Drosophilia flies that affects LTM. To find this, they set up a trauma for male flies by placing them with females who already mated. According to the courtship conditioning paradigm, in such situations mated females stress the unmated males to such an extent that they remember the experience, unwilling to ever mate with any more females – even if they were to be exposed to those that are unmated.
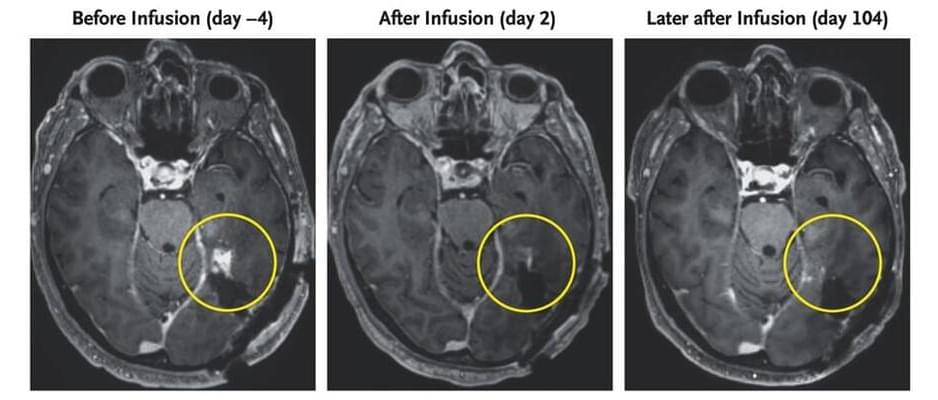
Brain scans of a 72-year-old man diagnosed with a highly aggressive form of cancer known as a glioblastoma have revealed a remarkable regression in his tumor’s size within days of receiving an infusion of an innovative new treatment.
Though the outcomes of two other participants with similar diagnoses were somewhat less positive, the case’s success still bodes well for the search for a way to effectively cure what is currently an incurable disease.
Glioblastomas are typically about as deadly as cancers can get. Emerging from supporting cells inside the central nervous system, they can rapidly develop into malignant masses that claim up to 95 percent of patient lives within five years.

Quantum cognition is a new research program that uses mathematical principles from quantum theory as a framework to explain human cognition, including judgment and decision making, concepts, reasoning, memory, and perception. This research is not concerned with whether the brain is a quantum computer. Instead, it uses quantum theory as a fresh conceptual framework and a coherent set of formal tools for explaining puzzling empirical findings in psychology. In this introduction, we focus on two quantum principles as examples to show why quantum cognition is an appealing new theoretical direction for psychology: complementarity, which suggests that some psychological measures have to be made sequentially and that the context generated by the first measure can influence responses to the next one, producing measurement order effects, and superposition, which suggests that some psychological states cannot be defined with respect to definite values but, instead, that all possible values within the superposition have some potential for being expressed. We present evidence showing how these two principles work together to provide a coherent explanation for many divergent and puzzling phenomena in psychology. (PsycInfo Database Record © 2020 APA, all rights reserved)
Humans can sometimes be hard to understand, much like quantum physics — unless you watch this channel regularly of course. That’s why a mathematician has come out with an idea of “quantum cognition”. What is this so-called quantum cognition? Does it explain why humans make irrational decisions? Let’s have a look.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donatebox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#sciencenews #science #physics #consciousness

Researchers identify molecular cues that make developing neurons remodel their connections.
At this very moment, the billions of neurons in your brain are using their trillions of connections to enable you to read and comprehend this sentence.
Now, by studying the neurons involved in the sense of smell, researchers from Kyushu University’s Faculty of Medical Sciences report a new mechanism behind the biomolecular bonsai that selectively strengthens these connections.
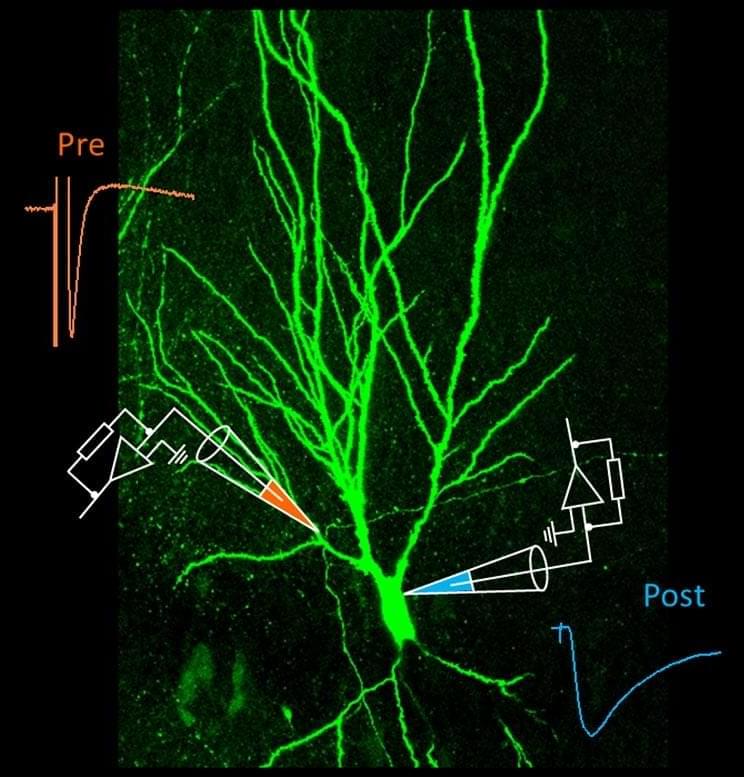
Key synapse acts as a “smart teacher,” sending messages against the usual flow of information in the brain.
Information flows in a well-defined direction in the brain: Chemical and electrical signals are passed from one neuron to the other across the synapse, from the pre-synaptic to the post-synaptic neuron. Now, Peter Jonas and his group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) show that information also travels in the opposite direction at a key synapse in the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for learning and memory.
At the so-called mossy fiber synapse, the post-synaptic CA3 neuron influences how the pre-synaptic neuron, the so-called mossy fiber neuron, fires. “We have shown, for the first time, that a retrograde information flow is physiologically relevant for pre-synaptic plasticity,” says Yuji Okamoto, a postdoc in the group of Peter Jonas at IST Austria and co-first author of the paper published in Nature Communications.
Black-capped chickadees have extraordinary memories that can recall the locations of thousands of morsels of food to help them survive the winter. Now scientists at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute have discovered how the chickadees can remember so many details: they memorize each food location using brain cell activity akin to a barcode. These new findings may shed light on how the brain creates memories for the events that make up our lives.