New research indicates tDCS headsets may help reduce post-breakup misery and depression:
Researchers theorized that using transcranial direct current stimulation in specific brain areas might alleviate the emotional distress linked to heartache.
New research indicates tDCS headsets may help reduce post-breakup misery and depression:
Researchers theorized that using transcranial direct current stimulation in specific brain areas might alleviate the emotional distress linked to heartache.
Today I’m thrilled to announce BrainBridge, the world’s first concept for a head transplant system, which integrates advanced robotics and artificial intelligence to execute complete head and face transplantation procedures. This state-of-the-art system offers new hope to patients suffering from untreatable conditions such as stage-4 cancer, paralysis, and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Official website: https://brainbridge.tech/
Follow me everywhere: https://muse.io/hashemalghaili.
#Science #Technology #Research #HeadTransplant #BrainBridge #Neuroscience
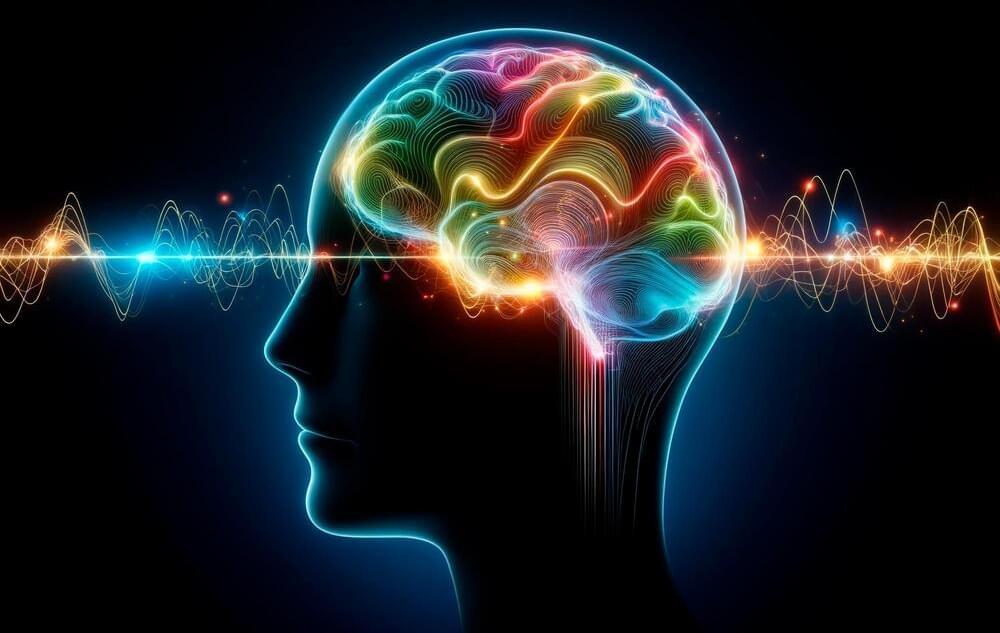

MIT neuroscientists propose a new framework that describes how thought arises from the coordination of neural activity driven by oscillating electric fields — a.k.a. brain “waves” or “rhythms.”
It could be very informative to observe the pixels on your phone under a microscope, but not if your goal is to understand what a whole video on the screen shows. Cognition is much the same kind of emergent property in the brain. It can only be understood by observing how millions of cells act in coordination, argues a trio of MIT neuroscientists. In a new article, they lay out a framework for understanding how thought arises from the coordination of neural activity driven by oscillating electric fields — also known as brain “waves” or “rhythms.”
The Significance of Brain Rhythms.

The capacity to adjust beliefs about one’s actions and their consequences in a constantly changing environment is a defining characteristic of advanced cognition. Disruptions to this ability, however, can negatively affect cognition and behavior, leading to such states of mind as paranoia, or the belief that others intend to harm us.
In a new study, Yale scientists uncover how one specific region of the brain might causally provoke these feelings of paranoia.
Their novel approach — which involved aligning data collected from monkeys with human data — also offers a new cross-species framework through which scientists might better understand human cognition through the study of other species.

Listen to this episode from Mind Chat on Spotify. Keith and Philip interview David Papineau (Professor of Philosophy at King’s College London) about his recent book ‘The Metaphysics of Sensory Experience’. David is also a materialist who believes in consciousness, so there’ll probably be a big old fight about that too. Link to David’s book: https://global.oup.com/academic/product/the-metaphysics-of-s…b&lang=en&
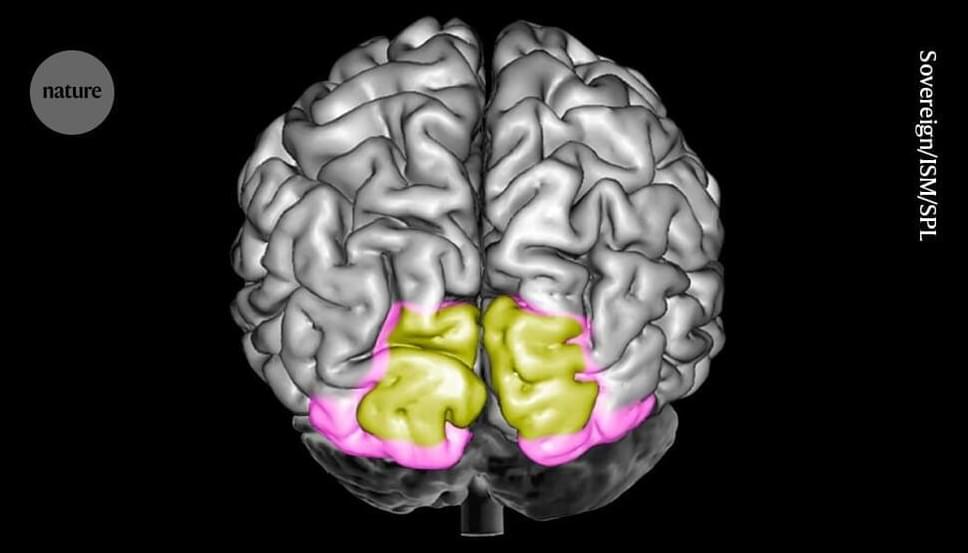
Picture a strawberry. Most people can easily distinguish between that image in their mind’s eye and an actual strawberry. Now researchers say that they’ve worked out how the brain draws this distinction and where in the brain the process happens.
According to a study1 in monkeys, the key part of the brain is the primary visual cortex, which is also involved in vision. The authors found that neurons in this region displayed a different activity pattern for images conjured up from memory compared with that for real-time visual input. They conclude that the primary visual cortex is crucial for recalling images stored in memory.
“It’s an intriguing study that goes beyond what we know in several ways,” says cognitive neuroscientist Floris de Lange at Radboud University in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, who was not involved in the work. But others in the field, such as Julio Martinez-Trujillo, a cognitive neurophysiologist at Western University in London, Ontario, Canada, says that another area of the brain, the prefrontal cortex, is more likely than the visual cortex to be key for recalling images.

To better treat and prevent depression, we need to understand more about the brains and bodies in which it occurs.
Curiously, a handful of studies have identified links between depressive symptoms and body temperature, yet their small sample sizes have left too much room for doubt.
In a more recent study published in February, researchers led by a team from the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) analyzed data from 20,880 individuals collected over seven months, confirming that those with depression tend to have higher body temperatures.

What connection does nicotine and cannabis use have on mental health stressors, including anxiety, depression, and discrimination, for young adults? This is what a recent study published in Addictive Behaviors hopes to address as a team of researchers led by Indiana University investigated how increased use of nicotine and cannabis in young adults also comes at a time when mental health stressors are also on the rise with them, as well. This study holds the potential to help researchers, medical professionals, and the public better understand the link between nicotine and cannabis use and mental health, especially with the legalization of recreational cannabis becoming more prevalent across the United States.
For the study, the researchers conducted a survey between 2019 and 2021 consisting of 2,478 young adults from Los Angeles between 18 to 29 years old with the following demographics: 57 percent Hispanic, 19 percent Asian, 15 percent White, 4 percent Black, and 3 percent as Multiracial. The participants were instructed to provide their mental health symptoms status (anxiety and depressions) and social stressors (discrimination), along with how much they use cannabis or nicotine, including vaping.
In the end, the researchers found a correlation between nicotine and cannabis use, along with some dual use, with higher rates of depression and anxiety with Hispanic young adults, with both Hispanic and Asian young adults having increased use of nicotine and cannabis correlating with higher rates of discrimination. For Black young adults, the researchers found increased use of nicotine products with higher anxiety while finding the opposite occurred for higher rates of depression and discrimination.