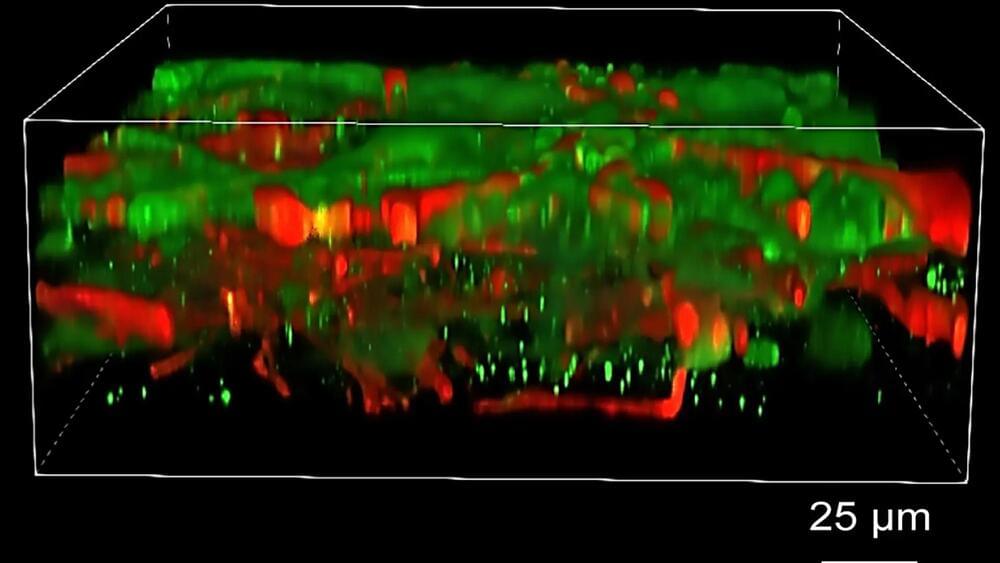
A new method for assembling neuron cultures horizontally instead of vertically helps solve for a longstanding issue.

While there is no denying ‘survival of the fittest’ still reigns supreme in the animal kingdom, a new study shows being smartest—or at least smarter—is pretty important, too.
Wear your support for the show with a Closer To Truth hoodie, T-shirt, or tank: https://bit.ly/3P2ogje.
What is it about human brains that enable both the regulation of bodily activities and the generation of mental thoughts? What are the mechanisms of human brain function? How do they integrate to give the sense of mental unity? What happens when something in the brain goes wrong—abnormalities, injury, disease? What is the future of brain science?
Dr. Kelsey Martin is Dean of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA as well as a professor of biological chemistry, psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences. Her research focuses on the cell biology of transcription-dependent forms of synaptic plasticity, particularly those underlying learning and memory.
Donate to Closer To Truth and help us keep our content free and without paywalls: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
Closer To Truth, hosted by Robert Lawrence Kuhn and directed by Peter Getzels, presents the world’s greatest thinkers exploring humanity’s deepest questions. Discover fundamental issues of existence. Engage new and diverse ways of thinking. Appreciate intense debates. Share your own opinions. Seek your own answers.
Their…
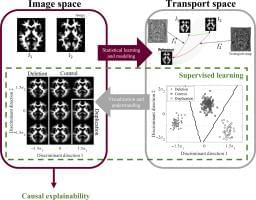
A multi-university research team co-led by University of Virginia engineering professor Gustavo K. Rohde has developed a system that can spot genetic markers of autism in brain images with 89 to 95% accuracy.
Their findings suggest doctors may one day see, classify and treat autism and related neurological conditions with this method, without having to rely on, or wait for, behavioral cues. And that means this truly personalized medicine could result in earlier interventions.
“Autism is traditionally diagnosed behaviorally but has a strong genetic basis. A genetics-first approach could transform understanding and treatment of autism,” the researchers wrote in a paper published June 12 in the journal Science Advances.

, while an interesting thought experiment, does not seem to account for the fact that many phenomena are materialistic or physical enough to have no resemblance with the qualities we typically attribute to consciousness, such as experience and motive.
Panprotopsychism, by contrast, does not require matter to be intrinsically conscious, only that it be comprised of features equaling consciousness when combined.
If certain kinds of quantum entanglement between particles such as electrons, more aptly described as wavicles, have superposed properties with likeness to the visible light spectrum when arranged amongst molecules and additional corpuscles, mechanisms of superposition may be the basic material unit of qualitative experience. These qualia, as fragments of psychical imagery and feeling, may flit in and out of existence rapidly within the most inorganic conditions, so that components of perception exist on a fundamental level while commonly not giving rise to experience and motive. But when these superpositions are held in prolonged orientations amongst brain matter and in nature generally, consciousness of carbon-based, human and alternative richness can emerge.

Throughout history, humans have sought to transcend the ordinary boundaries of consciousness, reaching for experiences beyond the everyday. They did this through various means, including the use of psychedelics and mind-altering substances. These substances have played a profound role in shaping ancient rituals, belief systems, and even governance. From the shamanic traditions of Siberia to the sophisticated ceremonies of the Maya, the use of psychoactive plants and compounds has been a ubiquitous feature of human culture. The influence of these substances extended far beyond mere spiritual exploration; they became intertwined with the very fabric of ancient societies, affecting political structures, social hierarchies, and religious practices. To fully understand their influence, we must study the intricate relationships between psychedelics, ritual practices, and governance in ancient civilizations, examining how these substances were used to achieve altered states of consciousness, connect with the divine, and wield power.
Visions From Beyond: The Role of Psychedelics in Ancient Rituals
Psychedelics have long been associated with religious and spiritual rituals, serving as gateways to the divine or as tools for gaining insight into the cosmos. In many ancient societies, these substances were not merely recreational but were integral to the religious experience, often seen as sacraments that enabled communication with gods or spirits.

Chinese scientists have developed a method using genetic engineering to potentially enhance brain-computer interface (BCI) technology by enlarging neurons for better signal transmission.
The researchers, with the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ National Centre for Nanoscience…
Gene sequence could be implanted with electrodes to make neurons larger and easier to ‘read’ in quest for better mind control of devices.
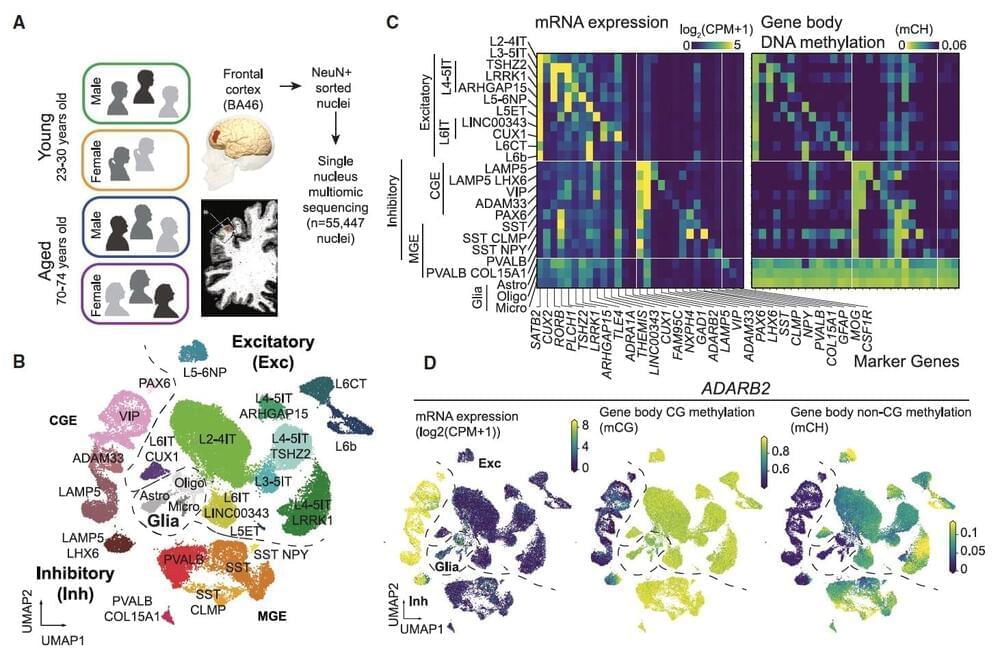
Aging is known to have profound effects on the human brain, prompting changes in the composition of cells and the expression of genes, while also altering aspects of the interaction between genes and environmental factors. While past neuroscience studies have pinpointed many of the molecular changes associated with aging, the age-related genetic factors influencing specific neuron populations remains poorly understood.
Recent studies on flies, mice, primates and human brain tissue utilizing single-cell or single-nucleus RNA-sequencing and genetic experimental techniques shed new light on these cell-type-specific changes. For instance, they unveiled the effects of aging on glial cells in the mouse and human brain, associations between cell-specific changes and modified chromatin proteins, and the influence of DNA methylation in the aging of various tissues.
Researchers at University of California (UC) San Diego and Salk Institute recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding how both age and sex impact human cortical neurons at a single-cell level. Their findings, published in Neuron, offer new insights into how aging affects cell composition, gene expression and DNA methylation across human brain cell types, while also uncovering differences between gene expression and DNA methylation in females and males.