LINKS: https://www.wired.com/story/openai-buy-ai-chips-startup-sam-…i/https:/.…
Category: neuroscience – Page 406

Time’s Secrets Unveiled: Study Challenges How We Perceive Time
Our brain measures time by counting experiences, not by following a strict chronological order.
A new study by a team of UNLV researchers suggests that there’s a lot of truth to the trope “time flies when you’re having fun.”
In their study, recently published in the journal Current Biology, the researchers discovered that our perception of time is based on the number of experiences we have, not on an internal clock. Additionally, they found that increasing speed or output during an activity appears to affect how our brains perceive time.


How Your Brain Remembers: How Episodic Memories Form
Summary: Researchers developed a computer model that mimics how the hippocampus stores new episodic memories without erasing old ones. This model demonstrates that the CA3 region of the hippocampus serves as an anchor point for memories, allowing efficient storage in surrounding regions.
The findings reveal insights into how the brain organizes personal experiences and maintains stability despite constant updates. The model shows promise for enhancing our understanding of memory retention and cognitive processing.
Cell-type specific epigenetic clocks to quantify biological age at cell-type resolution
The ability to accurately quantify biological age could help monitor and control healthy aging. Epigenetic clocks have emerged as promising tools for estimating biological age, yet so far, most of these clocks have been developed from heterogeneous bulk tissues, and are thus composites of two aging processes, one reflecting the change of cell-type composition with age and another reflecting the aging of individual cell-types. There is thus a need to dissect and quantify these two components of epigenetic clocks, and to develop epigenetic clocks that can yield biological age estimates at cell-type resolution. Here we demonstrate that in blood and brain, approximately 35% of an epigenetic clock’s accuracy is driven by underlying shifts in lymphocyte and neuronal subsets, respectively. Using brain and liver tissue as prototypes, we build and validate neuron and hepatocyte specific DNA methylation clocks, and demonstrate that these cell-type specific clocks yield improved estimates of chronological age in the corresponding cell and tissue-types. We find that neuron and glia specific clocks display biological age acceleration in Alzheimer’s Disease with the effect being strongest for glia in the temporal lobe. The hepatocyte clock is found accelerated in liver under various pathological conditions. In contrast, non-cell-type specific clocks do not display biological age-acceleration, or only do so more marginally. In summary, this work highlights the importance of dissecting epigenetic clocks and quantifying biological age at cell-type resolution.
The authors have declared no competing interest.
The Illumina DNA methylation datasets analyzed here are all freely available from GEO (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo).

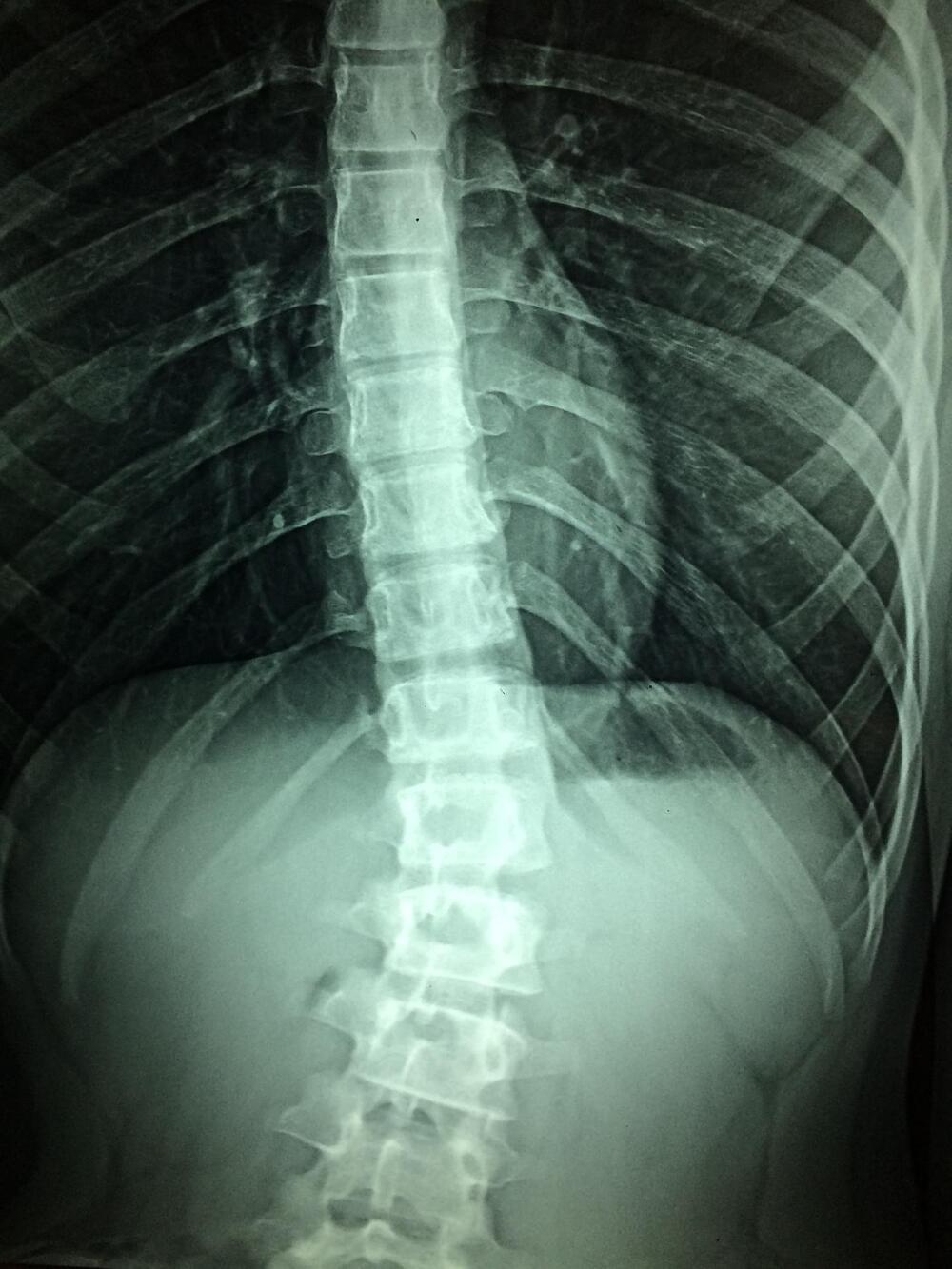
White matter may aid recovery from spinal cord injuries: Study
Injuries, infection and inflammatory diseases that damage the spinal cord can lead to intractable pain and disability. Some degree of recovery may be possible. The question is, how best to stimulate the regrowth and healing of damaged nerves.
At the Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS), scientists are focusing on a previously understudied part of the brain and spinal cord —white matter. Their discoveries could lead to treatments that restore nerve activity through the targeted delivery of electromagnetic stimuli or drugs.
As in the brain, the spinal cord is made up nerve cell bodies (gray matter), which process sensation and control voluntary movement, and axons (white matter), fibers that connect nerve cells and which project to the rest of the body.
Young Adult Health Habits Linked to Midlife Cognitive Decline
A UCSF study reveals that higher inflammation levels in young adults are associated with poorer cognitive performance in midlife, underscoring the importance of lifestyle choices in reducing inflammation and preventing cognitive decline.
Higher levels of inflammation in young adults, associated with factors like obesity, physical inactivity, chronic illness, stress, and smoking, are linked to decreased cognitive function in midlife, according to a new study from UC San Francisco.
Researchers previously linked higher inflammation in older adults to dementia, but this is one of the first studies to connect inflammation in early adulthood with lower cognitive abilities in midlife.
Brain Cancer Breakthrough: New Therapy Destroys Glioblastoma in Recently Unveiled Pathway
Researchers have discovered a new pathway used by cancer cells to infiltrate the brain and developed a promising therapy that targets this pathway with CAR T cells.
Their study showed significant preclinical success in increasing survival and eradicating tumors in animal models of glioblastoma and other brain cancers.
A team of Canadian and American research groups led by the Singh Lab at McMaster University have discovered a new pathway that is used by cancer cells to infiltrate the brain. The research also reveals a new therapy that shows promise in blocking and killing these tumors.