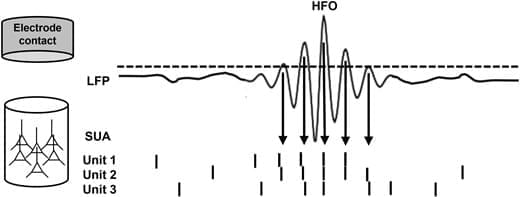
The results published by Tong et al. 60 reconcile the previous observations that increased power across a broad range of frequencies is composed of multiple HFO bursts detected at discrete frequencies. 32, 33, 85 In Figs 2 and 3, we summarize the general mechanism from micro-scale ensembles of firing neurons, through bursts of individual HFOs detected in particular trials at specific frequencies, to the resultant trial-averaged enhanced power across a broad frequency range. Coordinated firing in response to a stimulus presentation gives rise to HFOs at particular frequencies depending on the size and spread of the underlying neural ensemble (Fig. 3A and C). Other ensembles generate HFOs at particular frequencies in response to stimuli in subsequent trials. Eventually, multiple trials result in a uniform shift in power across a broad frequency range of the spectrum relative to a pre-stimulus baseline (Fig. 3C). Detections from specific trials can be displayed together as points at their corresponding peak-amplitude on a cumulative time-frequency plot, producing a pattern closely overlapping with the trial-averaged power spectrogram (Fig. 3D).
This is an explanation for the resultant broadband shift in power across the high-frequency spectrum associated with cognitive and motor tasks and increased neural firing, 92–95 which argued against oscillations at particular frequency bands. If the intermediate step of detecting individual bursts of oscillations on a trial-by-trial basis is skipped, the overall trial-averaged power will be most highly correlated with general firing rates in the entire neural population without any common temporal pattern or coordination to oscillations. If, however, independent constituent bursts of oscillations and the underlying firing in subsets of neural ensembles are first resolved one by one, then multiple patterns of coordinated activity emerge. In this large-scale mechanism, coordinated electrical activity from multiple neural sources generating oscillations at distinct frequencies could explain the broadband shifts in power across the spectrum. 24 Separate sources of HFO bursts detected at various frequencies remain to be demonstrated on the macro-and micro-recording scales.
Assuming that individual HFOs can indeed be separated based on their spectral features 96–98 and thus identify particular sources of LFP activities, it should be possible to resolve the neurophysiological substrates of memory and cognition proposed in our title question. High frequency LFP activities were suggested to track particular neuronal assemblies on the level of micro-contact LFP in rodents. 91 Intracranial recordings in non-human primates 86, 87 and in human patients 22, 32, 85 can also resolve distinct bursts in the frequency-time space of individual trials, which could hypothetically be the features of particular neuronal assemblies. 24 HFO bursts beyond the ripple frequency range, which were shown to be generated very locally on the scale of a single cortical column, 64 would correspond to arguably the fundamental level of neural organization and information processing. 99 In the next section, we will review the roles of temporal coordination in gamma and higher frequencies in supporting processes of memory and cognition.