By Nina Bai
Studying mice of different ages, Stanford Medicine scientists and colleagues found that neurons involved in spatial memory become less reliable later in life.

By Nina Bai
Studying mice of different ages, Stanford Medicine scientists and colleagues found that neurons involved in spatial memory become less reliable later in life.
What if watching a video didn’t just change your mind — but erased your existence?
In this speculative science deep dive, we explore SCP-4076, the infamous “Video Hurt System”, a VHS tape that destroys anything that observes it.
Through the lens of quantum collapse, memetic contagion, and information physics, we examine how a piece of analog media could defy the laws of reality itself.
Is SCP-4076 proof that knowledge can have mass? Could perception itself carry the power to rewrite existence?
Join us as we investigate the intersection of cognitive hazards, quantum theory, and metaphysical information, where curiosity becomes a weapon and observation erases the observer.
📅 New speculative science essays every weekday at 6 p.m. PST / 9 p.m. EST
🔔 Subscribe and turn on notifications — explore the edge of what’s possible.
💬 Tell us: would you play the tape?

Researchers from the Center for Precision Psychiatry at the University of Oslo and Oslo University Hospital have discovered extensive genetic links between neurological disorders like migraine, stroke and epilepsy, and psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia and depression. Published in Nature Neuroscience, this research challenges longstanding boundaries between neurology and psychiatry and points to the need for more integrated approaches to brain disorders.
“We found that psychiatric and neurological disorders share genetic risk factors to a greater extent than previously recognized. This suggests that they may partly arise from the same underlying biology, contrasting the traditional view that they are separate disease entities. Importantly, the genetic risk was closely linked to brain biology,” states Olav Bjerkehagen Smeland, psychiatrist and first author.
Infants born deaf or hard of hearing show adverse changes in how their brains organize and specialize, but exposure to sound and language may help them develop more normally, according to new research.
The study led by two neuroscientists found that infants with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) lacked the usual pattern of organization on the brain’s left side, which supports language and higher cognitive skills.
The findings also suggest that early auditory stimulation through hearing aids or cochlear implants, along with exposure to language, whether spoken or signed, could help preserve normal brain development.
Rice University bioengineers have demonstrated a nonsurgical way to quiet a seizure-relevant brain circuit in an animal model. The team used low-intensity focused ultrasound to briefly open the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the hippocampus, delivered an engineered gene therapy only to that region and later flipped an on-demand “dimmer switch” with an oral drug.
The research shows that a one-time, targeted procedure can modulate a specific brain region without impacting off-target areas of the brain. It is published in and featured on the cover of ACS Chemical Neuroscience.
“Many neurological diseases are driven by hyperactive cells at a particular location in the brain,” said study lead Jerzy Szablowski, assistant professor of bioengineering and a member of the Rice Neuroengineering Initiative. “Our approach aims the therapy where it is needed and lets you control it when you need it, without surgery and without a permanent implant.”
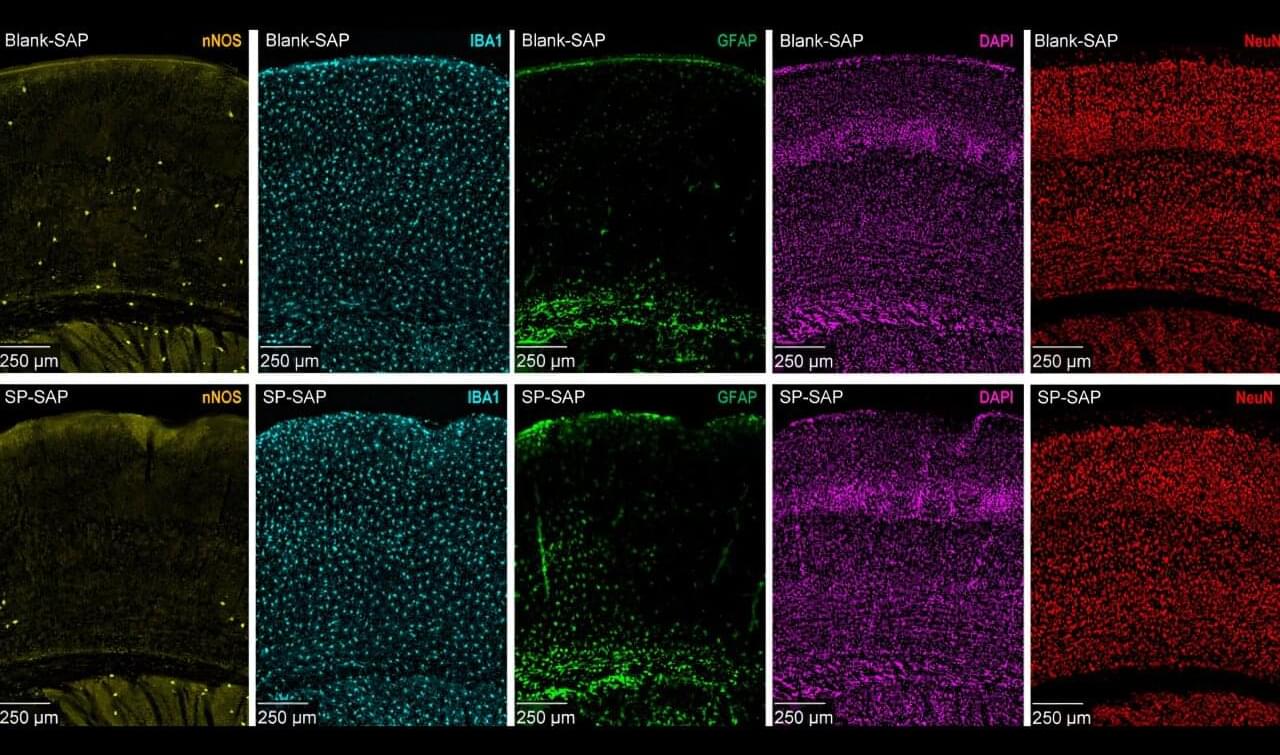
While the exact causes of neurodegenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia are still largely unknown, researchers have been able to identify a key characteristic in affected brains: reduced blood flow. Building upon this foundational understanding, a team at Penn State recently found that a rare neuron that is extremely vulnerable to anxiety-induced stress appears to be responsible for regulating blood flow and coordinating neural activity in mice.
The researchers found that eliminating type-one nNOS neurons—which make up less than 1% of the brain’s 80 billion neurons and die off when exposed to too much stress—resulted in a drop in both blood flow and electrical activity in mice’s brains, demonstrating the impact this neuron type has on the proper brain functions of animals, including humans.
The research appears in eLife.

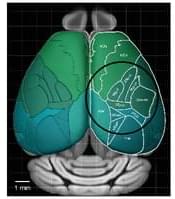
Our ability to perceive, think, or act relies on coordinated activity in large networks of neurons in the brain. This review examines recent progress in connecting ideas from statistical physics, such as maximum entropy methods and the renormalization group, to quantitative experiments that record the electrical activity of thousands of neurons simultaneously. This quantitative bridge between the new data and statistical physics models uncovers new, quantitatively reproducible behaviors and makes clear that abstract theoretical principles in studies of the brain can have the level of predictive power that we expect in other areas of physics.