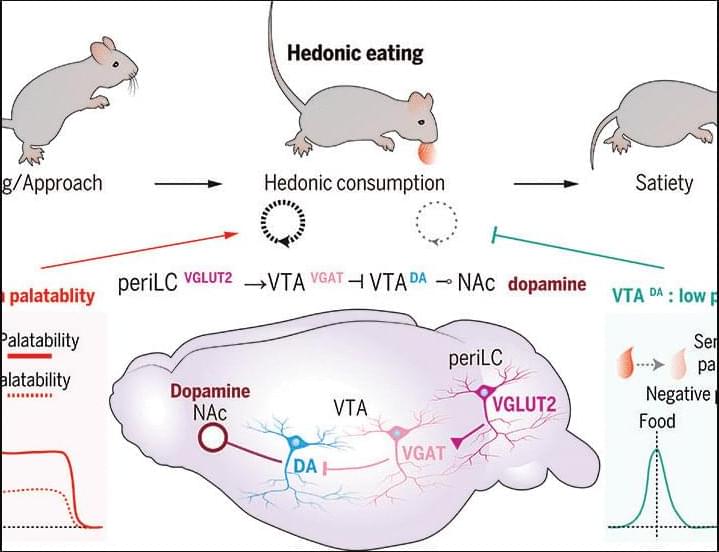
Hedonic eating is defined as food consumption driven by palatability without physiological need. However, neural control of palatable food intake is poorly understood. We discovered that hedonic eating is controlled by a neural pathway from the peri–locus ceruleus to the ventral tegmental area (VTA). Using photometry-calibrated optogenetics, we found that VTA dopamine (VTADA) neurons encode palatability to bidirectionally regulate hedonic food consumption. VTADA neuron responsiveness was suppressed during food consumption by semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide receptor 1 (GLP-1R) agonist used as an antiobesity drug. Mice recovered palatable food appetite and VTADA neuron activity during repeated semaglutide treatment, which was reversed by consumption-triggered VTADA neuron inhibition.