Background and ObjectivesVascular dysfunction contributes to Alzheimer disease (AD) and related dementias (ADRDs), but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Previous studies link midlife hemostasis and platelet aggregation measures to late-life…



A new study reveals a surprising mechanism that might be behind the beneficial effects of NAD+ in preclinical models of Alzheimer’s [1].
Which way to splice it?
Not every part of a DNA sequence gets translated into a protein. Each sequence consists of exons, which are included in the final RNA transcript, and introns, which are thrown away.

The results showed that participants who more strongly endorsed pseudoscientific beliefs tended to report a higher frequency of meaningful coincidences in their lives. They were also more likely to attribute these coincidences to non-random causes, such as destiny or a universal connection, rather than to chance. Among the explanations offered for coincidences, “pure chance” was the most commonly endorsed, but those who selected this option tended to score lower on the pseudoscience measure.
Participants also displayed a general bias toward avoiding repetition when simulating randomness, selecting fewer repeated outcomes than chance would predict. This repetition avoidance was particularly evident in the coin toss task. Importantly, those who more strongly endorsed pseudoscientific beliefs were also more likely to show this bias, especially in the coin task. This suggested a link between belief in pseudoscience and a distorted sense of what a random sequence should look like.
When the researchers looked at all the variables together, they found that two factors independently predicted higher endorsement of pseudoscientific beliefs. The first was how often participants explained coincidences with non-chance causes. The second was how strongly they avoided repetition in the coin task. These two cognitive tendencies—seeking causal explanations for coincidences and misunderstanding randomness—each appeared to contribute separately to belief in pseudoscience.
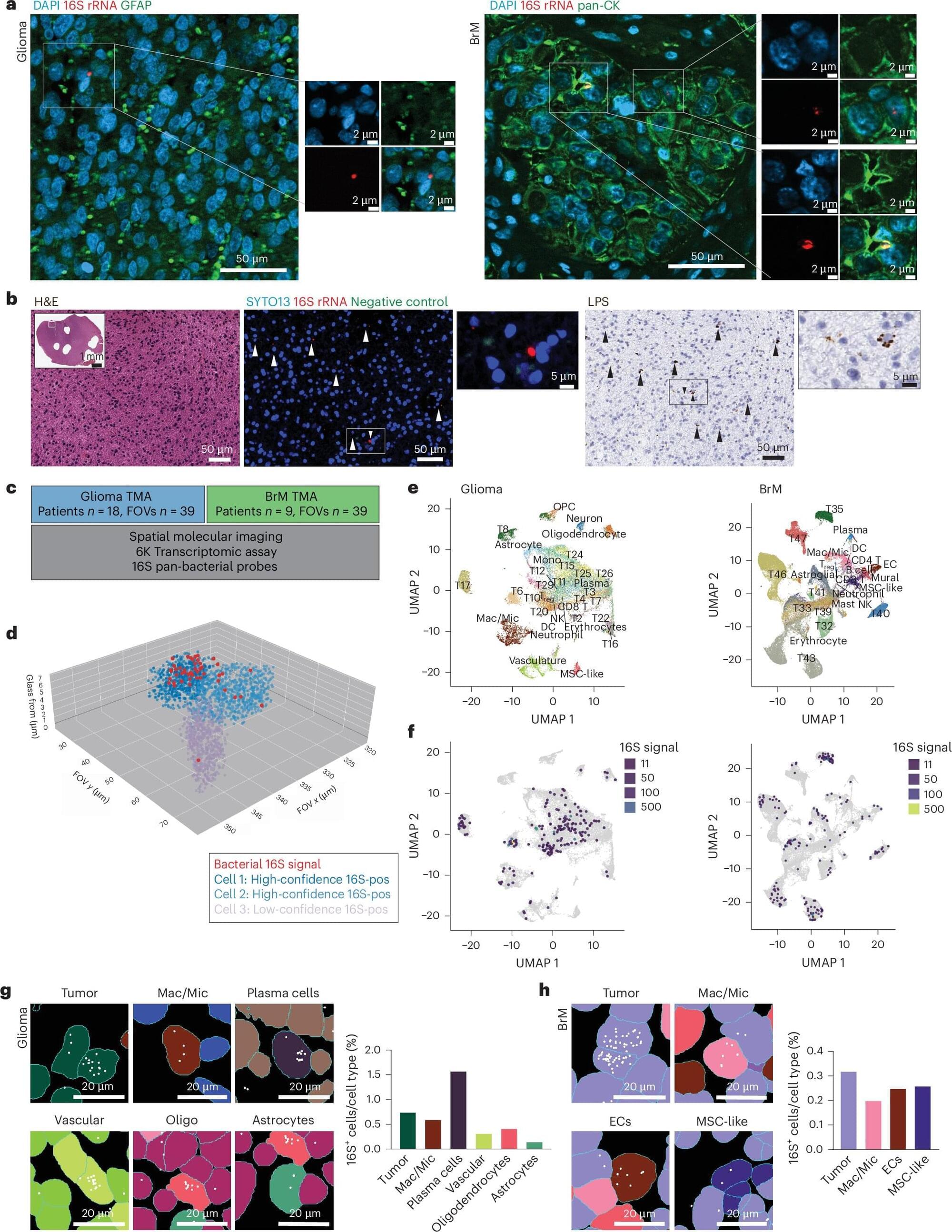
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have uncovered unexpected traces of bacteria within brain tumors. This discovery offers new insights into the environment in which brain tumors grow and sets the stage for future studies seeking to improve treatment outcomes.
Published today in Nature Medicine, the data revealed that bacterial genetic and cellular elements were present inside brain tumor cells and across the tumor microenvironment. These bacterial components appeared biologically active, potentially influencing tumor behavior and progression in patients with gliomas and brain metastases.
The multi-institutional study was led by Golnaz Morad, D.D.S, Ph.D., postdoctoral research fellow in Surgical Oncology, and Jennifer Wargo, M.D., professor of Surgical Oncology and Genomic Medicine and core member of the James P. Allison Institute—working in close collaboration with MD Anderson’s Platform for Innovative Microbiome and Translational Research (PRIME-TR).
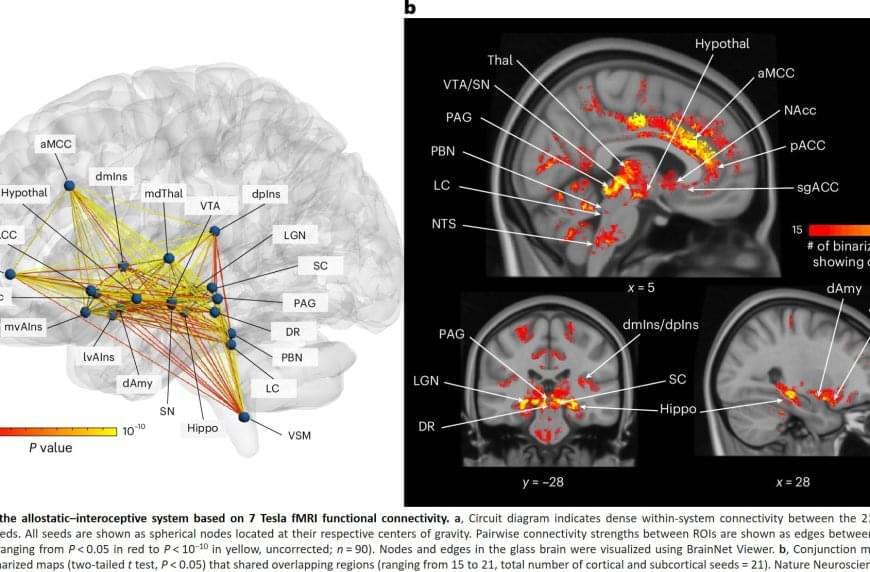
They also used a recently validated map of deep brain areas. This in vivo atlas, Brainstem Navigator, maps the regions involved in regulating the autonomic, immune and endocrine systems.
The authors analytic approach was guided by decades of basic research that has identified two main brain pathways in mammals: one set of pathways (allostatic) that sends signals from the brain to control the body’s organs, and the other set (interoceptive) that sends signals from the body to the brain, informing it about what’s happening inside us.
The findings replicated and expanded on their previous 3 Tesla work, confirming nearly all the direct connections identified in non-human mammals: 100% of those between cortical areas and 96% of those linking subcortical areas to both cortical and other subcortical areas. As expected, the authors found two-way connections between the brain areas that help manage the body’s needs (like the anterior cingulate cortex) and the areas that sense what’s happening inside the body (like the posterior insula). This means these regions communicate back and forth, helping the brain predict and regulate what the body needs.
Mounting evidence suggests that one of the brain’s central roles is to anticipate and meet the body’s energy needs. The findings place the monitoring and regulation of the body’s needs at the functional core of the human brain, showing the close connection between mental and physical health.
Previous studies in both animal models and humans have pointed to the existence of a distributed system in the brain that helps it anticipate and prepare for the body’s energy needs — a process called allostasis — as well as monitor the sensory conditions inside the body, known as interoception.
In an earlier study using 3 Tesla fMRI, the team mapped a network supporting allostasis and interoception in the human brain, but the comparatively limited spatial resolution and sensitivity of the 3 Tesla technology made it difficult to fully capture the system’s smaller structures in the brainstem, which are known to play a key role in these processes.

People can think, behave and function very differently. These observed differences are known to be the result of complex interactions between genetics, neurobiological processes and life experiences.
Understanding the factors underlying individual differences in behavior, cognition and mental health is a key objective of numerous psychology and behavioral science studies. One approach to explore these factors entails examining patterns of brain activity that spontaneously emerge when individuals are awake but not engaged in any tasks.
Earlier research aimed at uncovering individual-specific brain activity patterns has primarily looked at the neural fluctuations indicating communication or coupling between distant brain regions. In contrast, very few studies have focused on intra-regional neural dynamics (i.e., fluctuations that take place within individual brain regions over time).

This pace of discovery might be expected given the extreme intricacy of the brain and psychiatric disorders.
“The brain is incredibly complex — we’re talking about tens of billions of neurons with trillions of connections,” says Kozo Kaibuchi, director of the International Center for Brain Science (ICBS) at Fujita Health University, near Nagoya in Japan. “Psychiatric and neurological disorders are also highly diverse — often involving subtle changes on a spectrum rather than one obvious cause.”
On top of that, there are further obstacles that hinder progress in developing treatments for these conditions — the difficulty of imaging inside the human brain; the scarcity of human-like models; and the blood–brain barrier, which prevents most drugs from entering the brain.