Alternative models for studying aging have employed unicellular organisms such as the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Studying replicative aging in yeast has revealed insights into evolutionarily conserved enzymes and pathways regulating aging[ 12-14 ] as well as potential interventions for mitigating its effects.[ 15 ] However, traditional yeast lifespan analysis on agar plates and manual separation cannot track molecular markers and yeast biology differs from humans.[ 16 ]
Animal models, including nematodes, flies, and rodents, play a vital role in aging research due to their shorter lifespans and genetic manipulability, making them useful for mimicking human aging phenotypes.[ 17 ] These models have provided many insights into the fundamental understanding of aging mechanism. However, animal models come with several limitations when applied to human aging and age-related diseases. Key issues include limited generalizability due to species-specific differences in disease manifestation and physiological traits. For example, animal models often exhibit physiological differences, age at different rates, and may not fully replicate human conditions like cardiovascular disease,[ 18 ] immune response,[ 19 ] neurodegenerative diseases,[ 20 ] and drug metabolism.[ 21 ] Furthermore, in vivo models, such as rodents and non-human primates, suffer from limitations such as high costs, low throughput, ethical concerns, and physiological differences compared to humans. The use of shorter lifespan or accelerated aging models, along with the absence of long-term longitudinal data, can further distort the natural aging process and hinder our understanding of aging in humans. Additionally, many animal models rely on inbred strains, which lack genetic diversity and may not fully represent evolutionary complexity.[ 22 ]
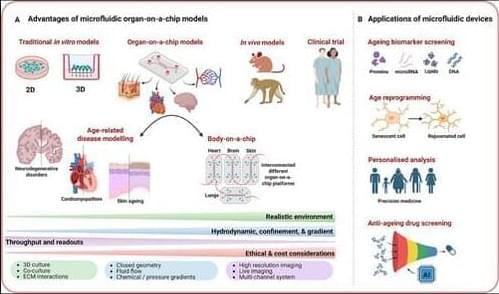
In recent years, microfluidics has emerged as a promising tool for studying aging, offering of physiologically relevant 3D environments with high-throughput capabilities that surpass the limitations of traditional 2D cultures and bridge the gap between animal models and human As a multidisciplinary technology, microfluidics processes or manipulates small volumes of fluids (from pico to microliters) within channels measuring 10–1000 µm.[ 23 ] Traditional fabrication methods, such as photolithography and soft lithography, particularly using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), remain widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and biocompatibility. However, newer approaches, including 3D printing, injection molding, and laser micromachining, offer greater flexibility for rapid prototyping and the creation of complex architectures. Design considerations are equally critical and are tailored to the specific application, focusing on parameters such as channel geometry, fluid dynamics, material properties, and the integration of on-chip components like valves, sensors, and actuators. A comprehensive overview of the design and fabrication of microphysiological systems is beyond the scope of this review; readers are referred to existing reviews for further detail.[ 24-26 ] Microfluidic devices offer numerous advantages, including reduced resource consumption and costs, shorter culture times, and improved simulation of pathophysiological conditions in 3D cellular systems compared to other model systems (Figure 1).[ 27 ] Therefore, microfluidics platforms have been extensively employed in various domains of life science research, such as developmental biology, disease modeling, drug discovery, and clinical applications,[ 28 ] positioning this technology as a significant avenue in the field of aging research.