A new study using direct recordings from human brains reveals how the amygdala and hippocampus coordinate to form and retrieve emotional memories.

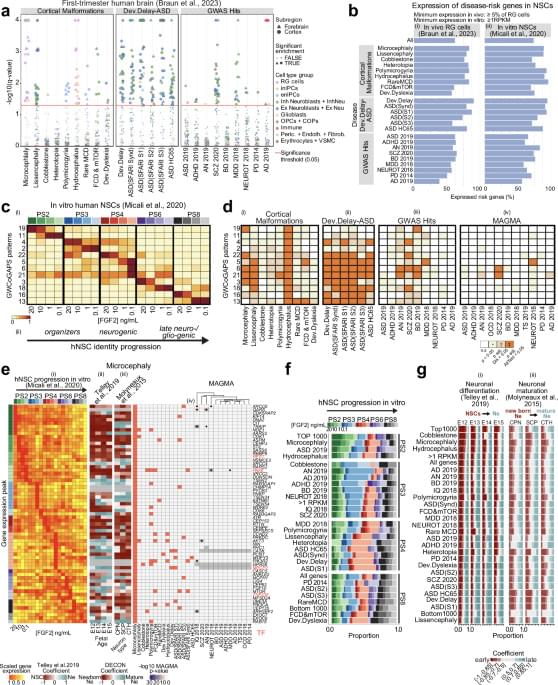

Copper is an essential trace element for normal development and function throughout the body, including the central nervous system (CNS). Alterations to cellular copper levels result in severe neurological consequences and are linked to a range of CNS disorders, positioning treatments that restore copper balance as promising therapies for these disorders. However, despite the clear relationship between copper balance and CNS health, there are limited tools to measure copper levels in vivo in humans. This constitutes a significant challenge for both diagnosing disorders of copper imbalance and monitoring the efficacy of copper-altering treatments for these disorders. Here we report the synthesis and characterization of Fluorine-labeled Naphthalimide Copper sensor 1 (F-NpCu1), a fluorescent sensor for copper that contains a fluorine atom for future radiolabeling for clinical application. We demonstrate that the probe exhibits good stability and is highly selective for copper above other transition metals present in biological tissues. Copper binding promotes covalent bond formation between the sensor and proximal cellular proteins. F-NpCu1 is nontoxic and can be measured using fluorescence microscopy in living cells and fixed tissue sections from both mouse brain and pancreas. Furthermore, F-NpCu1 exhibits good blood-brain-barrier permeability and can report differences in brain copper levels induced by copper modulating therapies in living mice using intravital fluorescence microscopy. This study represents a promising advance toward the development of the first clinical tool for measuring copper in living humans, including in the CNS, with radiolabeling studies underway to develop 18F-NpCu1 for PET imaging of copper in vivo.

In efforts to beat Alzheimer’s disease, researchers are looking at existing drugs that could tackle the condition, and a new study identifies two promising candidates that are currently used to treat cancer.
Already approved by regulators in the US – meaning potential clinical trials for Alzheimer’s could start sooner – the drugs are letrozole (usually used to treat breast cancer) and irinotecan (usually used to treat colon and lung cancer).
Researchers from the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and Gladstone Institutes started by looking at how Alzheimer’s altered gene expression in the brain.

University of Pennsylvania and Syracuse University scientists have discovered that a hindbrain-derived peptide, octadecaneuropeptide (ODN), can suppress appetite and improve glucose regulation without causing nausea or vomiting. Results suggest a glia-to-neuron signaling axis in the dorsal vagal complex that may be harnessed for treating obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Glial cells in the brainstem produce ODN, a signaling peptide whose physiological role in energy homeostasis has remained obscure. Researchers now find that directly activating this peptide system in the hindbrain induces weight loss, enhances glucose disposal, and lowers insulin resistance in obese animals.
Unlike existing therapies targeting GLP-1 receptors, ODN achieves these effects without triggering nausea-related behaviors or emesis in vomiting-competent models.
Could Meta be on the verge of transforming how we interact with our digital devices? If the company’s latest innovation takes off, we might soon be controlling our computers, cell phones and tablets with a simple flick of the wrist.
Researchers at Meta’s Reality Labs division have unveiled an experimental wristband that translates hand gestures and subtle finger movements into commands that interact with a computer. This allows a user to push a cursor around a screen or open an app without needing a mouse, touchscreen or keyboard. The technology can even transcribe handwriting in the air into text (currently at a speed of 20.9 words per minute).
In a paper published in Nature, the team describes how its sEMG-RD (surface electromyography research) works. The wristband uses a technique called electromyography to pick up electrical signals when the brain tells the hand to perform an action. It then converts those signals into commands that control a connected device, such as your phone.