Certain patterns of brain activity during awakening correlate with a lower likelihood of the bleary-eyed state called ‘sleep inertia’



New research suggests that psychological richness—a life of perspective-changing experiences—may matter just as much as happiness or meaning.
For centuries, scholars and scientists have defined the “good life” in one of two ways: a life that is rooted in happiness, characterized by positive emotions, or one that is centered on meaning, guided by purpose and personal fulfillment. But what if there is another, equally valuable path—one that prioritizes challenge, change and curiosity?
This third dimension, which may result in a more psychologically rich life for some, is being explored in a new study published in Trends in Cognitive Sciences, led by University of Florida psychologist Erin Westgate, Ph.D., in collaboration with Shigehiro Oishi, Ph.D., of the University of Chicago. According to their research, some people prioritize variety, novelty, and intellectually stimulating experiences, even when those experiences are difficult, unpleasant, or lack clear meaning.

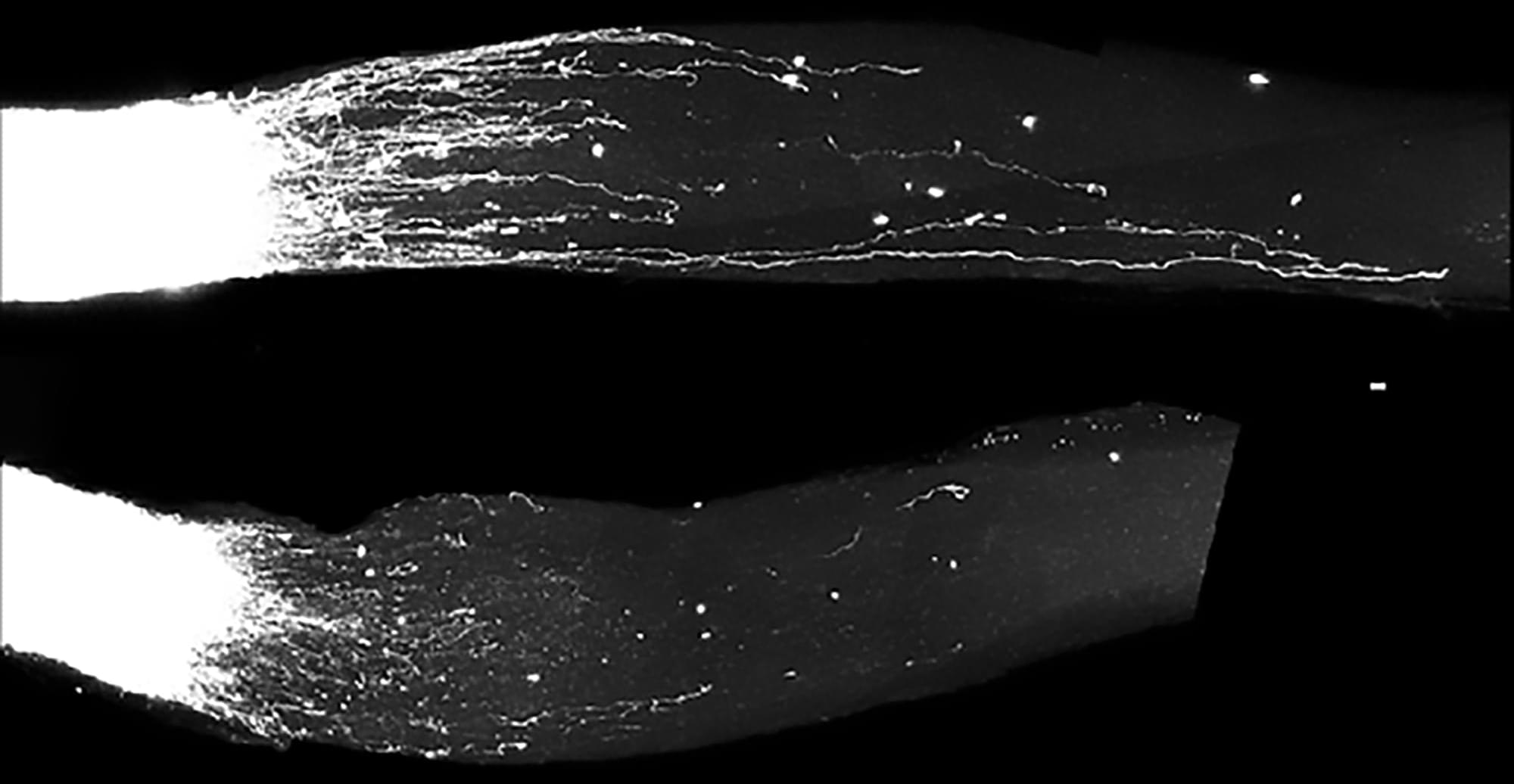
An interdisciplinary team working on balls of human neurons called organoids wanted to scale up their efforts and take on important new questions. The solution was all around them.
For close to a decade now, the Stanford Brain Organogenesis Program has spearheaded a revolutionary approach to studying the brain: Rather than probe intact brain tissues in humans and other animals, they grow three-dimensional brain-like tissues in the lab from stem cells, creating models called human neural organoids and assembloids.
Beginning in 2018 as a Big Ideas in Neuroscience project of Stanford’s Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute, the program has brought together neuroscientists, chemists, engineers, and others to tackle the neural circuits involved in pain, genes that drive neurodevelopmental disorders, new ways to study brain circuits, and more.



Antler blastema progenitor cells (ABPCs) are a distinct population of skeletal mesenchymal stem cells found in regenerating deer antlers, with strong stemness and renewal capacity in vitro. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as potential therapeutic candidates that can mediate donor cells’ beneficial effects. Here, we tested the effects of ABPC-derived EVs (EVsABPC) on aging in mice and rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). We identified a variety of unique factors in EVsABPC and showed that in vitro, EVsABPC attenuated phenotypes of senescence in bone marrow stem cells. In aged mice and macaques, EVsABPC substantially increased femoral bone mineral density. Further, intravenous EVsABPC improved physical performance, enhanced cognitive function and reduced systemic inflammation in aged mice, while reversing epigenetic age by over 3 months. In macaques, EVABPC treatment was also neuroprotective, reduced inflammation, improved locomotor function and reduced epigenetic age by over 2 years. Our findings position ABPCs as an emerging and practical source of EVs with translational value for healthy aging interventions.
Inspired by the regenerative capacity of deer antlers, Hao and colleagues report that antler blastema progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicle treatment counteracts bone loss and epigenetic aging and is neuroprotective in mice and macaques.

A new Yale study has revealed that neurons — the energy-hungry cells that connect and direct activity in the brain — are equipped with “backup batteries” that kick in to keep the brain running during periods of metabolic stress.
Writing in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers describe how neurons store their own glycogen, a form of sugar that helps neurons stay resilient when their main energy sources falter.

LONDON, Ont. – Dementia poses a major health challenge with no safe, affordable treatments to slow its progression.
Researchers at Lawson Research Institute (Lawson), the research arm of St. Joseph’s Health Care London, are investigating whether Ambroxol — a cough medicine used safely for decades in Europe — can slow dementia in people with Parkinson’s disease.
Published today in the prestigious JAMA Neurology, this 12-month clinical trial involving 55 participants with Parkinson’s disease dementia (PDD) monitored memory, psychiatric symptoms and GFAP, a blood marker linked to brain damage.
Parkinson’s disease dementia causes memory loss, confusion, hallucinations and mood changes. About half of those diagnosed with Parkinson’s develop dementia within 10 years, profoundly affecting patients, families and the health care system.