Opioids like morphine are widely used in medical practice due to their powerful pain-relieving effects, yet they carry the risk of serious adverse effects such as respiratory depression and drug dependence. For this reason, Japan has strict regulations in place to ensure that these medications are prescribed only by authorized physicians.
In the United States, the opioid OxyContin was once frequently prescribed, triggering a surge in the misuse of synthetic opioids such as fentanyl. As a result, the number of deaths caused by opioid overdose surpassed 80,000 in 2023, escalating into a national public health crisis now referred to as the “opioid crisis.”
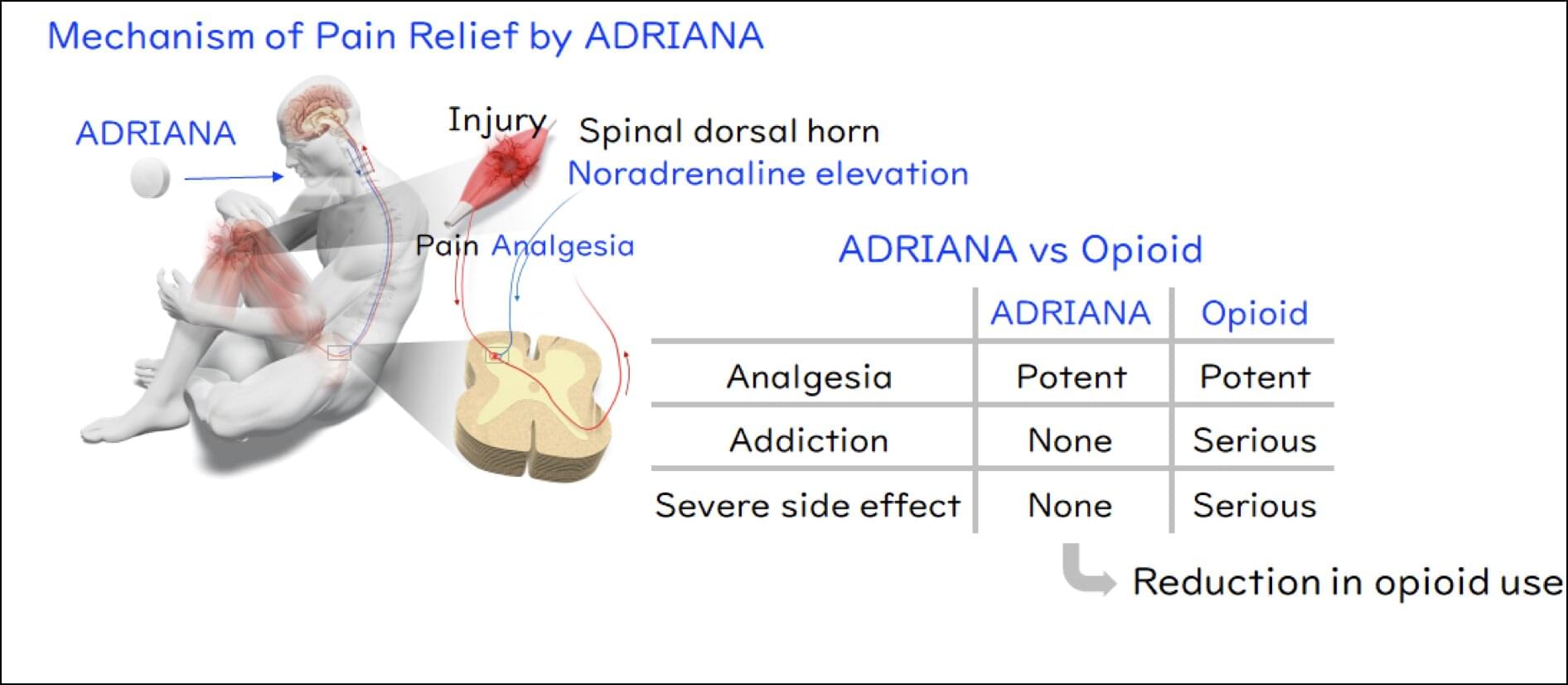
Opioids may soon have a rival, however. A team of researchers at Kyoto University has recently discovered a novel analgesic, or pain reliever, that exerts its effect through an entirely different mechanism. Clinical development of their drug ADRIANA is currently underway as part of an international collaborative effort.