Scientists have spent over 25 years trying — and failing — to build computer simulations of the smallest brain we know. Today, we finally have the tools to pull it off.


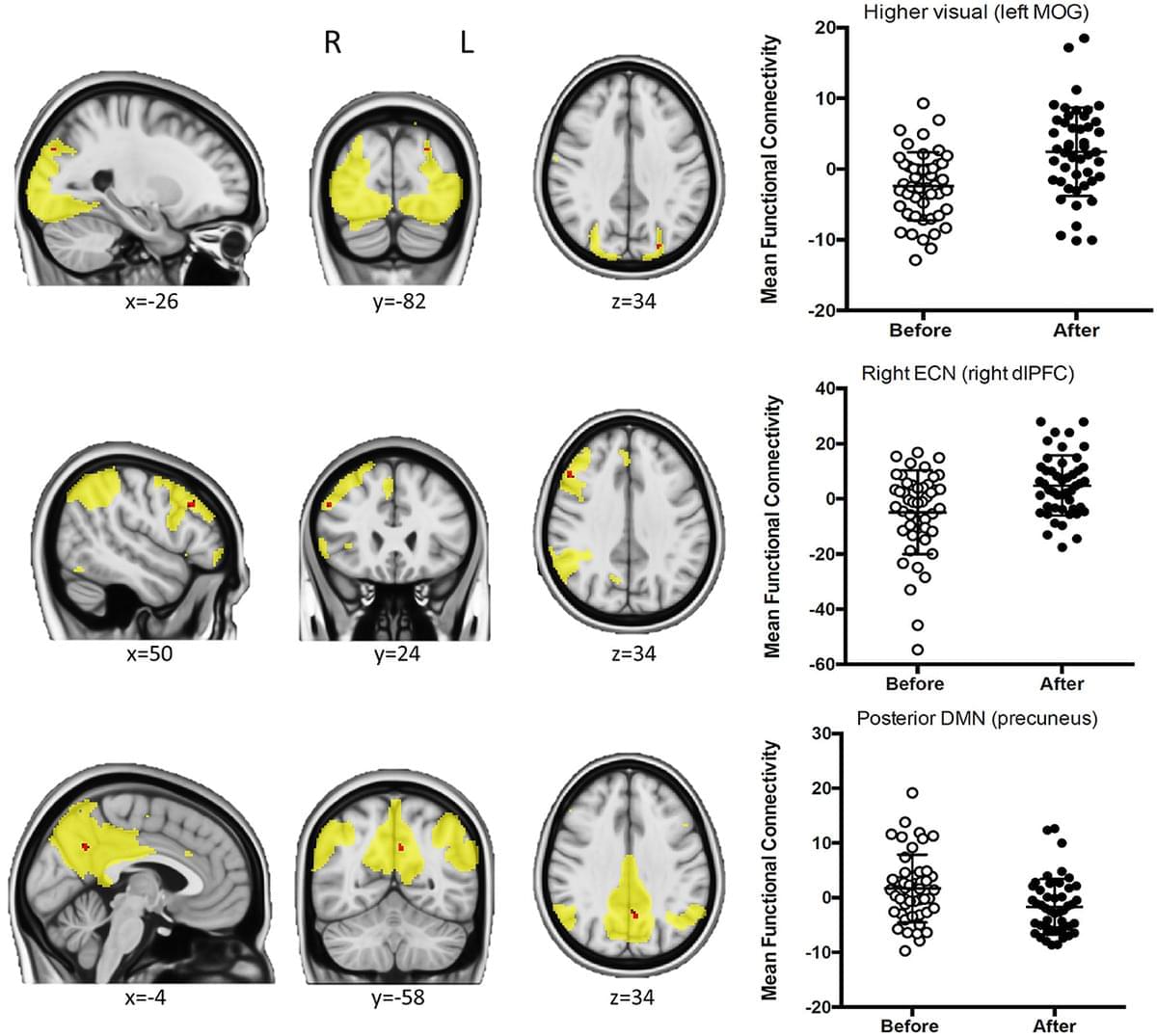
Habitual coffee consumers justify their life choices by arguing that they become more alert and increase motor and cognitive performance and efficiency; however, these subjective impressions still do not have a neurobiological correlation. Using functional connectivity approaches to study resting-state fMRI data in a group of habitual coffee drinkers, we herein show that coffee consumption decreased connectivity of the posterior default mode network (DMN) and between the somatosensory/motor networks and the prefrontal cortex, while the connectivity in nodes of the higher visual and the right executive control network (RECN) is increased after drinking coffee; data also show that caffeine intake only replicated the impact of coffee on the posterior DMN, thus disentangling the neurochemical effects of caffeine from the experience of having a coffee.
There is a common expectation, namely among habitual coffee drinkers, that coffee increases alertness and psychomotor functioning. For these reasons, many individuals keep drinking coffee to counteract fatigue, stay alert, increase cognitive performance, and increase work efficiency (Smith, 2002). Coffee beverages are constituted of numerous compounds known to affect human behavior, among which are caffeine and chlorogenic acids (Sadiq Butt et al., 2011). From the neurobiological perspective, both caffeine and chlorogenic acids have well-documented psychoactive actions, whereas caffeine is mostly an antagonist of the main adenosine receptors in the brain—A1 and A2A receptors, leading to the disinhibition of excitatory neurotransmitter release and enhancement of dopamine transmission via D2 receptors (Fredholm et al., 2005) to sharpen brain metabolism and bolster memory performance (Paiva et al.
Repetitive reaching tasks in mature female rats triggered persistent pain-like and sickness behaviors linked to a surge in IL-6-driven inflammation throughout muscles, blood, and the brain. These findings reveal how overuse injuries provoke both physical and mood-related symptoms through a neuroimmune cascade.
Brian Kennedy is a renowned biologist, leader in aging research, & director of the Center for Healthy Longevity at the National University of Singapore. In this episode, Brian shares insights from ongoing human aging studies, including clinical trials of rapamycin & how dosing strategies, timing, & exercise may influence outcomes. He presents two key models of aging—one as a linear accumulation of biological decline & the other as an exponential rise in mortality risk—& explains why traditional models of aging fall short. He also explains why most current aging biomarkers lack clinical utility & describes how his team is working to develop a more actionable biological clock. Additional topics include the potential of compounds like alpha-ketoglutarate, urolithin A, & NAD boosters, along with how lifestyle interventions—such as VO2 max training, strength building, & the use of GLP-1 & SGLT2 drugs—may contribute to longer, healthier lives.
View show notes here: https://bit.ly/44ShpRB
Become a member to receive exclusive content: https://peterattiamd.com/subscribe/
Sign up to receive Peter’s email newsletter: https://peterattiamd.com/newsletter/
0:00:00-Intro.
0:01:15-Brian’s journey from the Buck Institute to Singapore, & the global evolution of aging research.
0:09:12-Rethinking the biology of aging.
0:14:13-How inflammation & mTOR signaling may play a central, causal role in aging.
0:18:00-Biological role of mTOR in aging, & the potential of rapamycin to slow aging & enhance immune resilience.
0:23:32-Aging as a linear decline in resilience overlaid with non-linear health fluctuations.
0:36:03-Speculating on the future of longevity: slowing biological aging through noise reduction & reprogramming.
0:42:18-The role of the epigenome in aging, & the limits of methylation clocks.
0:47:14-Balancing the quest for immortality with the urgent need to improve late-life healthspan.
0:52:16-Comparing the big 4 chronic diseases: which are the most inevitable & modifiable?
0:57:27-Exploring potential benefits of rapamycin: how Brian is testing this & other interventions in humans.
1:09:14-Testing alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) for healthspan benefits in aging [1:01:45];
1:13:41-Exploring urolithin A’s potential to enhance mitochondrial health, reduce frailty, & slow aging.
1:17:35-Potential of sublingual NAD for longevity.
1:26:50-Other interventions that may promote longevity: spermidine, 17 HRT, & more.
1:34:33-Biological aging clocks, clinical biomarkers, & a new path to proactive longevity care.
1:45:01-Evaluating rapamycin, metformin, & GLP-1s for longevity in healthy individuals.
1:51:19-Why muscle, strength, & fitness are the strongest predictors of healthspan.
1:53:37-Why combining too many longevity interventions may backfire.
1:56:06-How AI integration could accelerate breakthroughs in aging research.
2:02:07-Need to balance innovation with safety in longevity clinics.
2:10:50-Peter’s reflections on emerging interventions & the promise of combining proven aging compounds.
——-
About:
The Peter Attia Drive is a deep-dive podcast focusing on maximizing longevity, & all that goes into that from physical to cognitive to emotional health. With over 90 million episodes downloaded, it features topics including exercise, nutritional biochemistry, cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, mental health, & much more.
Peter Attia is the founder of Early Medical, a medical practice that applies the principles of Medicine 3.0 to patients with the goal of lengthening their lifespan & simultaneously improving their healthspan.
A surprising new study has uncovered over 200 misfolded proteins in the brains of aging rats with cognitive decline, beyond the infamous amyloid and tau plaques long blamed for Alzheimer’s. These shape-shifting proteins don’t clump into visible plaques, making them harder to detect but potentially just as harmful. Scientists believe these “stealth” molecules could evade the brain’s cleanup systems and quietly impair memory and brain function. The discovery opens a new frontier in understanding dementia and could lead to entirely new targets for treatment and prevention.
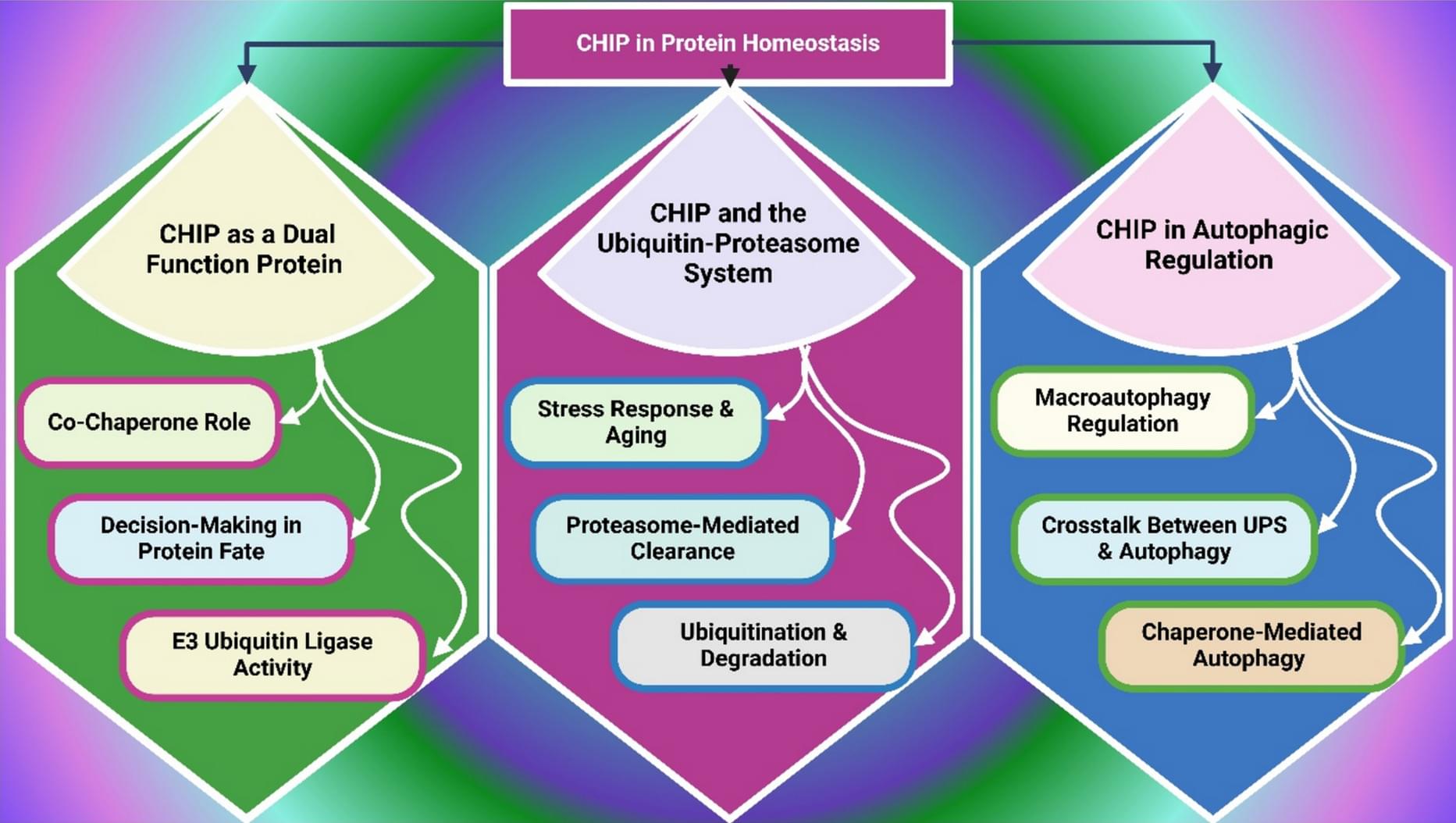
Degradation of proteostasis, mitochondrial function, and cellular stress resistance results in a build-up of damaged proteins, oxidative insult, and chronic inflammation, characteristic of aging. CHIP is essential for maintaining protein quality control and cellular homeostasis by having dual E3 ubiquitin ligase and co-chaperone activities. CHIP facilitates proteostasis by maintaining proteostasis in misfolded, aggregated proteins by promoting their degradation. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative imbalance, and cellular senescence are caused by its age-associated decline and contribute to neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, and oncogenic disease pathogenesis. Examples of recent pharmacological and gene-based strategies to correct CHIP and restore stress resilience have been made.
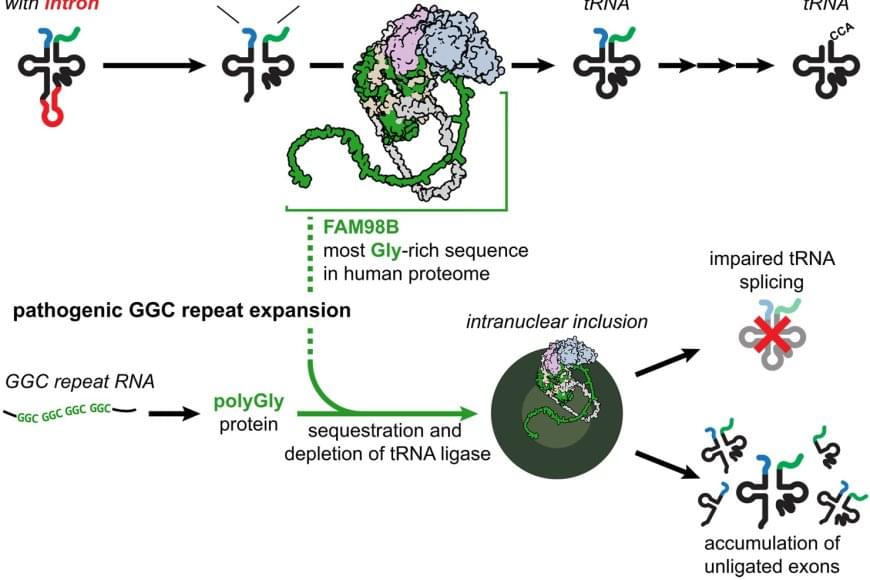
Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, are devastating and incurable diseases. Although many neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by abnormal protein aggregation in the brain, a limited understanding of whether and how aggregated proteins cause brain cell dysfunction and death represents a major barrier to developing effective treatments.
Inspired by similar approaches in cardiovascular disease and cancer, the researchers focused on rare genetic forms of neurodegeneration as a powerful way to uncover fundamental mechanisms tying protein aggregation to brain disease. Thier work unexpectedly linked protein aggregation in genetic forms of neurodegeneration to disrupted processing of transfer RNAs (tRNAs), revealing an important mechanism that might be therapeutically targeted in these disorders.
The authors were interested in genetic forms of neurodegeneration caused by GGC trinucleotide repeat expansions (DNA sequence mutations caused by copying this 3-letter sequence too many times in a row). These mutations produce aggregation-prone proteins with long stretches of a single repeated amino acid (glycine).
Bedrock co-founder Geoff Lewis has posted increasingly troubling content on social media, drawing concern from friends in the industry.