New research shows that when people listen to speech at different speeds, the auditory cortex does not adjust its timing but instead processes sound in a fixed time window.


The brain is famously plastic: Neurons’ ability to change their behavior in response to new stimuli is what makes learning possible. And even neurons’ response to the same stimuli changes over time—a phenomenon known as representational drift. Yet our day-to-day perception of the world is relatively stable. How so?
Resolving such puzzles matters for future brain-computer interfaces, sensory prostheses and therapies for neurological disease. On a quest for an answer, Rice University scientists have built ultraflexible probes thousands of times thinner than a human hair and used them to track neurons in the visual cortex of mice for 15 consecutive days as the animals viewed thousands of images—from line patterns to pictures of the natural world.
The devices, called nanoelectronic threads (NETs), embed seamlessly with brain tissue, allowing for high-fidelity chronic recordings of brain activity.

Spintronics devices will be key to realizing faster and more energy-efficient computers. To give us a better understanding of how to make them, a Kobe University team now showed how different manufacturing techniques influence the material properties of a key component.
Electronic devices could be made more efficient and faster if electrons could carry more information at once. This is the basic idea behind spintronics, where researchers try to use the electrons’ spin in addition to charge in data storage, processing and sensor devices to significantly improve our computers.
One component for such devices is the “magnetic tunnel junction,” which may be used, for example, for neuron-like behavior in information processing or in a new type of fast and non-volatile memory. They consist of two ferromagnets, usually a nickel-iron alloy, sandwiching a thin insulating layer such as graphene.
Depression, anxiety, PTSD and other maladies of the mind are plaguing our societies. Our medicines are now decades old, and their effectiveness is questionable. Around half of those taking antidepressants experience no benefits. Side effects are common, and relapse rates when stopping the pills can reach 80%.
If someone told you we have a remedy with nearly no relapse, no long term side effects, and life-altering potential, wouldn’t you be curious?
Enter Dr. Ayla Selamoglu (Newnham 2016). As a Trinity postdoc endorsed by biotechnologist Prof. Christopher Lowe OBE, her research centres on psychedelic medicine and drug development.
Psychedelic medicine has the potential to revolutionise psychiatry. And the revolution is starting here.
Dr. Ayla Selamoglu is an expert on psychedelic medicine. Her work shows how nature’s most mysterious compounds provide new ways to combat mental illness.
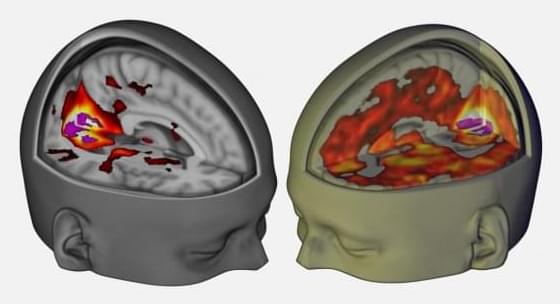
Researchers have identified a neurochemical signature that sets Parkinson’s disease apart from essential tremor — two of the most common movement disorders, but each linked to distinct changes in the brain.
In a new study in Nature Communications, scientists identified unique chemical signaling patterns of two key neurotransmitters — dopamine and serotonin — that distinguish these two disorders.
“This study builds on decades of work,” said a co-senior author, who with colleagues developed the multi-faceted technologies and the theoretical constructs for the work over their 15 years at the research institute.
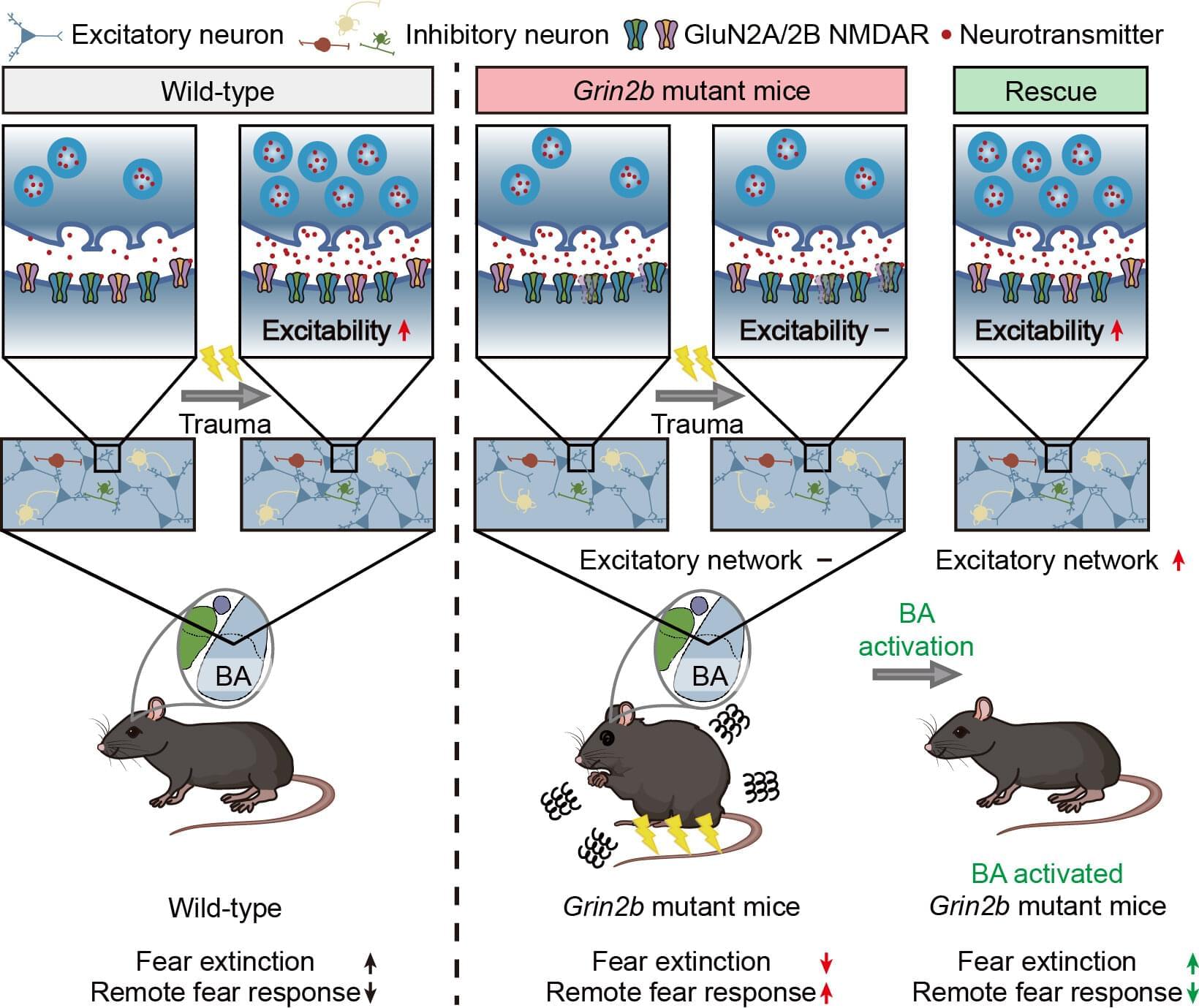
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is widely known for its core features, which include difficulties in social communication and repetitive behaviors. But beyond these, many individuals with ASD also struggle with comorbid conditions, particularly anxiety.
Nearly 40% of children with ASD experience anxiety disorders and often show unusually heightened fear responses. Studies have even suggested that people with ASD may be more vulnerable to trauma, unable to “erase” fear memories, which resembles symptoms seen in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Until now, most evidence for PTSD-like symptoms in ASD has relied on self-reports, leaving the underlying brain mechanisms unclear.

A low-dose long-term administration of cannabis can not only reverse aging processes in the brain, but also has an anti-aging effect. Researchers from the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) and the University of Bonn together with a team from Hebrew University (Israel) have now been able to show this in mice. They found the key to this in the protein switch mTOR, whose signal strength has an influence on cognitive performance and metabolic processes in the entire organism. The results are now presented in the journal “ACS Pharmacology & Translation Science”
Some of these cookies are necessary and are used to help make our site work. With your consent, we will also use cookies to improve your experience, analyse site usage and assist in our marketing efforts. By clicking ‘Accept all’, you consent to our use of cookies.