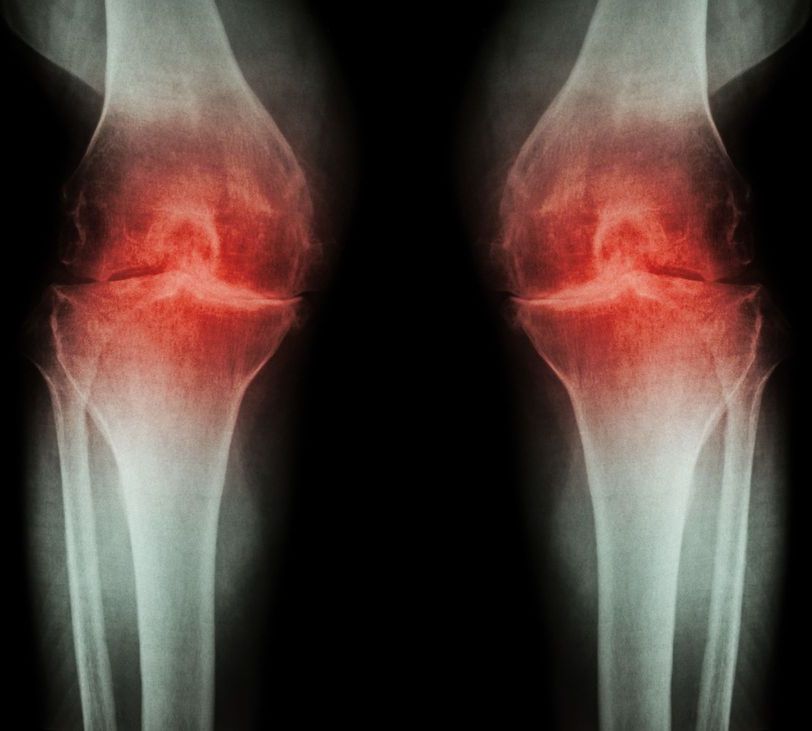
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common ailments of an aging population, but there aren’t many treatment options besides taking pain killers or getting a full joint replacement. Now, researchers at the Salk Institute have found that a combination of two experimental drugs appears to reverse the symptoms of the disorder, with successful tests conducted in rats and in human cells in the lab.
As we age, our bodies gradually lose the ability to repair damage as fast as it needs to. That means that tissues subjected to high-intensity long-term use, such as cartilage in joints, are especially prone to wearing out. That manifests itself in the common condition of osteoarthritis, resulting in pain when that joint moves.
In the past, two molecules have been identified as having decent potential for treating the disease – alpha-KLOTHO (αKLOTHO) and TGF beta receptor 2 (TGFβR2). Previous tests only showed moderate success, so the researchers on the new study decided to see if they fared any better when used together.