Just as Silicon Valley emerged from Cold War R&D, semiconductors, and startup culture, the next global innovation epicenter will be built around the longevity economy.



Donate to the Rejuvenation Science Institute:https://www.rejuvenescimento.org/donationIn this video, Nina Torres Zanvettor, vice-president of the Rejuvenatio…

A new study led by University of California, Irvine’s Center for the Neurobiology of Learning and Memory researchers found that aging changes the brain’s overall shape in measurable ways. Instead of focusing only on the size of specific regions, the team used a new analytic method to see how the brain’s form shifts and distorts over time.
The analysis revealed substantial alterations in brain shape, which were closely associated with declines in memory, reasoning and other cognitive functions. This suggests that the shape of the brain can serve as a reliable indicator of its overall health. The study appears in Nature Communications.
“Most studies of brain aging focus on how much tissue is lost in different regions,” said Niels Janssen, Ph.D., senior author and professor at Universidad de La Laguna in Spain and visiting faculty at the CNLM. “What we found is that the overall shape of the brain shifts in systematic ways, and those shifts are closely tied to whether someone shows cognitive impairment.”

There’s no escaping the unrelenting passage of time, but supercentenarians who live to see their 110th birthday have a peculiar ability to postpone the inevitable.
A thorough health evaluation of one of the world’s oldest people, Maria Branyas, suggests that one of the reasons she lived to 117 was that she possessed an exceptionally young genome.
Some of her rare genetic variants are linked to longevity, immune function, and a healthy heart and brain.
In this Cryosphere Chat we discuss the organ preservation to cryonics pipeline, our experiences trying to convince normies to sign up, using terms like hibernation or cryosleep instead of death, and more.
Links:
• Cryosphere Discord server: / discord.
• Cryonics subreddit: / cryonics.

The future of pacemaker technologies — wade demmer — VP, R&D, medtronic.
Wade Demmer is Vice President of Research & Development at Medtronic where he is responsible for the development of new generations of pacemakers (https://www.medtronic.com/en-us/l/patients/treatments-therap…ers.html). With extensive expertise in medical technology and innovation, he leads the company’s R&D efforts to develop cutting-edge healthcare solutions and is dedicated to advancing medical advancements that improve patient outcomes and transform healthcare delivery.
Wade began his career at Intel, where he gained valuable experience in technology development and engineering. Building on his technical expertise, he transitioned into the medical device industry, bringing a strong innovation-driven mindset to healthcare solutions.
Wade is best known for his pioneering work on pacemakers, where he contributed to the design and development of advanced cardiac pacing technologies. His innovative approaches have helped improve the reliability, longevity, and patient comfort of pacemaker devices, significantly impacting the field of cardiac care.
Wade received his Bachelor of Engineering (BEng), with a focus on Computer Engineering, from Iowa State University, and his MBA from University of Minnesota Carlson School of Management.
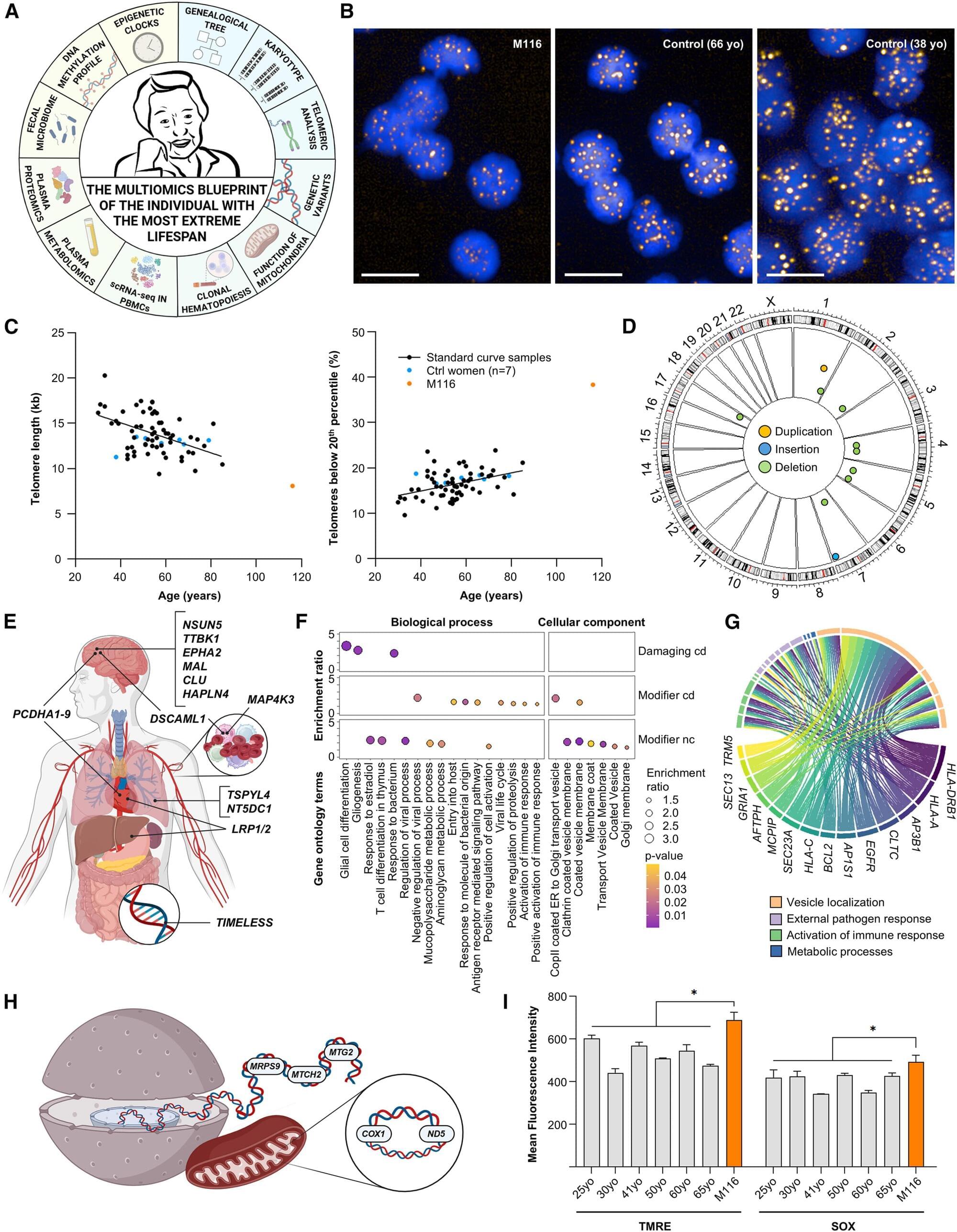
What is the secret of supercentenarians? While there is no magical “elixir of life” that allows us to live forever, this incredibly rare group of people who live to be 110 years or older appears to have some biological advantage. To identify the factors that underlie extreme longevity, scientists conducted a comprehensive study of Maria Branyas, who was the world’s oldest verified living person at the time of the study.