A study counts blood cells and footsteps to predict a hard limit to our longevity.



Senior director, milken institute center for the future of aging, milken institute; executive director, alliance to improve dementia care.
Nora Super is the Senior Director of the Milken Institute Center for the Future of Aging (CFA) (https://milkeninstitute.org/centers/center-for-the-future-of-aging) and the Executive Director of the Milken Institute Alliance to Improve Dementia Care (https://milkeninstitute.org/centers/center-for-the-future-of…tia-care).
Mr. Super provides strategic direction for the two primary focus areas of CFA: Financial Wellness and Healthy Longevity, and oversees data-driven research, meaningful policy initiatives, and impactful convenings around the world.
Launched in 2020, the Alliance to Improve Dementia Care seeks to transform and improve the complex health and long-term care systems that people at risk for and living with dementia must navigate.
Ms. Super studied political science at Tulane University and completed her master’s degree in public administration, with a concentration in health policy, at George Washington University, and is a respected thought leader, frequent speaker, and prolific writer on healthy longevity and the economic and social impact of global population aging. In 2019, she authored two major reports: “Reducing the Cost and Risk of Dementia: Recommendations to Improve Brain Health and Decrease Disparities” and “Age-Forward Cities for 2030.”

Circa 2010
Medical researchers use laboratory-grown human cells to learn the intricacies of how cells work and test theories about the causes and treatment of diseases. The cell lines they need are “immortal”—they can grow indefinitely, be frozen for decades, divided into different batches and shared among scientists. In 1951, a scientist at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland, created the first immortal human cell line with a tissue sample taken from a young black woman with cervical cancer. Those cells, called HeLa cells, quickly became invaluable to medical research—though their donor remained a mystery for decades. In her new book, The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks, journalist Rebecca Skloot tracks down the story of the source of the amazing HeLa cells, Henrietta Lacks, and documents the cell line’s impact on both modern medicine and the Lacks family.
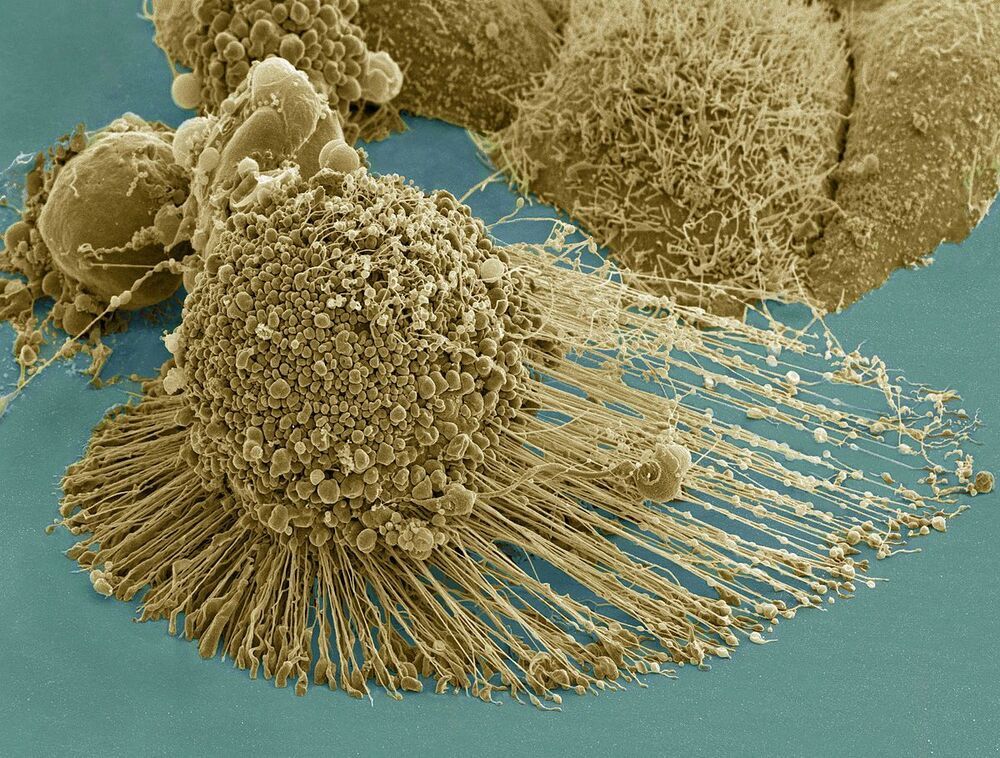
HeLa (/ ˈ h iː l ɑː / ; also Hela or hela) is an immortal cell line used in scientific research. It is the oldest and most commonly used human cell line.[1] The line is named after and derived from cervical cancer cells taken on February 8, 1951,[2] from Henrietta Lacks, a 31-year-old African-American mother of five, who died of cancer on October 4, 1951.[3] The cell line was found to be remarkably durable and prolific, which allows it to be used extensively in scientific study.[4][5]
Scanning electron micrograph of an apoptotic HeLa cell. Zeiss Merlin HR-SEM.

Some might like.
The research team of Gero, a Singapore-based biotech company in collaboration with Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo NY, has presented a study in Nature Communications on associations between aging and the loss of the ability to recover from stresses.
Recently, scientists have reported the first promising examples of biological age reversal by experimental interventions. Indeed, many biological clock types properly predict more years of life for those who choose healthy lifestyles or quit unhealthy ones, such as smoking. Still unknown is how quickly biological age is changing over time for the same individual, and distinguishing between the transient fluctuations and the genuine bioage change trend.
The emergence of big biomedical data involving multiple measurements from the same subjects brings about a whole range of novel opportunities and practical tools to understand and quantify the aging process in humans. A team of experts in biology and biophysics presented results of a detailed analysis of dynamic properties of the fluctuations of physiological indices along individual aging trajectories.

Might interest some.
A new study from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London has established that Intermittent Fasting (IF) is an effective means of improving long term memory retention and generating new adult hippocampal neurons in mice, in what the researchers hope has the potential to slow the advance of cognitive decline in older people.
The study, published today in Molecular Biology, found that a calorie restricted diet via every other day fasting was an effective means of promoting Klotho gene expression in mice. Klotho, which is often referred to as the “longevity gene” has now been shown in this study to play a central role in the production of hippocampal adult-born new neurons or neurogenesis.
Adult-born hippocampal neurons are important for memory formation and their production declines with age, explaining in part cognitive decline in older people.

Is this the reason why the general public view the emerging field of regenerative medicine with such scepticism? Has a combined cultural history of being bombarded with empty promises of longevity made us numb to such a prospect? Possibly, although I believe it might go deeper than old fashioned scepticism. After all, our species is hardly a stranger to believing something if we desire for it to be true, regardless of how much evidence is presented to us.
Maybe we are simply experiencing just another example of humans finding dramatic change to our way of life hard to comprehend and accept. After all, practically every major change in our recent history was largely believed to be an impossibility by the general public, right up until the point that it became the norm. Everything from the aeroplane to the internet was seen as science fiction, but yet today they are integral parts of our lives. Now, this is not to say that everything the general public is sceptical of will inevitably turn out to prove them wrong, but lessons from our history do show that when it comes to scientific progress, the public will not believe it until they can see it.
Some would believe that scepticism towards regenerative medicine strikes at something much deeper in our psych, as it threatened to fundamentally change our entire outlook on the world. For our entire lives, we have been taught by our interactions with others exactly how life is supposed to progress. You are supposed to suffer a gradual decay of mental and physical abilities, until eventually you die. That is just how it is, and if that were to ever change then we would all have to change how we think about the world. The concept of a 125 year old with the appearance of a 25 year old seems bizarre to us right now, and to many the idea of ever lasting health just goes against their fundamental beliefs of how the world functions to such an extent that they cannot comprehend anything different. Some would even go far as to defend the ageing process as being an integral part of life, displaying what can only be described as ‘Stockholm syndrome with extra steps’.
