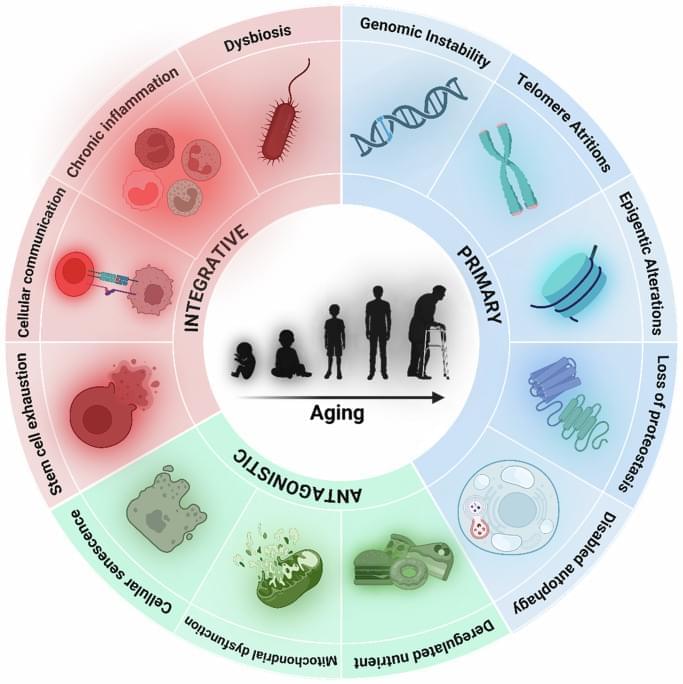
Experimental models such as heterochronic parabiosis and heterochronic plasma transfer have profoundly advanced our understanding of systemic aging, demonstrating that circulating factors can influence brain, vascular, and immune aging through cell nonautonomous mechanisms. These preclinical models have revealed that both pro-geronic and anti-geronic signals in blood can modulate neuroinflammation, neurovascular health, and cognitive resilience. However, despite their experimental promise, the clinical translation of these findings, particularly through plasma-based interventions in humans, remains fraught with uncertainty.