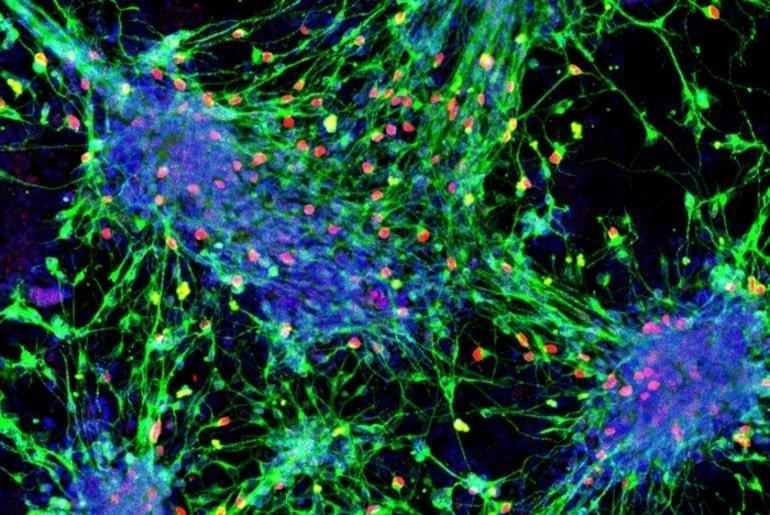
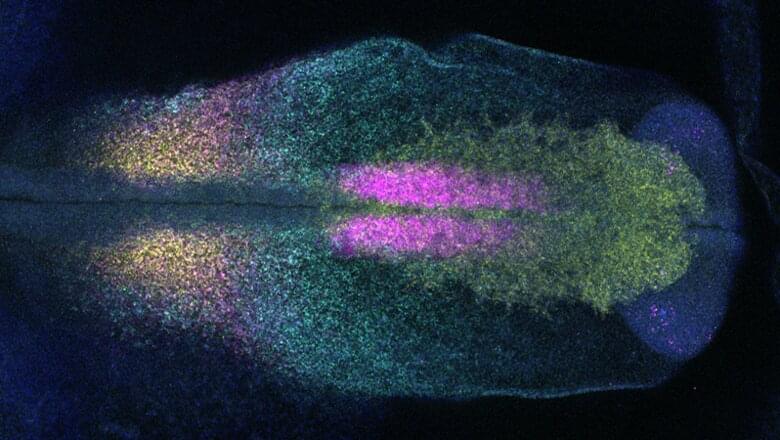
Summary: Researchers have created a new blueprint that outlines how embryonic stem cells from mice become sensory interneurons and identified a method for producing sensory interneurons in a lab setting. If the results can be replicated in human stem cells, researchers say the findings could contribute to the development of therapies to restore sensation to those suffering nerve damage and spinal cord injury.
Source: UCLA
Researchers at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have developed a first-of-its-kind roadmap detailing how stem cells become sensory interneurons — the cells that enable sensations like touch, pain and itch.