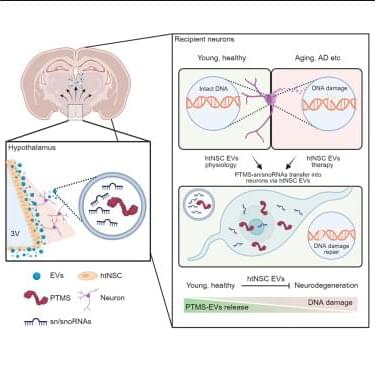
Can humans live for thousands of years? New DNA and longevity research suggests that aging may not be fixed—it may simply be the result of imperfect cellular repair. In this video, we explore how DNA damage, genetic repair mechanisms, and modern longevity science are reshaping our understanding of human lifespan.
This content is based on current research from USA and Europe, focusing on emerging breakthroughs in genetics, DNA repair therapies, and anti-aging science.
If you’re interested in health, biology, or the future of human longevity, this video is for you.
Disclaimer:
This video is for educational purposes only, is not intended to diagnose, treat, or cure any condition, and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for guidance related to your health.
#LongevityScience.
#DNARepair.
#AntiAging.
#GeneticsResearch.
#HealthFacts.
#BioLogicHealth.
#ScienceExplained.
#HealthyAging