Maintaining good overall health is key to living a long life, but we may want to particularly focus on the state of our brain and immune system




Potential treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and other neurodegenerative diseases may already be out there in the form of drugs prescribed for other conditions. A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Stanford University and the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) are using artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) to try to find them.
Clinical trials for new drugs can take up to 5–7 years, so repurposing existing drugs is one of the best ways to deliver treatments quickly. AI/ML can make it even faster. By analyzing long-term electronic health records (EHRs) of patients with ALS, the team can identify drugs — or combinations of drugs — prescribed for other conditions that may influence the progression of the disease. The drugs’ “off-target” effects may not only affect patient survival but also provide insight into how neurodegenerative diseases work and inform better therapies.
“If you talk to any ALS caregiver, you will be moved because the disease has such a grim prognosis, so being able to do something is tremendously motivating,” said Priyadip Ray, a staff scientist in LLNL’s Computational Engineering Division (CED) who leads the effort.
Tesla’s launch of a robo-taxi network marks the beginning of a significant transportation disruption that will transform mobility, economy, geopolitics, and urban landscapes with the widespread adoption of electric autonomous vehicles ## ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Transportation Revolution.
🚗 Q: How will Tesla’s Robotaxi network impact transportation? A: Tesla’s Robotaxi network in Austin, Texas marks the ignition point for transportation disruption, with multiple companies competing to provide taxi rides without human drivers, potentially capturing 80–90% market share in 10–15 years.
🛢️ Q: What industries will be disrupted by autonomous electric vehicles? A: Autonomous electric vehicles will disrupt the oil and agriculture industries, as vehicles are the number one users of crude oil, and corn is the top agricultural product in the US, used to produce ethanol for gasoline.
🌆 Q: How will urban planning change with the rise of autonomous vehicles? A: Cities will repurpose parking spaces for retail, living areas, and solar panels, transforming urban planning and enabling new forms of transportation, including drones and aircraft.
Environmental Impact.
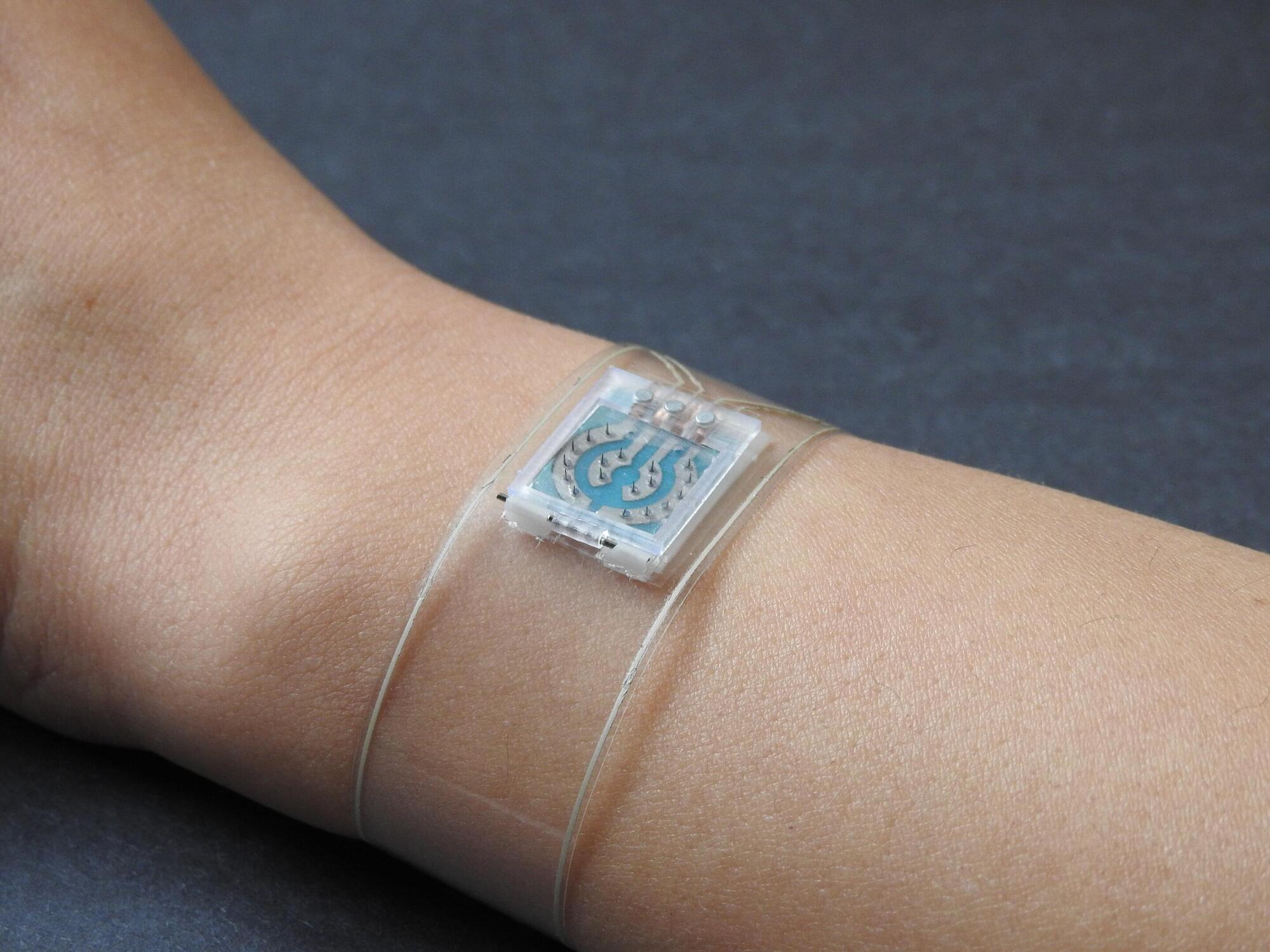
A new wearable wristband could significantly improve diabetes management by continuously tracking not only glucose but also other chemical and cardiovascular signals that influence disease progression and overall health. The technology was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
The flexible wristband consists of a microneedle array that painlessly samples interstitial fluid under the skin to measure glucose, lactate and alcohol in real time using three different enzymes embedded within the tiny needles. Designed for easy replacement, the microneedle array can be swapped out to tailor wear periods. This reduces the risk of allergic reactions or infection while supporting longer-term use.
Simultaneously, the wristband uses an ultrasonic sensor array to measure blood pressure and arterial stiffness, while ECG sensors measure heart rate directly from wrist pulses. These physiological signals are key indicators of cardiovascular risk, which is often elevated in people with diabetes but is rarely monitored continuously outside of a clinical setting.
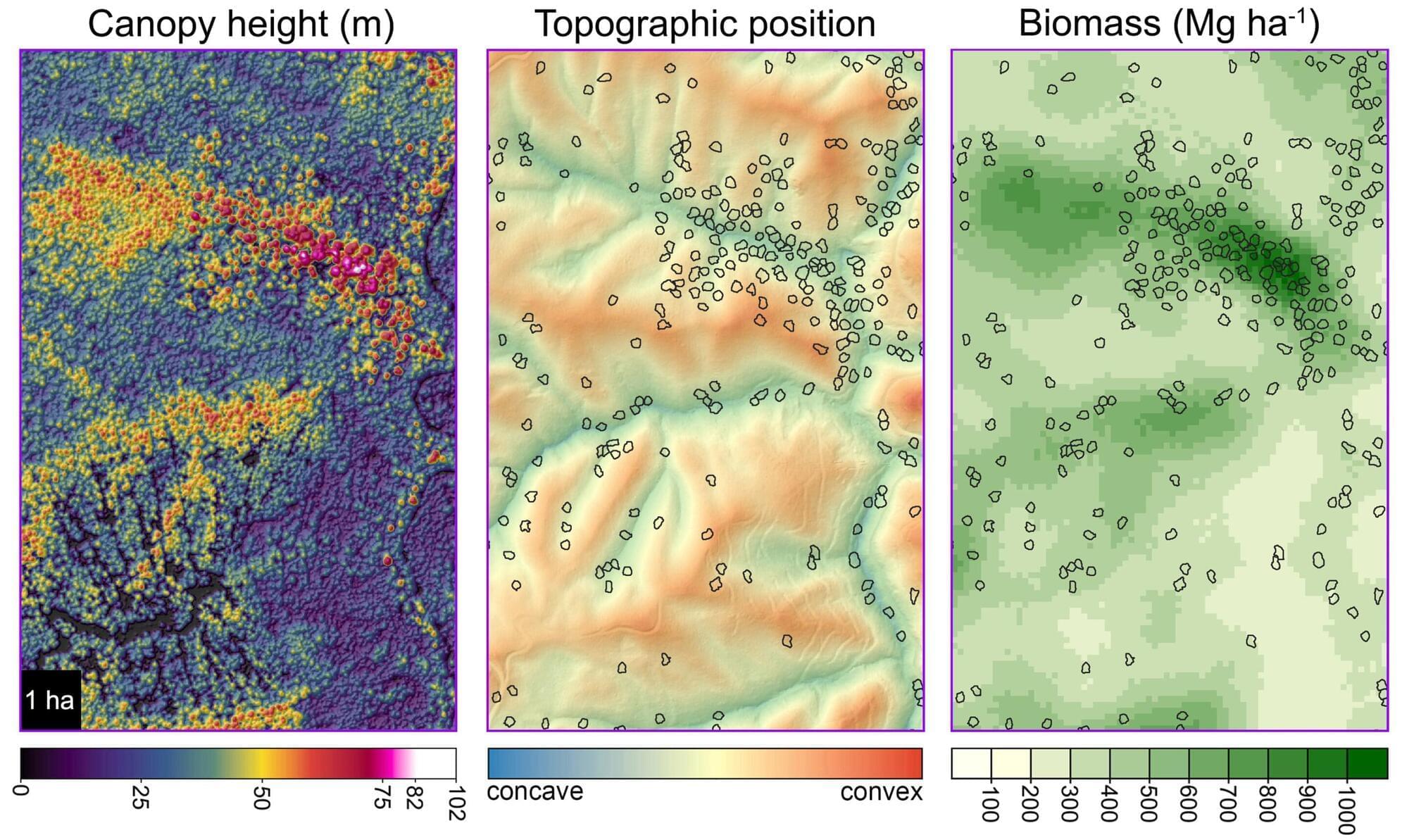
Even-aged forest management is geared towards timber production with ecosystem health as a lesser consideration. This creates a dichotomy where forests are treated either as plantations or reserves. Uneven-aged management can bring compromise to conflicting land uses by reducing ecosystem impacts while still allowing timber extraction. Whereas selection forestry focuses on which trees are taken, retention forestry focuses on protecting features that will remain after logging. These biological legacies provide ecosystem continuity.
Retained trees are often chosen based on their habitat value. Snags and living trees that are diseased, damaged, or dying provide cavities, decaying wood, and other microhabitats for a diversity of biota. Defects that make high-quality habitat trees tend to cause the collapse of large and old trees, so it’s important to designate healthy recruitment trees for the future. Retention forestry that focuses only on habitat trees may be inconsistent with the goals of long-term carbon storage and ecosystem resilience.
An article just published in Forest Ecology and Management explores the idea of “exceptional trees” and why we might consider choosing a subset of the most robust trees for permanent retention in managed forests. We present methods for precisely estimating aboveground biomass across the landscape and assess the contribution of exceptional trees to biomass and productivity. Our study focuses on Sequoia sempervirens (redwood) in California’s Demonstration State Forests.
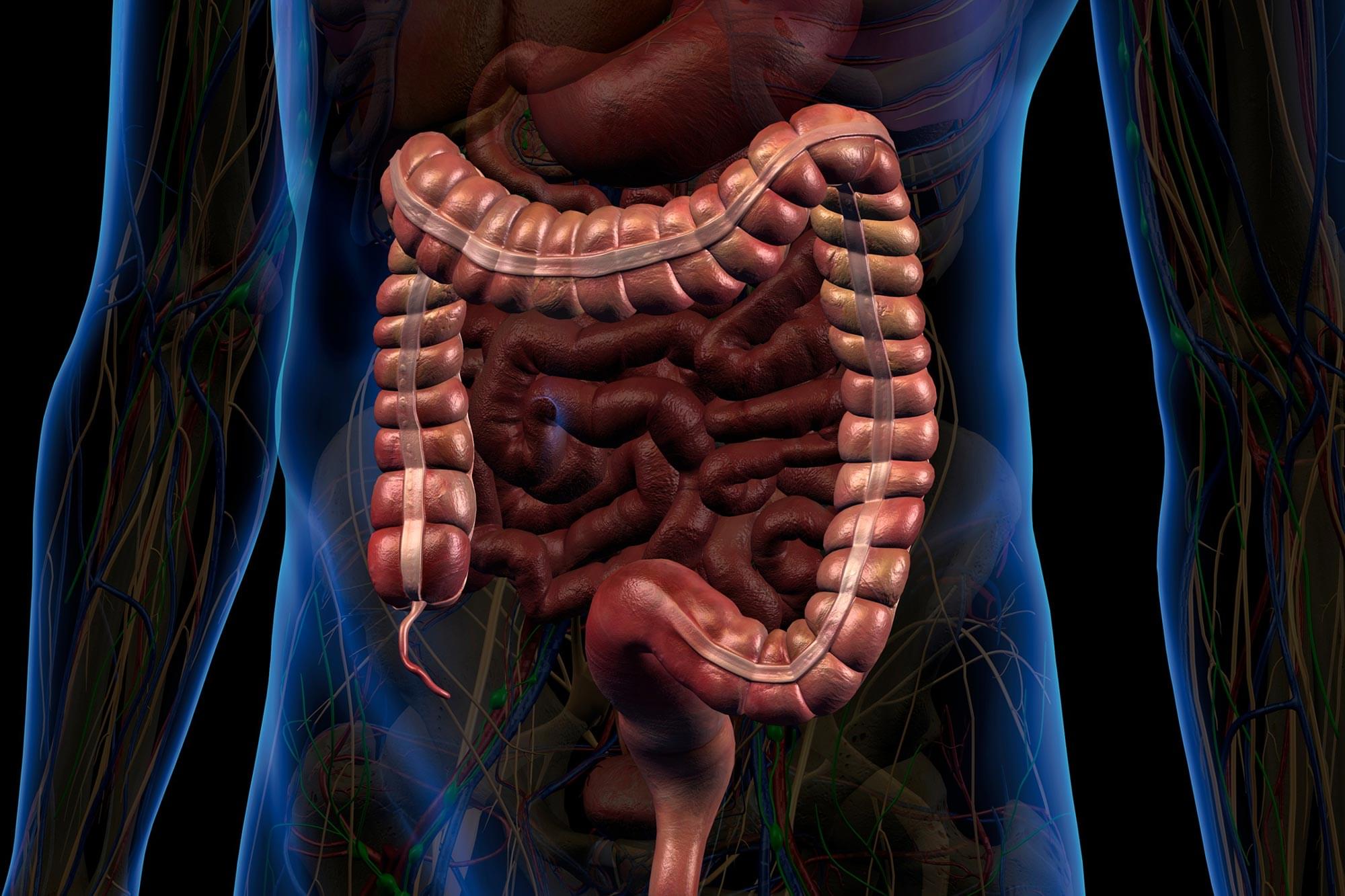
Researchers are gaining a deeper appreciation for the critical role the gastrointestinal (GI) tract plays in maintaining overall health. Beyond its primary responsibilities in digestion, the GI system contributes to the production of hormones, immune cells, and neurotransmitters that influence brain function and emotional well-being.
Because of this, the GI tract contains a wide array of biomarkers that are valuable for diagnosing, tracking, and managing disease—from short-chain fatty acids associated with metabolic syndrome to cytokines linked to inflammation.
However, current technologies fall short when it comes to capturing this biochemical information directly from the GI tract. Existing methods, such as fecal sampling and tissue biopsies, are often invasive, costly, and unable to deliver continuous or comprehensive real-time data throughout the length of the digestive system.

Deep within the arid and rugged terrains of Rajasthan roams a remarkable creature—the camel, often referred to as the “ship of the desert.” Known for their endurance, unique gait, and ability to survive extreme conditions, camels have long fascinated both scientists and locals alike.
Over time, they’ve been subjects of various studies that revealed surprising abilities, from surviving on sparse resources to even consuming snakes as part of traditional practices. Scientists are now exploring camel tears for rare enzymes and medicinal compounds that could revolutionise treatments for infections, inflammation, and eye diseases. But now, a new claim places camel tears in the spotlight for their potential medical value.
According to a study reportedly conducted by the Central Veterinary Research Laboratory in Dubai, camel tears may have the extraordinary ability to neutralise venom from up to 26 snake species. If validated, this could mark a significant turning point in snakebite treatment, especially in countries like India, where venomous snakebites are a major public health challenge. Though the findings have yet to be peer-reviewed or widely published, the potential has generated global attention for its revolutionary implications in antivenom research.
Camel tears may neutralise venom from 26 snake species. A Dubai lab study suggests this. It could help snakebite treatment, especially in India. Camel tears have bioactive compounds. These may neutralise snake venom toxins. This could lead to affordable snakebite drugs. Camel tears also fight desert infections. They contain proteins and lysozyme. This discovery may help toxicology and medicine.
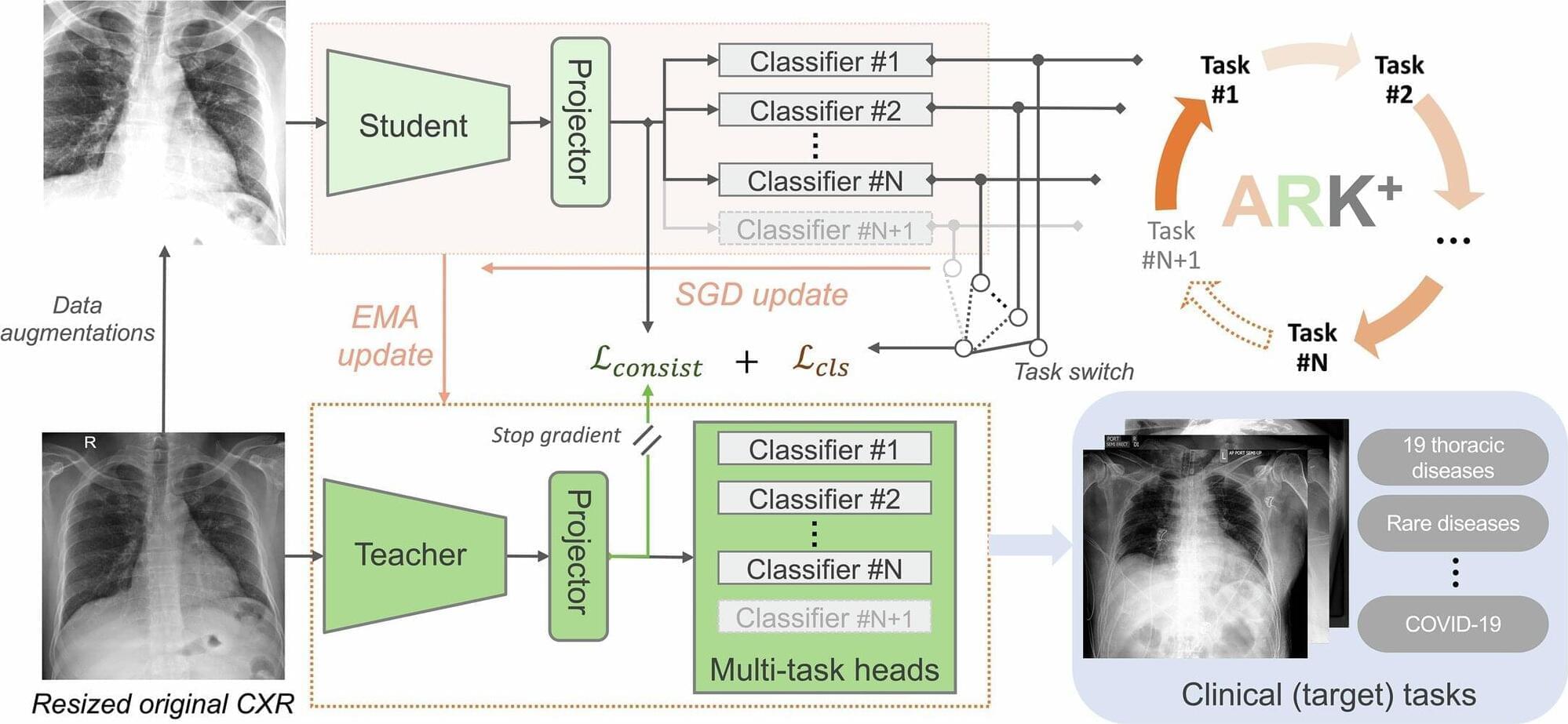
Can artificial intelligence (AI) potentially transform health care for the better?
Now, rising to the challenge, an Arizona State University team of researchers has built a powerful new AI tool, called Ark+, to help doctors read chest X‑rays better and improve health care outcomes.
“Ark+ is designed to be an open, reliable and ultimately useful tool in real‑world health care systems,” said Jianming “Jimmy” Liang, an ASU professor from the College of Health Solutions, and lead author of the study recently published in Nature.
Quantum Computing Innovation In Pharma — Dr. Thomas Ehmer, Ph.D. — Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Dr. Thomas Ehmer, Ph.D. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/tehmer/) is a seasoned technology strategist with over two decades of experience in IT innovation, business development, and R&D within the pharmaceutical industry, and co-founder of the Quantum Interest Group, at Merck KGaA Darmstadt, Germany (https://www.emdgroup.com/en).
Dr. Ehmer currently is in the Sector Data Office — AI Governance and Innovation Incubator at Merck KGaA Darmstadt, Germany, where he scouts emerging and disruptive technologies, demonstrating their potential value for R&D applications, with a focus on quantum technologies.
Throughout his career at Merck KGaA Darmstadt, Germany, Dr. Ehmer has played a pivotal role in shaping IT strategy, business process optimization, and digital transformation across the entire pharmaceutical value chain, currently focusing on transparent AI and how and where emerging technology can help patients live a better life. His expertise spans technology scouting, business analysis, and IT program leadership, having successfully driven major global projects.
Beyond his corporate career, Dr. Ehmer is an active private seed investor and has contributed to quantum computing research and applications in drug discovery, authoring publications on the potential of quantum computing and machine learning in pharmaceutical R&D (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9783527840748.ch26).