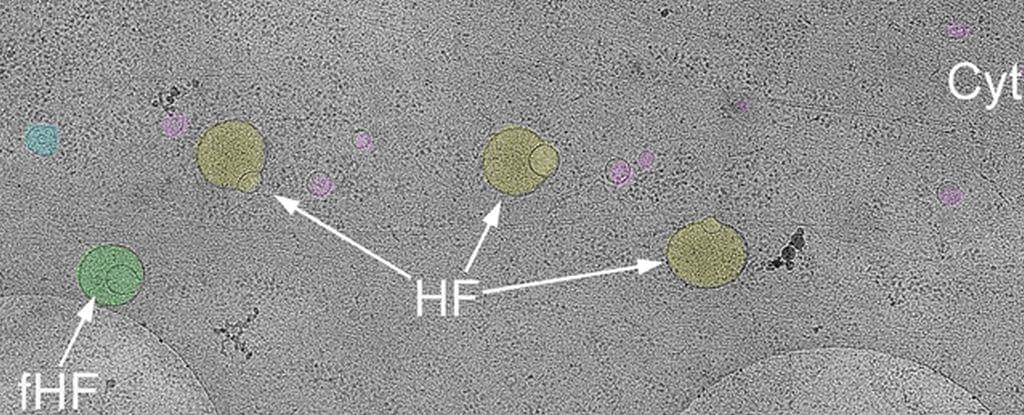
After centuries of mapping the human body in ever-finer detail, scientists are still making discoveries. Here we are, in 2025, and a previously unknown cellular structure that could be vital to our health has just been added to the anatomy books.
The membrane-bound organelle appears to play a huge role in helping cells sort, discard, and recycle their contents. It’s called a hemifusome, and a team of scientists says it could shed new light on disease.
“This is like discovering a new recycling center inside the cell,” said biophysicist Seham Ebrahim of the University of Virginia. “We think the hemifusome helps manage how cells package and process material, and when this goes wrong, it may contribute to diseases that affect many systems in the body.”