We’ve turned a social construct into a health problem.


The drugs, sutezolid and delpazolid, have demonstrated strong antimicrobial activity and a notably better safety profile compared to linezolid, with the potential to replace this current cornerstone in the treatment of drug-resistant TB.
The findings were published in two articles in The Lancet Infectious Diseases. Research partners in Europe included Radboud University Medical Center in the Netherlands and the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Munich, the Fraunhofer Institute for Translational Medicine and Pharmacology ITMP, the Center for International Health at LMU University Hospital and Helmholtz Munich.

New research suggests that medical AI chatbots are woefully unreliable at understanding how people actually communicate their health problems.
As detailed in yet-to-be-peer-reviewed study presented last month by MIT researchers, an AI chatbot is more likely to advise a patient not to seek medical care if their messages contained typos. The errors AI is susceptible to can be as seemingly inconsequential as an extra space between words, or if the patient used slang or colorful language. And strikingly, women are disproportionately affected by this, being wrongly told not to see a doctor at a higher rate than men.
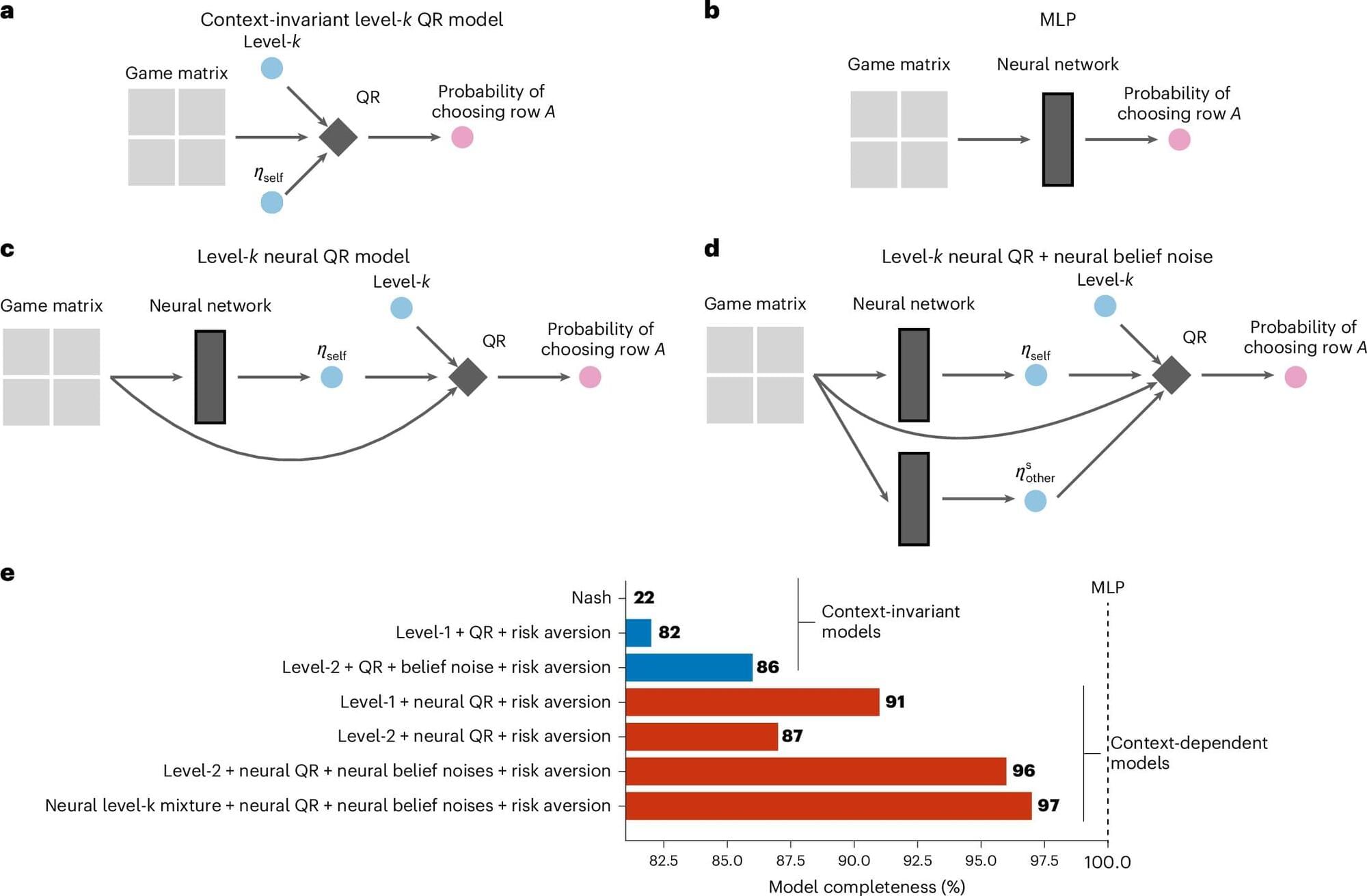
Throughout their everyday lives, humans are typically required to make a wide range of decisions, which can impact their well-being, health, social connections, and finances. Understanding the human decision-making processes is a key objective of many behavioral science studies, as this could in turn help to devise interventions aimed at encouraging people to make better choices.
Researchers at Princeton University, Boston University and other institutes used machine learning to predict the strategic decisions of humans in various games. Their paper, published in Nature Human Behavior, shows that a deep neural network trained on human decisions could predict the strategic choices of players with high levels of accuracy.
“Our main motivation is to use modern computational tools to uncover the cognitive mechanisms that drive how people behave in strategic situations,” Jian-Qiao Zhu, first author of the paper, told Phys.org.


A new large-scale study spotlights postoperative delirium as a preventable and high-impact complication which is driven by patient frailty and surgical stress—and one that can be addressed through low-cost, evidence-based interventions.
The findings, which appear in JAMA Network Open, provide a call to action for clinicians, health systems, patients, and families to prioritize brain health throughout perioperative care.
“Postoperative delirium isn’t a minor complication—it’s analogous to acute brain failure, a medical emergency that should be recognized and addressed,” said Laurent Glance, MD, a professor of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) and senior author of the study.

Basel, July 8, 2025 – Novartis today announced Coartem® (artemether-lumefantrine) Baby has been approved by Swissmedic as the first malaria medicine for newborns and young infants. The new treatment, also known as Riamet® Baby in some countries, was developed in collaboration with Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) to treat the potentially deadly mosquito-borne disease.
Eight African countries also participated in the assessment and are now expected to issue rapid approvals under the Swiss agency’s Marketing Authorization for Global Health Products procedure.1 Novartis plans to introduce the infant-friendly treatment on a largely not-for-profit basis to increase access in areas where malaria is endemic.
“For more than three decades, we have stayed the course in the fight against malaria, working relentlessly to deliver scientific breakthroughs where they are needed most,” said Vas Narasimhan, CEO of Novartis. “Together with our partners, we are proud to have gone further to develop the first clinically proven malaria treatment for newborns and young babies, ensuring even the smallest and most vulnerable can finally receive the care they deserve.”