
Category: genetics – Page 559



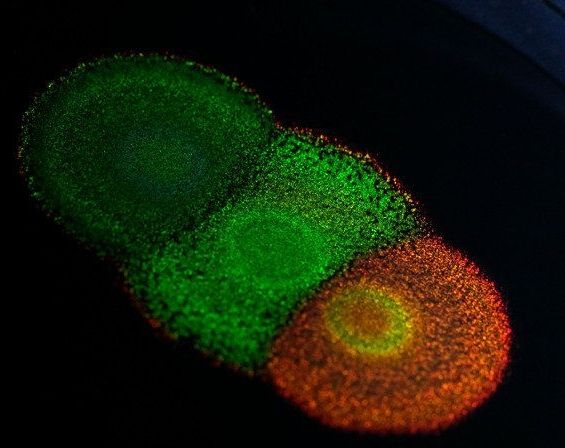
In living color: Brightly-colored bacteria could be used to ‘grow’ paints and coatings
Researchers have unlocked the genetic code behind some of the brightest and most vibrant colours in nature. The paper, published in the journal PNAS, is the first study of the genetics of structural colour — as seen in butterfly wings and peacock feathers — and paves the way for genetic research in a variety of structurally coloured organisms.
The study is a collaboration between the University of Cambridge and Dutch company Hoekmine BV and shows how genetics can change the colour, and appearance, of certain types of brightly-coloured bacteria. The results open up the possibility of harvesting these bacteria for the large-scale manufacturing of nanostructured materials: biodegradable, non-toxic paints could be ‘grown’ and not made, for example.
Flavobacterium is a type of bacteria that packs together in colonies that produce striking metallic colours, which come not from pigments, but from their internal structure, which reflects light at certain wavelengths. Scientists are still puzzled as to how these intricate structures are genetically engineered by nature, however.
Human beings could achieve immortality by 2050
Dr Ian Pearson, a leading futurologist from Ipswich, claims that if people can survive until 2050 they could live forever thanks to advances in AI, android bodies and genetic engineering.

Breakthrough as scientists grow sheep embryos containing human cells
Advance brings us closer to growing transplant organs inside animals or being able to genetically tailor compatible organs, say researchers.
Nicola Davis in Austin.
Boosting Bone Healing Using a Key Protein
Today, we would like to highlight a recent study in which researchers show a way to selectively accelerate bone regeneration. They have achieved this by delivering Jagged-1 to injuries instead of the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) that have been traditionally used.
What is jagged-1?
Jagged-1 is an osteoinductive protein that activates the Notch signaling pathway, which regulates bone healing at the site of injury. Osteoinduction is the process by which osteogenesis is induced.

New CRISPR method strategically targets gene mutations to correct DMD heart defect
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have developed a CRISPR technique to efficiently correct the function of heart cells in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). It involves making a single cut at strategic points along patient’s DNA, with the team claiming their new approach has the potential to correct most of the 3,000 mutations that cause DMD.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is one of nine neuromuscular disorders that affect the strength of muscles and nerves, specifically caused by defects in the gene that makes the dystrophin protein. Typically, one in every 3,500 boys born will be diagnosed with the disease at around three to four years of age, with their ability to walk gradually decreasing until they reach young adolescence. Most patients live until their 30s, but will require a wheelchair and respirator as the muscles in vital organs deteriorate over time.