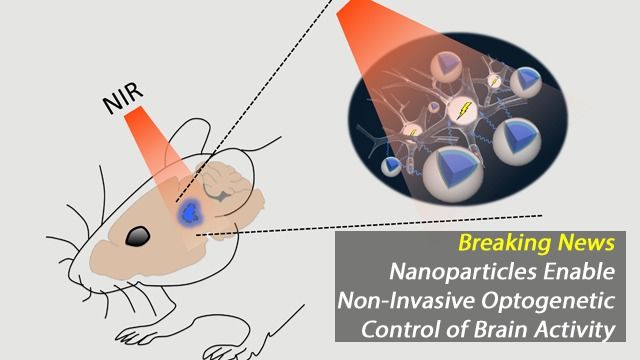
You can’t peer very far down into a well or below the surface of the ocean before things go dark—light does not penetrate to such depths. Though the brain is far from bottomless, neuroscientists face the same lack of light when they try to study living deep-brain structures. This is especially frustrating given that optogenetics, a method for manipulating genetically tagged brain cells with light, has exploded in popularity over the past decade. “Optogenetics has been a revolutionary tool for controlling neurons in the lab, and hopefully someday in the clinic,” says Thomas McHugh, research group leader at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan. “Unfortunately, delivering light within brain tissue requires invasive optical fibers.”
McHugh and colleagues now have a solution for sending light to new depths in the brain. As they report in Science on February 9, upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) can act as a conduit for laser light delivered from outside the skull. These nanoparticles absorb near-infrared laser light and in turn emit visible photons to areas that are inaccessible to standard optogenetics. This method was used to turn on neurons in various brain areas as well as silence seizure activity and evoke memory cells. “Nanoparticles effectively extend the reach of our lasers, enabling the ‘remote’ delivery of light and potentially leading to non-invasive therapies,” says McHugh.
In optogenetics, blue-green light is used to turn neurons on or off via light-responsive ion channels. Light at these wavelengths, however, scatters strongly and is at the other end of the spectrum from the near-infrared light that can penetrate deeper into brain tissue. UCNPs composed of elements from the lanthanide family can act as a bridge. Their ‘optogenetic actuation’ turns low-energy near-infrared laser light into blue or green wavelengths for control of specifically labeled cells. Though such bursts of light deliver considerable energy to a small area, temperature increases or cellular damage were not observed.