Neurochemicals such as serotonin and dopamine play crucial roles in cognitive and emotional functions of our brain. Vesicular monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) is one of the genes responsible for transporting neurotransmitters and regulating neuronal signaling. A research team led by Tohoku University has reconstructed ancestral VMAT1 proteins, revealing the functional changes in neurotransmitter uptake of VMAT1 throughout the course of human evolution.
Human bodies are made up of millions of cells. Each individual contains a specific set of instruction of codes that make up all of a living thing’s genetic material. These instructions are known as genomes. PhD candidate Daiki Sato and Professor Masakado Kawata of the Graduate School of Life Sciences at Tohoku University, and two of the authors involved in the current study, previously discovered VMAT1 to be one of the genes that had evolved throughout human lineage.
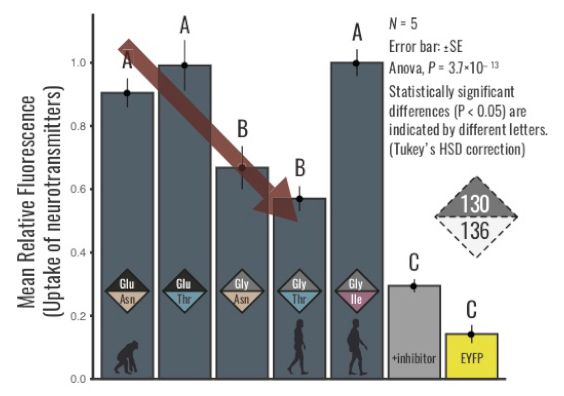
VMAT 1 contains two human-specific mutations, or where the genomes changed, with the change being represented as 130Glu to 130Gly and from 136Asn to 136Thr. Previous studies have shown that having the new 130Gly/136Thr variant decreases the uptake of neurotransmitters and is associated with higher depression and/or anxiety. In this study, Sato, Kawata and their colleagues revealed the evolutionary changes in neurotransmitter uptake of VMAT1 by reconstructing ancestral VMAT1 proteins. First they applied a fluorescent substrate to visualize and quantify the neurotransmitter uptake of each genotype. The ancestral (130Glu/136Asn) VMAT1 protein exhibited an increased uptake of neurotransmitters compared to a derived (130Gly/136Thr) genotype. Given that the derived (130Gly/136Thr) genotype is shown to be associated with depression and/or anxiety in modern human populations. “This results of our study reveal that our ancestors may have been able to withstand higher levels of anxiety or depression,” noted the authors.
In this study, Sato, Kawata and their colleagues revealed the evolutionary changes in neurotransmitter uptake of VMAT1 by reconstructing ancestral VMAT1 proteins. First they applied a fluorescent substrate to visualize and quantify the neurotransmitter uptake of each genotype. The ancestral (130Glu/136Asn) VMAT1 protein exhibited an increased uptake of neurotransmitters compared to a derived (130Gly/136Thr) genotype. Given that the derived (130Gly/136Thr) genotype is shown to be associated with depression and/or anxiety in modern human populations. “This results of our study reveal that our ancestors may have been able to withstand higher levels of anxiety or depression,” noted the authors.
The researcher’s next step is to identify the neurological and behavioral consequences of the mutations in mice to clarify how the variants contributed to our brain evolution. “This would be the striking evidence that links evolution of our genome and brain,” said the authors. The researchers hope that this finding provides insights into our diverse psychological traits including psychiatric disorders.